Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
is there somewhere else i can send the question to like an email address because Im not sure why youre not seeing it. 5.10 The



is there somewhere else i can send the question to like an email address because Im not sure why youre not seeing it. 
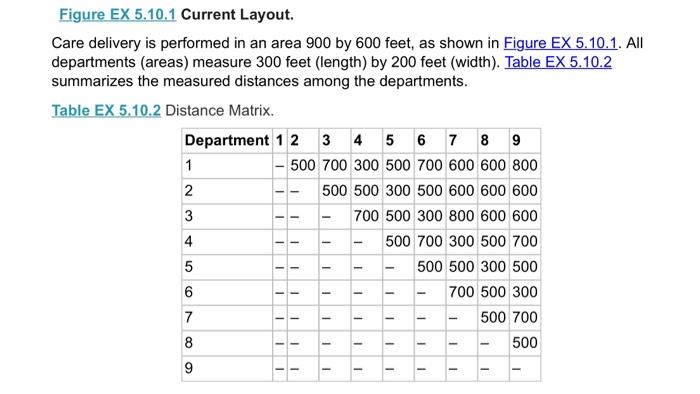
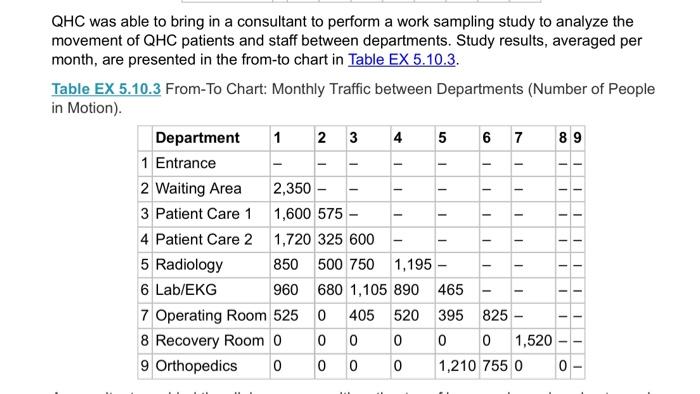

