Is acetic acid the unknown acid based on this data? Explain 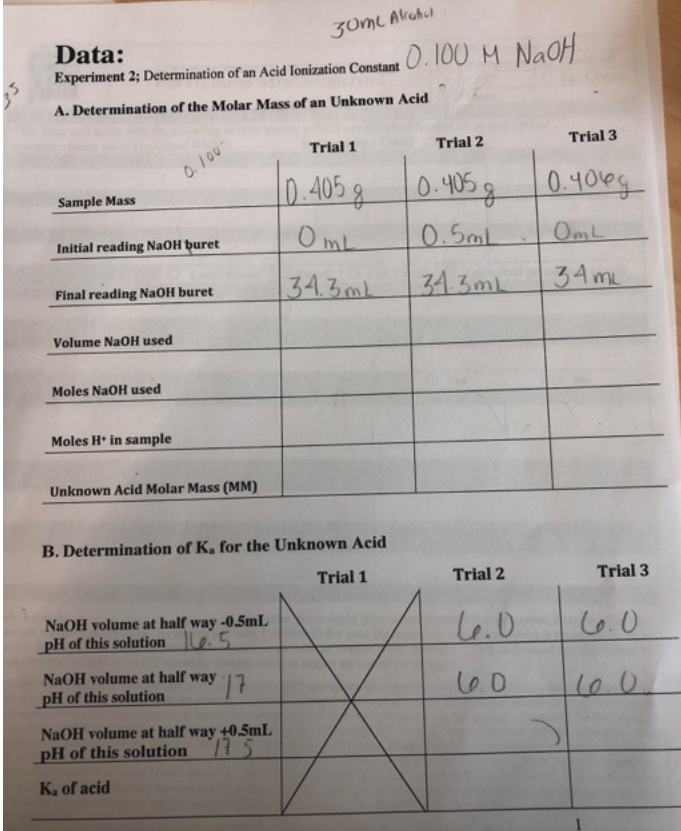 ata.
ata. 

Data: Experiment 2; Determination of an Acid Ionization Constant 0.100MNaH A. Determination of the Molar Mass of an Unknown Acid Experiment 2 Determination of an Acid Ionization Constant When an acid is mixed with a base the following chemical reaction occurs: (1) H+(aq)+OH(aq)H2O The reaction can be considered to proceed completely to the right and can be used to determine the amounts of acid or base in unknown solutions. Our experiment uses a titration technique where a basic solution is added from a buret to a measured volume of unknown acid solution until the number of moles of OH+ion added is equal to the number of moles of H+ion present in the acid. At the equivalence point of the titration: (2) no. moles H+originally present =no. moles OHadded The equivalence point is determined by using a chemical called an indicator that changes color at the proper point in the titration. One of the most common indicators is phenolphthalein, which is colorless in acid solutions but becomes pink when the pH of the solution becomes basic. In this experiment you will use a NaOH solution of known concentration to titrate a sample of a solid organic acid. By titrating a weighed sample of the unknown acid with the NaOH solution you can, by Equation 2, find the number of moles H+ion that your sample can furnish. If your acid has one acidic hydrogen in the molecule then the number of moles of acid will equal the number of moles of H+that react during the titration. The molar mass of the acid will then equal the number of grams of acid used divided by the moles of H+ion titrated: (3) MM=no.molesofH+ionno.gramsofacid A weak acid, HA, dissociates in water solution according to the equation: (4) HA(aq)H+(aq)+A(aq) A solution of HA will obey the equilibrium condition given by the equation: (5) Ka=[HA][H+][A] When a solution of HA is half way to the equivalence point there will be equal parts of [HA] and [A] and so: (6) Ka=[H+]in a half-neutralized solution Experimental Procedure A. Determination of the Molar Mass of an Acid Obtain a sample of 0.35 grams of a solid unknown acid and weigh it on the analytical balance to 0.001g. Grind the acid into a powder if it has "chunks" in it. To your 125mL flask add the sample and 20mL of alcohol to start the dissolving process; once dissolved as much as will dissolve then add two drops of phenolphthalein to your flask. Don't worry if it doesn't all dissolve. Record the initial level of 0.100MNaOH in your buret and then titrate the solution of the solid acid. If the acid appears to be relatively insoluble add NaOH until the pink color persists and then swirl to dissolve the solid. Avoid overshooting the end point. The final pink end point should appear on addition of one drop of NaOH. Record the final level in the NaOH buret. Conduct a second and third trial but record the volume and pH of the acid solution when around half of the required NaOH has been added. Record (at a minimum) the volume and pH at half way, half way 0.5mL and half way +0.5mL. B. Determination of Ku for the Unknown Acid In the second and third titration in Part A you converted a solution of HA into one containing near equal parts of NaA by adding NaOH to the half way point. You measured the volume and pH at half way, half way 0.5mL and half way +0.5mL and then completed the titration to the end point. Using these three measurements determine what the pH would be when half of the NaOH used was delivered. In that solution [HA] will equal [A] and so it will obey equation (6). DISPOSAL: Place all collected liquids into the Acid/Base container under the fume hood. 2
 ata.
ata. 







