


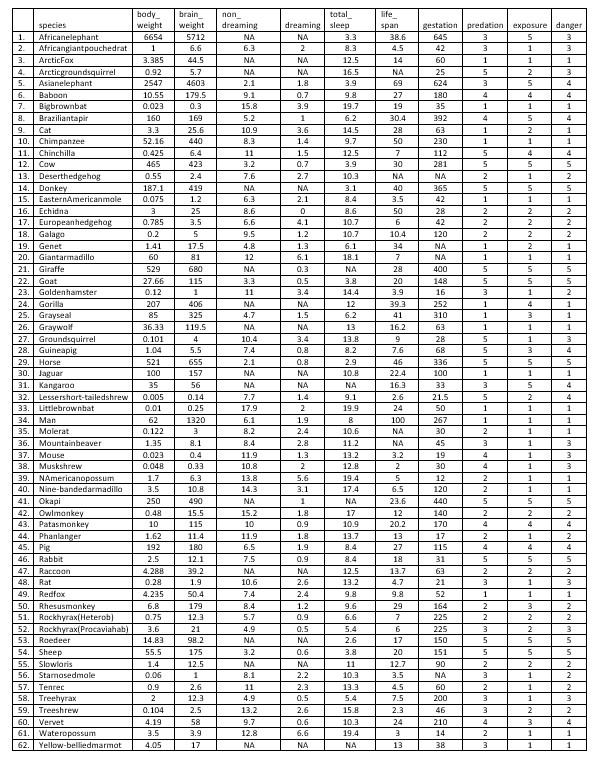
Instructions 1. Choose a dataset to work with. You may choose 2. Ensure that the two variables you choose to focus on are either both quantitative variables, or both qualitative variables. 3. Distinguish the independent (explanatory) variable from the dependent (response) variable. 4. Formulate a statistical question. Examples of good statistical questions include To what extent is gender related to career choice? What, if any, is the relationship between the amount paid to the stars of a film and the film's gross income? 5. Analyse the data, using methods appropriate to the type of data. Include all graphs, calculations, tables and screenshots of results produced by digital technology used in your analysis. (Note, you do not have to calculate means, standard deviations, correlation coefficients, etc. by hand. Please use one of the digital technologies suggested throughout the unit or another type of technology if you are familiar with it.) 6. Interpret the results of the data analysis. Comment on the quality of the data and your conclusions. For example, might there be any 'lurking variables' affecting your results? 7. Describe how you could provide an opportunity for your year 7 10 mathematics class to collect some primary data to investigate the same statistical question, or a similar question, if that would not be feasible. (For example, if you chose to work with the 'Sleep in mammals' dataset, your students might design a new study looking into the sleep patterns of one particular mammal - the human!) In your response, include the year level, content descriptor and code relevant to the investigation. Suggest a digital technology, and the particular aspects of the digital technology, that would be appropriate for use by your students when conducting the investigation. 8. In an appendix, include the data extracted from the original dataset that you used for your investigation. (For example, if you chose to work with the 'Sleep in mammals' dataset, and only used the first three columns, "Species", "Body weight," and "Brain weight," then only include these three columns in the table of data.) Ensure any column headings are easy to interpret, and if not, include a key. 10.3 species 1. Africanelephant 2. Africangiant pouchedrat 3. Arctic Fox 4. Arcticgroundsquirrel 5. Asianelephant 6. Baboon 7. Bigbrownbat 8. Braziliantapir 9. Cat 10. Chimpanzee 11. Chinchilla 12. Cow 13. Deserthedgehog 14. Donkey 15. Eastern Americanmale 16. Echidna 17. European hedgehog 18. Galaga 19. Genet 20. Giantarmadillo 21. Giraffe 22. Goat 23. Goldenhamster 24. Gorilla 25. Grayscal 26. Graywall 27. Groundsquirrel 