Question
Iodine reacts with a ketone in aqueous solution to give an iodoketone. The stoichiometric equation is: I2 + ketone -> iodoketone + H+ + I-
Iodine reacts with a ketone in aqueous solution to give an iodoketone. The stoichiometric equation is: I2 + ketone -> iodoketone + H+ + I-
The rate of reaction can be measured by measuring the disappearance of I2 with time. The data for initial rates and initial concentrations are as follows:
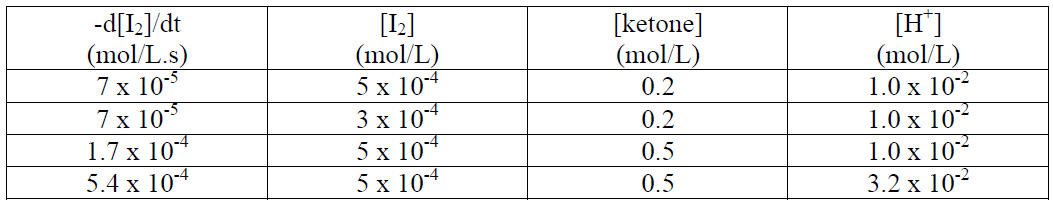
(a) Find the order of the rate of reaction with respect to I2, ketone and H+
(b) Write a differential equation expressing your findings in part (a) and calculate the average rate constant
(c) How long will it take to synthesize 10^-4 mol/L of the iodoketone starting with 0.5 mol/L of ketone and 0.001 mol/L of I2, if the H+ concentration is held constant at 0.1 mol/L?
(d) What will happen to the reaction if we double the concentration of ketone? Or iodine? Or H+?
-d[1]/dt (mol/L.s) 7 x 10-5 7 x 105 1.7 x 10-4 5.4 x 10-4 [1] (mol/L) 5 x 10-4 3 x 10-4 5 x 10-4 5 x 10-4 [ketone] (mol/L) 0.2 0.2 0.5 0.5 [H*] (mol/L) 1.0 x 10- 1.0 x 10 1.0 x 102 3.2 x 10
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The given reaction is Iodene Ketone Iodoketone H I The rate of the reaction R dI 2 dt diodoketonedt Let the order of the reaction with respect to I 2 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
60618495ab1a1_55371.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
60618495ab1a1_55371.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


