Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
income variable costing, please use the headings provided so I can follow Requirement 2b. Prepare Ned's Entrees's January and February income statements usi Ned's Entrees
income variable costing, please use the headings provided so I can follow 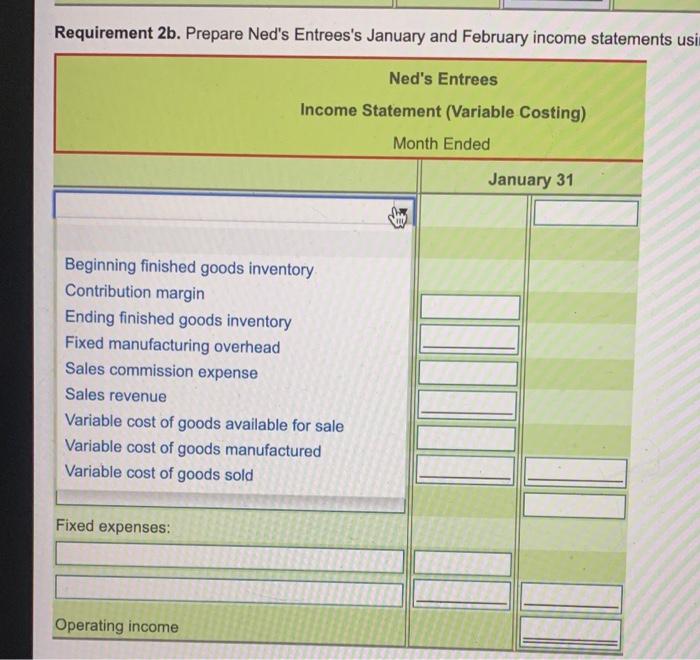
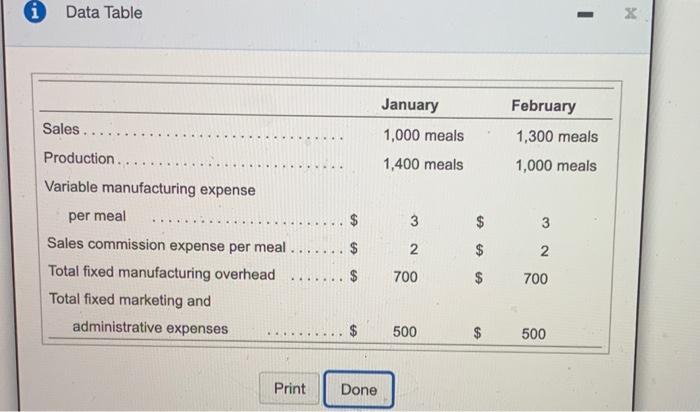

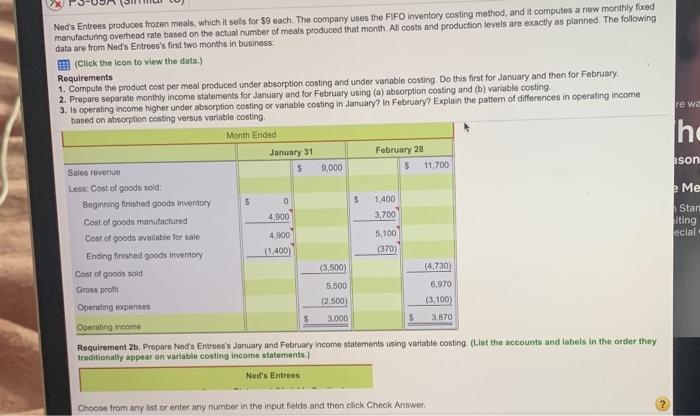 Requirement 2b. Prepare Ned's Entrees's January and February income statements usi Ned's Entrees Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended January 31 Beginning finished goods inventory Contribution margin Ending finished goods inventory Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales commission expense Sales revenue Variable cost of goods available for sale Variable cost of goods manufactured Variable cost of goods sold Fixed expenses: Operating income i Data Table 1 x January Sales .. Production... Variable manufacturing expense 1,000 meals 1,400 meals February 1,300 meals 1,000 meals per meal 3 3 2 $ $ $ 2 ---- Sales commission expense per meal.... Total fixed manufacturing overhead Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses 700 700 500 $ 500 Print Done cm. th The re wa ho ason Ned's Entrees produces frozen meals, which it sels for 59 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly foxed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from Ned's Entrees's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data.) Requirements 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for January and then for February 2. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February using (a) absorption costing and (b) variable costing 3. Is operating income higher under absorption costing or variable costing in January in February? Explain the pattern of differences in operating income based on absorption costing versus variable costing Month Ended January 31 February 28 Sales revenue 5 9,000 5 11,700 Less: Cost of goods sold: Beginning finished goods inventory $ 0 $ 1.400 Cost of goods manufactured 3,700 Cost of goods available for sale 4,900 5,100 Ending finished goods inventory (1.400) (370) Cost of goods sold (3,500) (4.730) Gross profit 5.500 6,970 Operating expenses (2.500) (3,100) Operating income 3,000 3,870 Requirement 2b. Prepare Pad's Entrees's January and February Income statements using variable conting (Lint the accounts and labels in the order they traditionally appear on variable costing income statements.) Me 4.900 Stan iting ecial Ned's Entrees Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check
Requirement 2b. Prepare Ned's Entrees's January and February income statements usi Ned's Entrees Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended January 31 Beginning finished goods inventory Contribution margin Ending finished goods inventory Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales commission expense Sales revenue Variable cost of goods available for sale Variable cost of goods manufactured Variable cost of goods sold Fixed expenses: Operating income i Data Table 1 x January Sales .. Production... Variable manufacturing expense 1,000 meals 1,400 meals February 1,300 meals 1,000 meals per meal 3 3 2 $ $ $ 2 ---- Sales commission expense per meal.... Total fixed manufacturing overhead Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses 700 700 500 $ 500 Print Done cm. th The re wa ho ason Ned's Entrees produces frozen meals, which it sels for 59 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly foxed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs and production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from Ned's Entrees's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data.) Requirements 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for January and then for February 2. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February using (a) absorption costing and (b) variable costing 3. Is operating income higher under absorption costing or variable costing in January in February? Explain the pattern of differences in operating income based on absorption costing versus variable costing Month Ended January 31 February 28 Sales revenue 5 9,000 5 11,700 Less: Cost of goods sold: Beginning finished goods inventory $ 0 $ 1.400 Cost of goods manufactured 3,700 Cost of goods available for sale 4,900 5,100 Ending finished goods inventory (1.400) (370) Cost of goods sold (3,500) (4.730) Gross profit 5.500 6,970 Operating expenses (2.500) (3,100) Operating income 3,000 3,870 Requirement 2b. Prepare Pad's Entrees's January and February Income statements using variable conting (Lint the accounts and labels in the order they traditionally appear on variable costing income statements.) Me 4.900 Stan iting ecial Ned's Entrees Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check
income variable costing, please use the headings provided so I can follow 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