28. Guineapis 29. Horse 30. Jaguar 31. Kangarda 32. Lessershort-tailedshrew 33. Littlebrownbat 34. Man 35. Molerat 36. Mountainbeaver 37. Mouse 38. Muskshrew 39. NAmericanopossum 40. Nine-bandedarmadilla 41. Okapi 42. Owlmankey 43. Patasmonkey 44. Phanlanger 45. Pig 46. Rabbit 47. Raccoon 48. Rat 49. Redfox 50. Rhesusmonkey 51. Rackhyrax(Heterob) 52. Rackhyrax(Pracaviahab) 53. Roedeer 54. Sheep 55. Slowloris 56. Stamasedmale 57. Tenrec 58. Treehyrax 59. Treeshrew 60. Vervet 61. Wateropossum 62. Yellow-belliedmarmat body weight 6654 1 3.385 0.92 2547 10.55 0.023 160 3.3 52.16 0.425 465 0.55 187.1 0.075 3 0.785 0.2 1.41 60 529 27.66 0.12 207 85 36.33 0.101 1.04 521 100 35 0.005 0.01 62 0.122 1.35 0.023 0.048 1.7 3.5 250 0.48 10 1.62 192 2.5 4.288 0.28 4.235 6.8 0.75 3.6 14.83 55.5 1.4 0.06 0.9 2 0.104 4.19 3.5 4.05 brain weight 5712 6.6 44.5 5.7 4603 179.5 0.3 169 25.6 440 6.4 423 2.4 419 1.2 25 3.5 5 17.5 81 680 115 1 406 325 119.5 4 5.5 655 157 56 0.14 0.25 1320 3 8.1 0.4 0.33 6.3 10.8 490 15.5 115 114 180 12.1 39.2 1.9 50.4 179 12.3 21 98.2 175 12.5 1 2.6 12.3 2.5 58 3.9 17 non dreaming NA 6.3 NA NA 2.1 9.1 15.8 5.2 10.9 8.3 11 3.2 7.6 NA 6.3 8.6 6.6 9.5 4.8 12 NA 3.3 11 NA 4.7 NA 10.4 7.4 2.1 NA NA 7.7 17.9 6.1 8.2 8.4 11.9 10.8 13.8 14.3 NA 15.2 10 11.9 6.5 7.5 NA 10.6 7.4 8.4 5.7 4.9 NA 3.2 NA 8.1 11 4.9 13.2 9.7 12.8 NA total dreaming sleep NA 3.3 2 8.3 NA 12.5 NA 16.5 1.8 3.9 0.7 9.8 3.9 19.7 1 6.2 3.6 14.5 1.4 9.7 1.5 12.5 0.7 3.9 2.7 NA 3.1 2.1 2.4 0 2.6 4.1 10.7 1.2 10.7 1.3 6.1 6.1 18.1 0.3 NA 0.5 3.8 3.4 14.4 NA 12 1.5 6.2 NA 13 3.4 13.8 0.a 8.2 0.8 2.9 NA 10.8 NA NA 1.4 9.1 2 19.9 1.9 8 2.4 10.6 2.8 11.2 1.3 13.2 2 12.8 5.6 19.4 3.1 17.4 1 NA 1.8 17 0.9 10.9 1.8 1.9 8.4 0.9 8.4 NA 12.5 2.6 13.2 2.4 98 1.2 9.6 0.9 6.6 0.5 5.4 NA 2.6 0.6 3.8 NA 11 2.2 10.3 2.3 13.3 0.5 5.4 2.6 15.8 0.6 10.3 6.6 19.4 NA NA life span 38.6 45 14 NA 69 27 19 30.4 28 50 7 30 NA 40 3.5 50 6 10.4 34 7 28 20 3.9 39.3 41 16.2 9 7.6 46 22.4 16.3 2.6 24 100 NA NA 3.2 2 5 6.5 23.6 12 20.2 13 27 18 13.7 4.7 9.a 29 7 6 17 20 12.7 3.5 45 7.5 2.3 24 gestation predation exposure danger 645 3 5 3 42 3 1 3 60 1 1 1 25 5 2 3 624 3 5 4 180 4 4 4 35 1 1 1 392 4 5 4 63 1 2 1 230 1 1 1 112 5 4 4 281 5 5 5 NA 2 1 2 365 5 5 5 42 1 1 1 28 2 2 2. 42 2 2 2. 120 2. 2 2 NA 1 2 1 NA 1 1 1 400 5 5 S 148 5 5 5 16 3 1 2 252 1 4 1 310 1 1 63 1 1 1 28 5 1 3 68 5 3 4 336 5 5 5 100 1 1 1 33 3 5 4 21.5 5 2 4 SO 1 1 1 267 1 1 1 30 2 1 1 45 3 1 3 19 4 1 3 30 4 1 3 12 2 1 1 120 2 1 1 440 5 5 S 140 2 2 2 170 4 4 4 17 2 1 2 115 4 4 4 31 5 5 S 63 2 2 2 21 3 1 3 52 1 1 1 164 2 3 2 225 2 2 2 225 3 2 3 150 5 5 5 151 5 5 5 90 2 2 2 NA 3 1 2 60 2 1 2 200 3 1 3 46 3 2 2 210 4 3 4 14 2 1 1 38 3 1 1 13.7 13 Instructions 1. Choose a dataset to work with. You may choose 2. Ensure that the two variables you choose to focus on are either both quantitative variables, or both qualitative variables. 