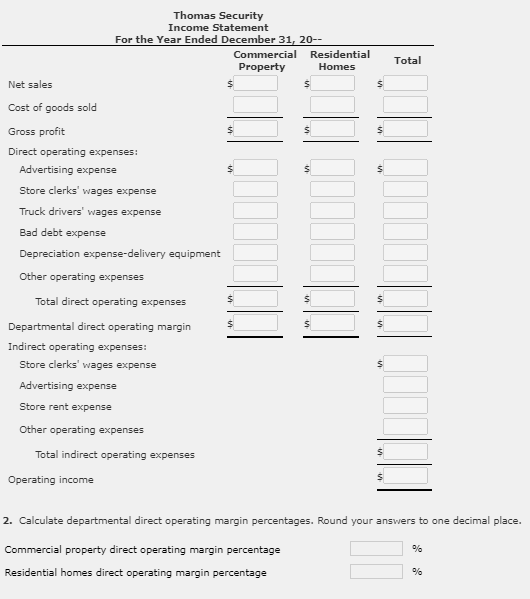
Income Statement With Departmental Direct Operating Margin and Total Operating Income
Durwood Thomas operates the business Thomas Security that sells security equipment for commercial property and residential homes. The following information is provided for the year ended December 31, 20--:
| | Commercial Property | | Residential Homes |
| Net sales | $464,300 | | $135,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | 279,000 | | 54,800 |
| Direct operating expenses: | | | |
| Advertising expense | 34,700 | | 19,800 |
| Store clerks wages expense | 30,000 | | 18,500 |
| Truck drivers wages expense | 15,400 | | 15,400 |
| Bad debt expense | 8,100 | | 3,050 |
| Depreciation expensedelivery equipment | 5,850 | | 4,050 |
| Other operating expenses | 21,000 | | 9,900 |
| Indirect operating expenses: | | | |
| Store clerks wages expense | | $9,700 | |
| Advertising expense | | 14,900 | |
| Store rent expense | | 19,800 | |
| Other operating expenses | | 9,700 | |
Required:
1. Prepare an income statement showing departmental direct operating margin and total operating income.
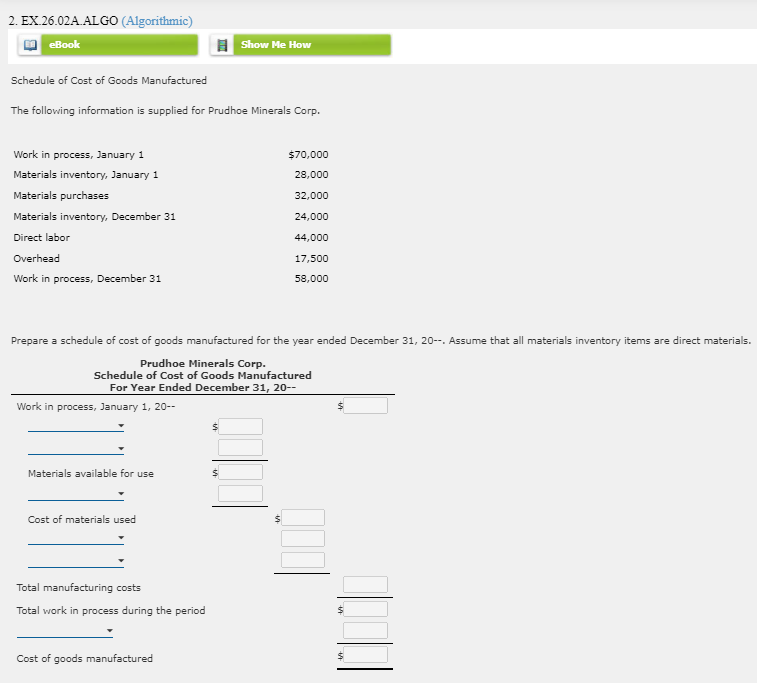

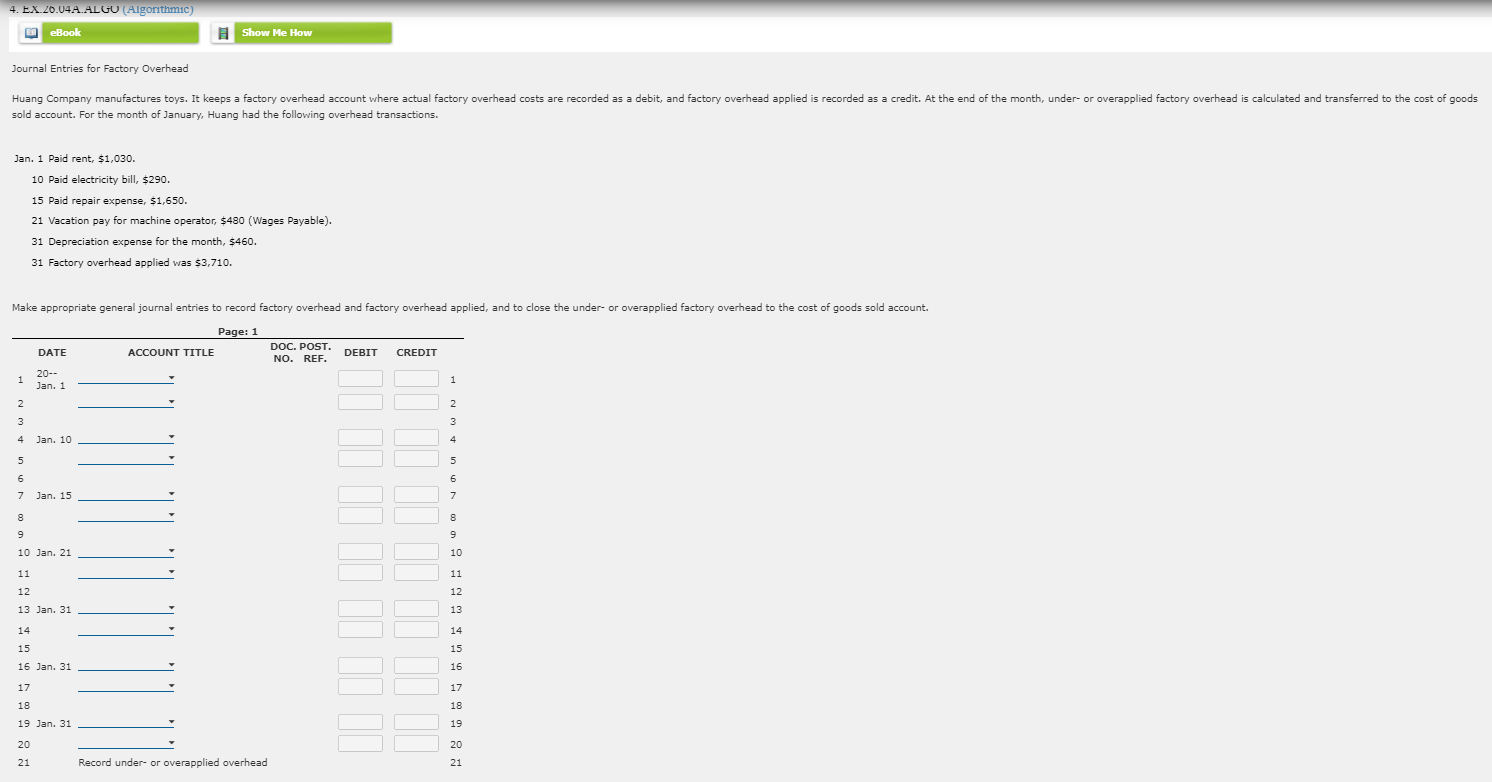
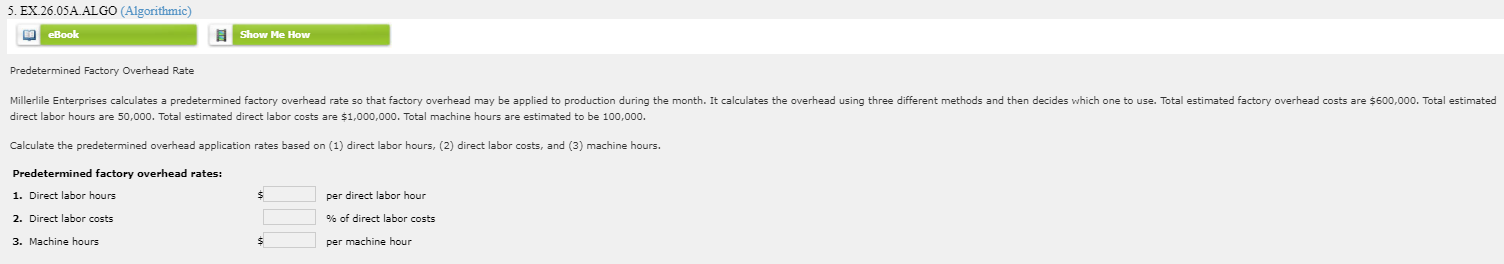
Total s S Thomas Security Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 20-- Commercial Residential Property Homes Net sales $ s Cost of goods sold $ Gross profit S Direct operating expenses: Advertising expense S Store clerks' wages expense Truck drivers' wages expense Bad debt expense Depreciation expense-delivery equipment S Other operating expenses $ Total direct operating expenses Departmental direct operating margin Indirect operating expenses: Store clerks' wages expense Advertising expense Store rent expense Other operating expenses Total indirect operating expenses Operating income s 2. Calculate departmental direct operating