Integer array totalNumbers List is read from input. Declare an integer array named twiceNumbers List. Then, assign each element in twiceNumbers List with the
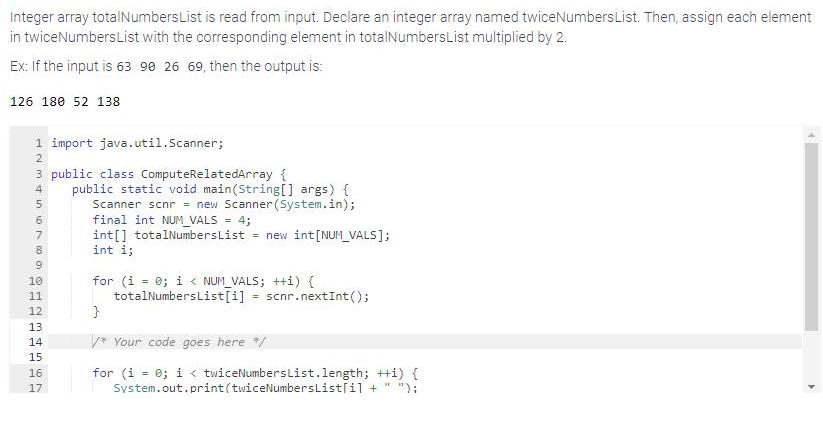
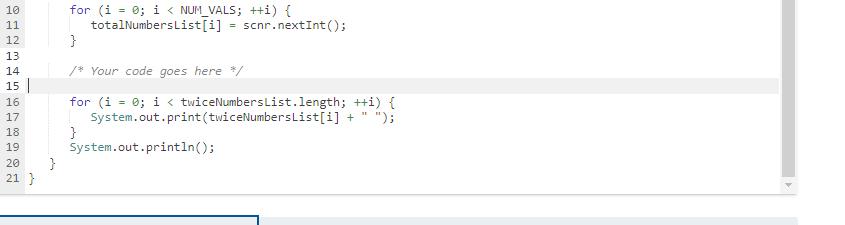
Integer array totalNumbers List is read from input. Declare an integer array named twiceNumbers List. Then, assign each element in twiceNumbers List with the corresponding element in totalNumbers List multiplied by 2. Ex: If the input is 63 90 26 69, then the output is: 126 180 52 138 1 import java.util.Scanner; 3 public class ComputeRelatedArray { N34 in 100 0 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 25 11 12 13. 14 15 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scnr = new Scanner(System.in); final int NUM_VALS = 4; int[] totalNumbers List = new int [NUM_VALS]; int i; for (i = 0; i < NUM_VALS; ++i) { totalNumbersList[i] scnr.nextInt(); } /* Your code goes here */ for (i = 0; i < twiceNumbersList.length; ++i) { System.out.print(twiceNumbersList[i] + 10 1223 11 14 15 | 16 17 18 19 20 } 21 } for (i = 0; i < NUM_VALS; ++i) { totalNumbers List[i] scnr.nextInt (); } /* Your code goes here */ for (i = 0; i < twiceNumbers List.length; ++i) { System.out.print (twiceNumbersList[i] + 31 "); } System.out.println(); =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