3. Distinguish the independent (explanatory) variable from the dependent (response) variable. 4. Formulate a statistical question. Examples of good statistical questions include To what extent is gender related to career choice? What, if any, is the relationship between the amount paid to the stars of a film and the film's gross income? 5. Analyse the data, using methods appropriate to the type of data. Include all graphs, calculations, tables and screenshots of results produced by digital technology used in your analysis. (Note, you do not have to calculate means, standard deviations, correlation coefficients, etc. by hand. Please use one of the digital technologies suggested throughout the unit or another type of technology if you are familiar with it.) 6. Interpret the results of the data analysis. Comment on the quality of the data and your conclusions. For example, might there be any 'lurking variables' affecting your results? 7. Describe how you could provide an opportunity for your year 7 10 mathematics class to collect some primary data to investigate the same statistical question, or a similar question, if that would not be feasible. (For example, if you chose to work with the 'Sleep in mammals' dataset, your students might design a new study looking into the sleep patterns of one particular mammal - the human!) In your response, include the year level, content descriptor and code relevant to the investigation. Suggest a digital technology, and the particular aspects of the digital technology, that would be appropriate for use by your students when conducting the investigation. 8. In an appendix, include the data extracted from the original dataset that you used for your investigation. (For example, if you chose to work with the 'Sleep in mammals' dataset, and only used the first three columns, "Species", "Body weight," and "Brain weight," then only include these three columns in the table of data.) Ensure any column headings are easy to interpret, and if not, include a key. 10.3 species 1. Africanelephant 2. Africangiant pouchedrat 3. Arctic Fox 4. Arcticgroundsquirrel 5. Asianelephant 6. Baboon 7. Bigbrownbat 8. Braziliantapir 9. Cat 10. Chimpanzee 11. Chinchilla 12. Cow 13. Deserthedgehog 14. Donkey 15. Eastern Americanmale 16. Echidna 17. European hedgehog 18. Galaga 19. Genet 20. Giantarmadillo 21. Giraffe 22. Goat 23. Goldenhamster 24. Gorilla 25. Grayscal 26. Graywall 27. Groundsquirrel 28. Guineapis 29. Horse 