

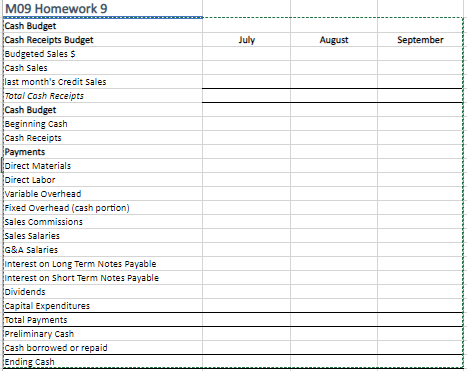
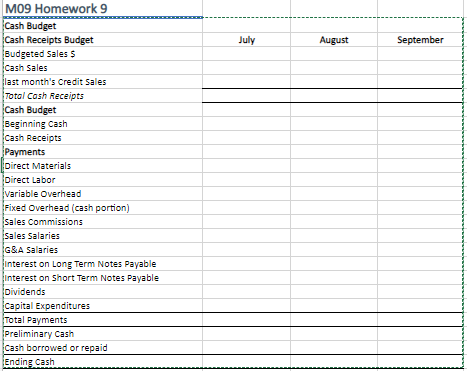
Instructions: Use the Balance Sheet below for Creasy, Inc plus the additional information provided on the next tab to create the operating budget, cash budget, budgeted income statement, and budgeted balance sheet for Creasy Inc. Creasy Inc. June 30, 2021 Assets Cash 100,000 Accounts Receivable 720,000 Raw materials Inventory 185,220 Finished goods inventory 431,250 Total current Assets 1,436,470 Equipment Net 600,000 Less: Accumulated Depreciation (42,000) Equipment Net 558.000 Total Assets 1,994.470 Llabilities and Equity Accounts Payable 308,700 Short-term notes payable 25.000 Total current liabilities 333,700 Long-term note payables 500,000 Total Liabilities 833,700 Common stock 1,000,000 Retained earnings 160,770 Total stockholders' equity 1,160,770 Total liabilities + equity 1,994, 470 MO9 Homework 9 Additional Information a) Sales for June totalled 20,000 units. Expected sales (in units) are: 23,000 (July); 25,000 (August); 27,000 (September); 23,000 (October) The product's selling price is $40/unit b) company policy calls for the given month's ending findished goods inventory to equal 75% of the next month's expected unit sales. The June 30 finished goods inventory is 17,250 units, which complies with the policy. The products' manufacturing cost if S25 per unit, inlcluding per unit costs of $12.50 for materials (3 lbs. at $4,20 per lb.) $10 for direct labor (0.5 hours x $20 direct labor rate per hour) $1.50 for variable overhead, and $0.50 for fixed overhead Fixed overhead consists of $7,000/month for depreciation and $3,000/month for rent. Company policy also calls for a given month's ending raw materials inventory to equal 50% of next month's expected materials needed for production. The June 30 inventory is 44,1000 pounds units of materials, which complies with the policy. The company expects to have 45,350 pounds of materials inventory on September 30. c) Sales representatives' commissions are 9% of slaes and are paid in the month of the sales. The sales manager's monthly salary will be $5,000 in July and August and will increase by 5% in September d) Monthly general and administrative expenses include $10,000 administrative salaries and 0.3% monthly interest on the long term note payable. e) The company expects 10% of sales to be for cash and the remaining 90% on credit. Receivables are collected in full in the month following the sale (none is collected in the month of the sale). f) All direct materials purchases are on credit, and no payables arise from any other transactions. One month's purchases are fully paid in the next month. Materials cost $4.20 per pound. ) The minimum ending cash balance for all months is $100,000 if necessary, the company borrows enough cash using a short-term note to reach the minimum. Short-term notes require an interest payament of 0.5% at each month-end (before any repayment). if the ending cash balance exceeds the minimum, the excess will be applied to repaying the short-term notes payable balance. h) Dividends of $80,000 are to be declared and paid in July. i) No cash payments for income taxes are to be made during the third calendar quarter. Income taxes will be assessed at 22% in the quarter. 1) Equipment purchaes of $25,000 are scheduled September July August September MO9 Homework 9 Cash Budget Cash Receipts Budget Budgeted Sales $ Cash Sales last month's Credit Sales Total Cash Receipts Cash Budget Beginning Cash Cash Receipts Payments Direct Materials Direct Labor Variable Overhead Fixed Overhead (cash portion) Sales Commissions Sales Salaries G&A Salaries Interest on Long Term Notes Payable Interest on Short Term Notes Payable Dividends Capital Expenditures Total Payments Preliminary Cash Cash borrowed or repaid Ending Cash July August September MO9 Homework 9 Cash Budget Cash Receipts Budget Budgeted Sales $ Cash Sales last month's Credit Sales Total Cash Receipts Cash Budget Beginning Cash Cash Receipts Payments Direct Materials Direct Labor Variable Overhead Fixed Overhead (cash portion) Sales Commissions Sales Salaries G&A Salaries Interest on Long Term Notes Payable Interest on Short Term Notes Payable Dividends Capital Expenditures Total Payments Preliminary Cash Cash borrowed or repaid Ending Cash