margin percentages. Round your answers to one decimal place. Commercial property direct operating margin percentage Residential homes direct operating margin percentage % 2. EX.26.02A. ALGO (Algorithmic) eBook Show Me How Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured The following information is supplied for Prudhoe Minerals Corp. $70,000 28,000 32,000 Work in process, January 1 Materials inventory, January 1 Materials purchases Materials inventory, December 31 Direct labor Overhead Work in process, December 31 24,000 44,000 17,500 58,000 Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year ended December 31, 20--. Assume that all materials inventory items are direct materials. Prudhoe Minerals Corp. Schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured For Year Ended December 31, 20-- Work in process, January 1, 20-- Materials available for use s Cost of materials used Total manufacturing costs Total work in process during the period $ Cost of goods manufactured 3. EX.26.03A. ALGO (Algorithmic) eBook Show Me How Journal Entries for Material, Labor, and Overhead Hilburn Manufacturing Corporation had the following transactions for its job order costing operation. Jan. 1 Purchased materials on account, $17,200. 15 Issued direct materials to Job No. 104, $10,500. 20 Issued indirect materials (factory overhead), $4,900. 31 Incurred direct labor, Job No. 104, $8,700. 31 Incurred indirect labor (factory overhead), $2,500. 31 Incurred other indirect costs (factory overhead; credit Accounts Payable), $2,300. Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions. Page: 1 DOC. POST. DATE ACCOUNT TITLE NO. REF. DEBIT CREDIT 20-- 1 Jan. 1 1 N 2 2 3 3 4 Jan. 15 4 5 5 6 6 7 Jan. 20 7 8 8 9 9 10 Jan. 31 10 11 11 12 12 13 Jan. 31 13 14 14 15 15 0 16 Jan. 31 16 17 17 18 18 4. EX.20.04A.ALGO (Algorithmic) ED eBook Show Me How Journal Entries for Factory Overhead