30. Jaguar 31. Kangarda 32. Lessershort-tailedshrew 33. Littlebrownbat 34. Man 35. Molerat 36. Mountainbeaver 37. Mouse 38. Muskshrew 39. NAmericanopossum 40. Nine-bandedarmadilla 41. Okapi 42. Owlmankey 43. Patasmonkey 44. Phanlanger 45. Pig 46. Rabbit 47. Raccoon 48. Rat 49. Redfox 50. Rhesusmonkey 51. Rackhyrax(Heterob) 52. Rackhyrax(Pracaviahab) 53. Roedeer 54. Sheep 55. Slowloris 56. Stamasedmale 57. Tenrec 58. Treehyrax 59. Treeshrew 60. Vervet 61. Wateropossum 62. Yellow-belliedmarmat body weight 6654 1 3.385 0.92 2547 10.55 0.023 160 3.3 52.16 0.425 465 0.55 187.1 0.075 3 0.785 0.2 1.41 60 529 27.66 0.12 207 85 36.33 0.101 1.04 521 100 35 0.005 0.01 62 0.122 1.35 0.023 0.048 1.7 3.5 250 0.48 10 1.62 192 2.5 4.288 0.28 4.235 6.8 0.75 3.6 14.83 55.5 1.4 0.06 0.9 2 0.104 4.19 3.5 4.05 brain weight 5712 6.6 44.5 5.7 4603 179.5 0.3 169 25.6 440 6.4 423 2.4 419 1.2 25 3.5 5 17.5 81 680 115 1 406 325 119.5 4 5.5 655 157 56 0.14 0.25 1320 3 8.1 0.4 0.33 6.3 10.8 490 15.5 115 114 180 12.1 39.2 1.9 50.4 179 12.3 21 98.2 175 12.5 1 2.6 12.3 2.5 58 3.9 17 non dreaming NA 6.3 NA NA 2.1 9.1 15.8 5.2 10.9 8.3 11 3.2 7.6 NA 6.3 8.6 6.6 9.5 4.8 12 NA 3.3 11 NA 4.7 NA 10.4 7.4 2.1 NA NA 7.7 17.9 6.1 8.2 8.4 11.9 10.8 13.8 14.3 NA 15.2 10 11.9 6.5 7.5 NA 10.6 7.4 8.4 5.7 4.9 NA 3.2 NA 8.1 11 4.9 13.2 9.7 12.8 NA total dreaming sleep NA 3.3 2 8.3 NA 12.5 NA 16.5 1.8 3.9 0.7 9.8 3.9 19.7 1 6.2 3.6 14.5 1.4 9.7 1.5 12.5 0.7 3.9 2.7 NA 3.1 2.1 2.4 0 2.6 4.1 10.7 1.2 10.7 1.3 6.1 6.1 18.1 0.3 NA 0.5 3.8 3.4 14.4 NA 12 1.5 6.2 NA 13 3.4 13.8 0.a 8.2 0.8 2.9 NA 10.8 NA NA 1.4 9.1 2 19.9 1.9 8 2.4 10.6 2.8 11.2 1.3 13.2 2 12.8 5.6 19.4 3.1 17.4 1 NA 1.8 17 0.9 10.9 1.8 1.9 8.4 0.9 8.4 NA 12.5 2.6 13.2 2.4 98 1.2 9.6 0.9 6.6 0.5 5.4 NA 2.6 0.6 3.8 NA 11 2.2 10.3 2.3 13.3 0.5 5.4 2.6 15.8 0.6 10.3 6.6 19.4 NA NA life span 38.6 45 14 NA 69 27 19 30.4 28 50 7 30 NA 40 3.5 50 6 10.4 34 7 28 20 3.9 39.3 41 16.2 9 7.6 46 22.4 16.3 2.6 24 100 NA NA 3.2 2 5 6.5 23.6 12 20.2 13 27 18 13.7 4.7 9.a 29 7 6 17 20 12.7 3.5 45 7.5 2.3 24 gestation predation exposure danger 645 3 5 3 42 3 1 3 60 1 1 1 25 5 2 3 624 3 5 4 180 4 4 4 35 1 1 1 392 4 5 4 63 1 2 1 230 1 1 1 112 5 4 4 281 5 5 5 NA 2 1 2 365 5 5 5 42 1 1 1 28 2 2 2. 42 2 2 2. 120 2. 2 2 NA 1 2 1 NA 1 1 1 400 5 5 S 148 5 5 5 16 3 1 2 252 1 4 1 310 1 1 63 1 1 1 28 5 1 3 68 5 3 4 336 5 5 5 100 1 1 1 33 3 5 4 21.5 5 2 4 SO 1 1 1 267 1 1 1 30 2 1 1 45 3 1 3 19 4 1 3 30 4 1 3 12 2 1 1 120 2 1 1 440 5 5 S 140 2 2 2 170 4 4 4 17 2 1 2 115 4 4 4 31 5 5 S 63 2 2 2 21 3 1 3 52 1 1 1 164 2 3 2 225 2 2 2 225 3 2 3 150 5 5 5 151 5 5 5 90 2 2 2 NA 3 1 2 60 2 1 2 200 3 1 3 46 3 2 2 210 4 3 4 14 2 1 1 38 3 1 1 13.7 13










