Question
Introduction- Maintaining useful employment of all sections of New Zealand society is seen as a healthy indicator of a flexible, productive and inclusive society. Understanding
Introduction-
Maintaining useful employment of all sections of New Zealand society is seen as a healthy indicator of a flexible, productive and inclusive society. Understanding the drivers of unemployment is the first step in understanding solutions to improving Mori employment.
The purpose of this Investigation is to determine if there is a relationship between Mori unemployment rates and the Household Living-costs Price Indexes for Mori.
Importance: This research will help us determine if Mori Unemployment decreases when three critical Mori Household Living costs increase or vice versa.
Investigation: Does the measure of Household Living-costs Price Indexes for Mori have an effect on the unemployment rate for Mori.
Data Description
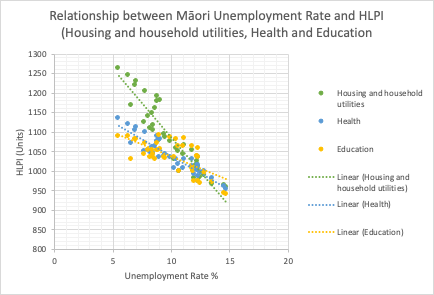
The data collected for this Investigation came from the website Infoshare (http://infoshare.stats.govt.nz) and compared the Mori Unemployment Rate to the Household Living Cost Price Indexes (HLPI) for Mori. The Household Living Cost Price Indexes is measured in units, whereas the Unemployment rate is measured in percentages. The data used in this analysis is time-series data as the observations being made are recorded quarterly every year.
The mean for Mori unemployment is 10.8%. Meanwhile the average of Mori Household Living-cost price Index is 1025.4. Other comments about our data set are that the range for Mori unemployment is 8.1% with the minimum being 6.6% and the maximum 14.7%. The range for Mori Household Living-cost price Index is 154 with a minimum of 962 and a max of 1116.
A limitation with our data set is the scale of our sample. Our sample only covers a timespan of ten years which is a relatively limited amount of time. Hypothetically, if our data set expanded over a longer period of time our regression models' results could look substantially different compared to our actual obtained results.
Our primary data sources were accessed and determined from theStatistics New Zealand infoshare website. We chose this website as it is a reputable source for data and allows immediate access to quarterly information pertaining to the Mori HLPI, or household living price index, and information on the Mori unemployment rate relationally. We were able to identify Mori from the data as the group we were analyzing, and we chose the dependent variables: housing and utilities, Health and education. We have a 10-year window from the third quarter of 2012 to the second quarter of 2022. With a sample size of roughly 40 observations, we purposefully enforced this chronology to more accurately depict an approximation of the overall data available and to actively represent potential patterns affecting Mori over the years due to possible systematic inequalities or related to economic events. Possible limitations however could come from our dependent variable of unemployment rate can only be accessed as a percentage whereas HLPI is measured in
Story
The process of hypothesis testing is used to evaluate the strength of the evidence from the sample and offers a framework for making decisions pertaining to the population. It provides a method, in our case the Emperical Method, for understanding how reliably one can extrapolate observed findings in a study sample to the larger population from which the sample was drawn. To evaluate whether a specific hypothesis is supported, the researcher develops a specific hypothesis, analyses sample data, and then makes use of the data to make that determination.
Therefore, the key finding of our study, which forms the basis of our hypothesis, focuses on the relationship between Maori unemployment and Maori household cost of living price indexes, with particular attention to housing and household utility, health, and education. This will be tested empirically using the Maori Unemployment Rate (%) and the Maori Household Cost of Living Price Index, specifically for Housing and Household Utility, Health, and Education (HLPI units), for the years divided quarterly from 2012Q3 to 2022Q2.
Empirical method Independent- Unemployment rate for Mori. Dependent -HLPI particularly fromHousing and Household utility, Health, Education. In order to analyse and interpret our given question we recognised the requirement for a linear regression analysis and multiple regression analysis to connect the variables and comprehend how they are related to one another and particularly the correlation to our hypothesis in order to analyse our given question, "Effects of Unemployment on Mori in relation to Housing, Education, and Food." We decided to conduct a multiple linear regression model as we believe it better represents the overall data when we are able to break the HLPI data into its most contributing factors for our question. And multiple regression allows for more than 1 input or dependent variable to be analysed. By looking at the multiple input variables simultaneously we are able to interpret more clearly what factors could be contributing more or less towards the question and interacting with the unemployment rates.
| UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (%) | HOUSING (HLPI) | HEALTH (HLPI) | EDUACATION (HLPI) | |
| MIN | 5.5 | 959 | 954 | 940 |
| MEAN | 10.085 | 1083.4 | 1036.4 | 1037.1 |
| MEDIAN | 10.1 | 1070.5 | 1033 | 1040.5 |
| MAX | 14.7 | 1262 | 1135 | 1091 |
In order to interpret the data we also decided to incorporate a small summary table of the data by min, mean, median and mode. From the data we were able to collate that the minimum unemployment rate sat at 5.5 in 2022Q2 the lowest it has been in the studied time period. While at this time the HLPI coincidentally is at its max in 2022Q2 at 1262, 1135 and 1090. While the Max unemployment rate observed was 14.7 in 2012Q3 where the HLPI data was observed to be 959, 954 and 940 with correlates to their respective min values.
| SUMMARY OUTPUT | |||||||||
| Regression Statistics | |||||||||
| Multiple R | 0.93155508 | ||||||||
| R Square | 0.86779487 | ||||||||
| Adjusted R Square | 0.85677778 | ||||||||
| Standard Error | 0.87220068 | ||||||||
| Observations | 40 | ||||||||
| ANOVA | |||||||||
df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | |||||
| Regression | 3 | 179.764575 | 59.9215251 | 78.7680361 | 6.9564E-16 | ||||
| Residual | 36 | 27.3864248 | 0.76073402 | ||||||
| Total | 39 | 207.151 | |||||||
Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | P-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | ||
| Intercept | 42.6392822 | 8.88419345 | 4.7994545 | 0.00002769 | 24.6213028 | 60.6572617 | 24.6213028 | 60.6572617 | |
| Housing and household utilities | -0.020066 | 0.00845923 | -2.3720844 | 0.02315456 | -0.0372221 | -0.0029099 | -0.0372221 | -0.0029099 | |
| Health | -0.0080436 | 0.01791756 | -0.4489212 | 0.65617931 | -0.0443821 | 0.02829493 | -0.0443821 | 0.02829493 | |
| Education | -0.0023897 | 0.0051118 | -0.4674965 | 0.64296229 | -0.012757 | 0.00797747 | -0.012757 | 0.00797747 |
Empirical Results
With an intercept of 42.6392822 it is implied that if the the Housing and Household utilities (H&H), Health(H) and Education (E) (respective to units) were all equal to zero, the Maori (where at least one member of the household reported Maori ethnicity) Unemployment Rate (UR) would be 42.64% of working age population (16-65 years). We see based on the Coefficient for the remaining variables that if H&H utilities were to increase by 1 unit the Maori UR would decrease by 0.0201% (-0.020066). That if the Maori H spending was to increase by 1 unit the Coefficient states that the UR would decrease by 0.0080% (-0.0080436) and have a jump in one unit of spending within the HLPI for E were to increase in a unit of 1 then the Maori UR would decrease by 0.0024% (-0.0023897) respectfully.
By knowing the Intercept and coefficients we are able to formulate the equation for the Maori unemployment rate.
Maori UR y-hat = 42.6392- 0.0201(H&H)- 0.0080(H) - 0.0024(E) (Units based off HLPI index)
The R2 Value output for this regression is 0.8678, which is a relatively high R2 score; the closer the R2 is to 1.0, the better the fit for the data. A correlation of 86.78% between Mori unemployment rates and Household and Housing utilities, Health, and Education, with a value of 0.8678, indicates that our model fits the data well, but that there are still other factors that influence Mori unemployment rates.
We will be using hypothesis testing to test whether Housing and Household utilities, Health and Education have a significant impact on Mori Unemployment Rates. Our null hypothesis (H0) states that there is no statistical correlation between the Maori Unemployment and the Household and Housing utilities, Health and Education. An alternative hypothesis (H1) is that there is a relationship between Housing and Household utilities, Health, Education and Mori Unemployment Rates.
H0: H&H=>0.05 or H1: H&H
H0: H=> 0.05 or H1: H
H0: E=> 0.05 or H1: E
Is a 0.05 P-Value Significant?
A p-value less than 0.05 is typically considered to be statistically significant, in which case the null hypothesis should be rejected. A p-value greater than 0.05 means that deviation from the null hypothesis is not statistically significant, and the null hypothesis is not rejected.
For Household and Housing utilities (H&H) the P-value is 0.02315, the P-value is less than 0.05 and shows no statistical significance towards there being a correlation between these two variables, therefore we can reject the null hypothesis.
For both Health (H) and Education (E) the alternative hypothesis is shown as Health shows a 0.6562 P-value and Education with 0.6430 P-value. Being higher than 0.05 means that both Health and Education have statistical significance with the alternative so we cannot reject the null hypothesis.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