Huang Company manufactures toys. It keeps a factory overhead account where actual factory overhead costs are recorded as a debit, and factory overhead applied is recorded as a credit. At the end of the month, under-or overapplied factory overhead is calculated and transferred to the cost of goods sold account. For the month of January, Huang had the following overhead transactions. Jan. 1 Paid rent, $1,030. 10 Paid electricity bill, $290. 15 Paid repair expense, $1,650. 21 Vacation pay for machine operator, $480 (Wages Payable). 31 Depreciation expense for the month, $460. 31 Factory overhead applied was $3,710. Make appropriate general journal entries to record factory overhead and factory overhead applied, and to close the under- or overapplied factory overhead to the cost of goods sold account. Page: 1 DOC. POST. DATE ACCOUNT TITLE DEBIT CREDIT NO. REF. 20-- 1 1 Jan. 1 2 2 3 3 4 Jan. 10 4 5 5 6 6 7 Jan. 15 7 8 8 9 9 10 Jan. 21 10 11 11 12 12 13 Jan. 31 13 14 14 15 15 16 Jan. 31 16 17 17 18 18 19 Jan. 31 19 20 20 21 Record under- or overapplied overhead 21 5. EX 26.05A ALGO (Algorithmic) eBook Show Me How Predetermined Factory Overhead Rate use. Total estimated factory overhead costs are $600,000. Total estimated Millerlile Enterprises calculates a predetermined factory overhead rate so that factory overhead may be applied to production during the month. It calculates the overhead using three different methods and then decides which one direct labor hours are 50,000. Total estimated direct labor costs are $1,000,000. Total machine hours are estimated to be 100,000. Calculate the predetermined overhead application rates based on (1) direct labor hours, (2) direct labor costs, and (3) machine hours. Predetermined factory overhead rates: 1. Direct labor hours $ per direct labor hour 2. Direct labor costs 3. Machine hours % of direct labor costs per machine hour $











