Question
Integrative Case 11.1. Walmart Dividends-Based Valuation of Walmarts Common Equity LO 11-3 LO 11-4 LO 11-5 LO 11-6 LO 11-7 Integrative Case 10.1 involves projecting
Integrative Case 11.1. Walmart
Dividends-Based Valuation of Walmarts Common Equity
-
LO 11-3 LO 11-4 LO 11-5 LO 11-6 LO 11-7
Integrative Case 10.1 involves projecting financial statements for Walmart for Years +1 through +5. The following data for Walmart include the actual amounts for fiscal 2020 and the projected amounts for Years +1 through +5 for comprehensive income and common shareholders equity, assuming it will use implied dividends as the financial flexible account to balance the balance sheet (amounts in millions).
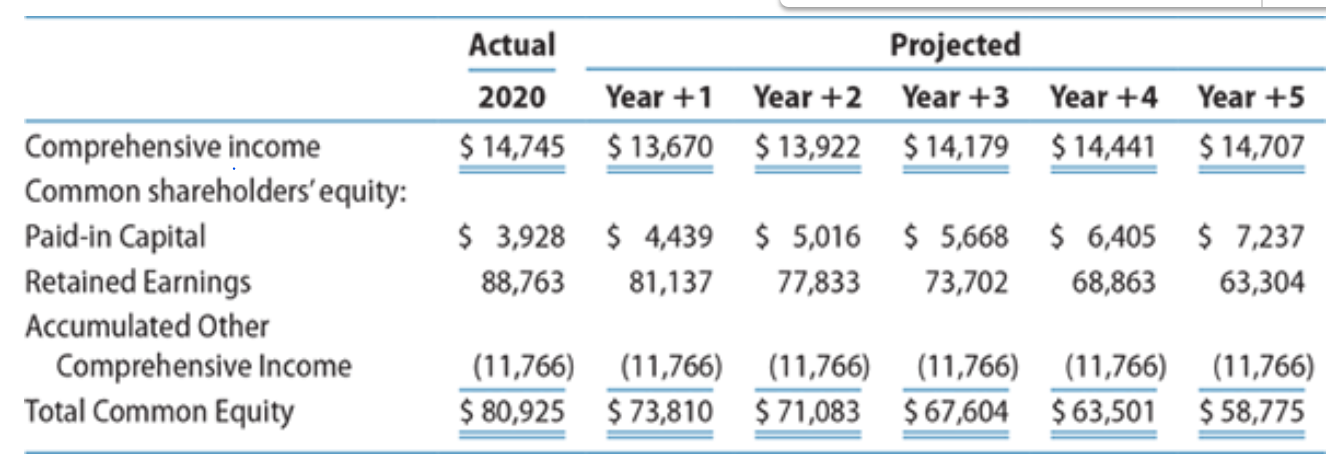
Assume that the market equity beta for Walmart at the end of fiscal 2020 was 0.50. Assume that the risk-free interest rate was 3.0% and the market risk premium was 6.0%. Also assume that Walmart had 2,821 million shares outstanding at the end of fiscal 2020 and the share price was $138.69.
Required
-
Use the CAPM to compute the required rate of return on common equity capital for Walmart .
-
Compute the weighted average cost of capital for Walmart as of the start of Year +1. In addition to the market value of common equity capital, Walmart also had the following components of its capital structure:
Debt: Walmart had $44,533 million in outstanding interest-bearing debt on the balance sheet. Assume that the balance sheet value of debt is approximately equal to the market value. Assume that Walmart will incur interest expense of 5.5% on debt capital and that its average tax rate will be 31.0%.
Operating Leases: Walmart had $14,375 million in operating lease obligations on the balance sheet. Assume that the balance sheet value of these lease obligations is approximately equal to the market value. Assume that Walmart will incur interest expense of 6.1% on operating lease obligations and that its average tax rate will be 31.0%.
Finance Leases: Walmart had $4,338 million in finance lease obligations on the balance sheet. Assume that the balance sheet value of these lease obligations is approximately equal to the market value. Assume that Walmart will incur interest expense of 6.8% on finance lease obligations and that its average tax rate will be 31.0%.
Preferred Stock: Walmart has no preferred stock.
Noncontrolling Interests: Walmart had $6,606 million in equity capital from noncontrolling interests. Assume that this equity capital carries a 5.0% required rate of return. Also assume noncontrolling interests will receive dividends equal to the required rate of return each year.
-
Use the clean surplus accounting approach to derive the projected dividends for common shareholders for Years +1 through +5 based on the projected comprehensive income and shareholders equity amounts. (Throughout this case, you can ignore dividends to noncontrolling interests.)
-
Use the clean surplus accounting approach to project the continuing dividend to common shareholders in Year +6. Assume that the steady-state long-run growth rate will be 3% in Years +6 and beyond.
-
Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate, compute the sum of the present value of dividends to common shareholders for Walmart for Years +1 through +5.
-
Using the required rate of return on common equity from Requirement a as a discount rate and the long-run growth rate from Requirement d, compute the continuing value of Walmart as of the beginning of Year +6 based on its continuing dividends in Years +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value, bring continuing value back to present value at the start of Year +1.
-
Compute the value of a share of Walmart common stock, as follows:
-
Compute the sum of the present value of dividends including the present value of continuing value.
-
Adjust the sum of the present value using the midyear discounting adjustment factor.
-
Compute the per-share value.
-
-
Using the same set of forecast assumptions as before, recompute the value of Walmart shares under two alternative scenarios. To quantify the sensitivity of your share value estimate for Walmart to these variations in growth and discount rates, compare (in percentage terms) your value estimates under these two scenarios with your value estimate from Requirement g.
-
Scenario 1: Assume that Walmarts long-run growth will be 2.5%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of return on equity is 0.5 percentage point higher than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a.
-
Scenario 2: Assume that Walmarts long-run growth will be 3.5%, not 3% as before, and assume that its required rate of return on equity is 0.5 percentage point lower than the rate you computed using the CAPM in Requirement a.
-
-
What reasonable range of share values would you expect for Walmart common stock? Where is the current price for Walmart shares relative to this range? What do you recommend?
-
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