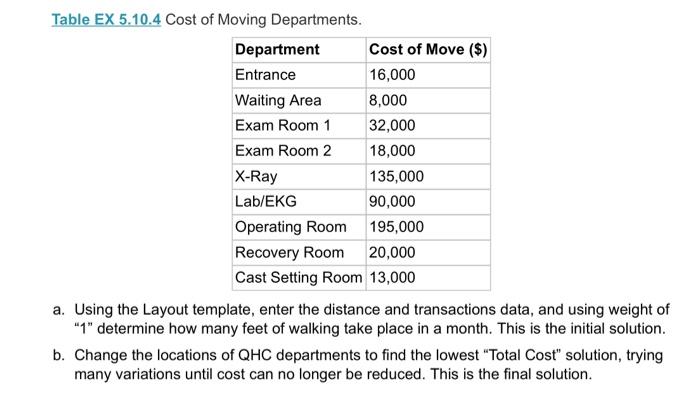

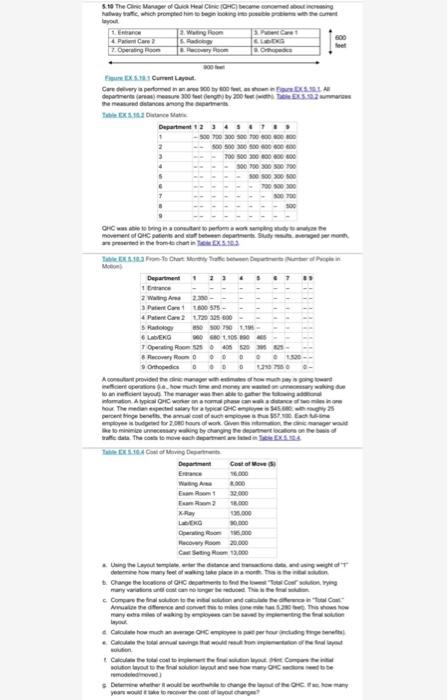
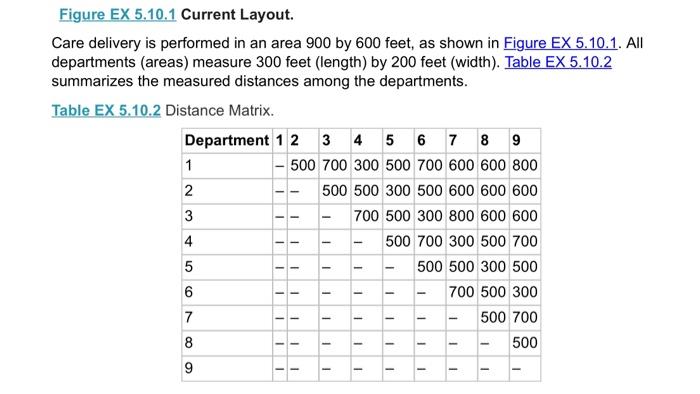
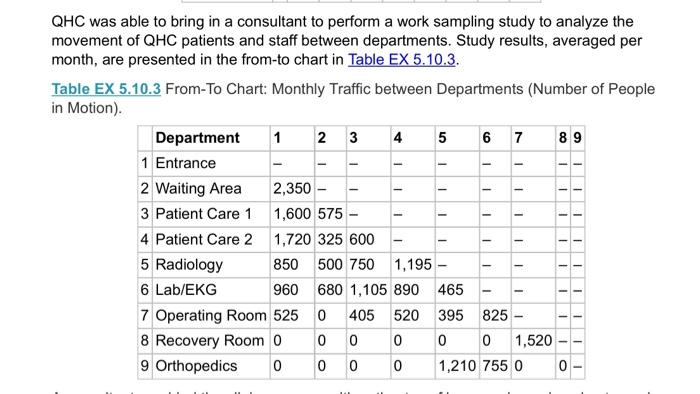
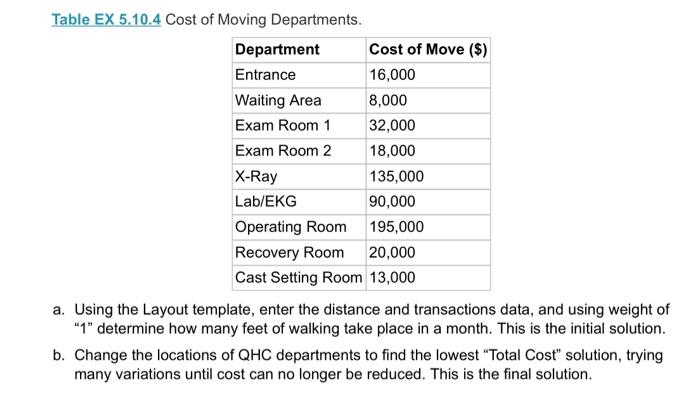
5.10 The Clinic Manager of Healin OHC) become comedor alwaytric which prominenten your 12. W Z. Operating Room 5 SEXS1 Layout Careery petored in 00 deprimera 300 fot hemden 1. Die Department 1 2 3 4 500 70000 700 500 200 000 500 DHC miring consomwoning movement of Opensando en department ed intromechan303 Department. 21 1 Wine 2 Patient Care 1800 595- Patient Car? 1120 325 800 5 2007 - LADENO 90 SO 1.10500 5 Operating Rooms 4000- Recomery Room Ortopedie DOO Acomat provided the image with you Nie persone chimneymary to recent tous The manager when there omation AOC wonenaroma powstanom The media expected story to CSS betor 2.000 ord work with the heto minimize saying by changing the deteriores traille du The com to move ahead Twingo Depen Cost of Em 6.000 WA000 Em 32.000 En 2000 KRay 5.000 LG 000 Dom. com 20.000 Car Sting Room 13.000 the Laurence and determine how my foot of wing Change the color of the Cong Compare the one them and Co At the end of the vows & Cote how muchos perto de - Caulir the en Call the other.Com solution tayout to the layout and um Determine whether would be the change the theo 5.10 The Clinic Manager of Quick Heal Clinic (QHC) became concerned about increasing hallway traffic, which prompted him to begin looking into possible problems with the current layout. 1. Entrance 2. Waiting Room 3. Patient Care 1 600 4. Patient Care 2 5. Radiology 6. Lab/EKG feet 7. Operating Room 8. Recovery Room 9. Orthopedics 900 feet Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout. Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Table EX 5.10.2 Distance Matrix. Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 - 500 700 300 500 700 600 600 800 2 500 500 300 500 600 600 600 3 700 500 300 800 600 600 4 500 700 300 500 700 5 500 500 300 500 6 700 500 300 7 500 700 8 500 9 1 - - - - - - - - - 1 1 - 1 1 1 1 1 - - - - - 1 11 - - 1 - 8 1 1 - - 1 - QHC was able to bring in a consultant to perform a work sampling study to analyze the movement of QHC patients and staff between departments. Study results, averaged per month, are presented in the from-to chart in Table EX 5.10.3. Table EX 5.10.3 From-To Chart: Monthly Traffic between Departments (Number of People in Motion). Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Entrance 2 Waiting Area 2,350 - 3 Patient Care 1 1,600 575 - 4 Patient Care 2 1,720 325 600 5 Radiology 850 500 750 1,195 6 Lab/EKG 960 680 1,105 890 465 7 Operating Room 525 0 405 520 395 825 - 8 Recovery Room 0 0 0 0 0 0 1,520 9 Orthopedics 0 0 0 0 1,210 755 0 0 - - - - 1 1 - -- - - - - - - - - 1 - 1 - 1 A consultant provided the clinic manager with estimates of how much pay is going toward inefficient operations (i.e., how much time and money are wasted on unnecessary walking due to an inefficient layout). The manager was then able to gather the following additional information. A typical QHC worker on a normal phase can walk a distance of two miles in one hour. The median expected salary for a typical QHC employee is $45,680; with roughly 25 percent fringe benefits, the annual cost of such employee is thus $57,100. Each full-time employee is budgeted for 2,080 hours of work. Given this information, the clinic manager would like to minimize unnecessary walking by changing the department locations on the basis of traffic data. The costs to move each department are listed in Table EX 5.10.4. Table EX 5.10.4 Cost of Moving Departments. Department Cost of Move ($) Entrance 16,000 Waiting Area 8,000 Exam Room 1 32,000 Exam Room 2 18,000 X-Ray 135,000 Lab/EKG 90,000 Operating Room 195,000 Recovery Room 20,000 Cast Setting Room 13,000 a. Using the Layout template, enter the distance and transactions data, and using weight of "1" determine how many feet of walking take place in a month. This is the initial solution. b. Change the locations of QHC departments to find the lowest "Total Cost" solution, trying many variations until cost can no longer be reduced. This is the final solution. C. Compare the final solution to the initial solution and calculate the difference in "Total Cost." Annualize the difference and convert this to miles (one mile has 5,280 feet). This shows how many extra miles of walking by employees can be saved by implementing the final solution layout d. Calculate how much an average QHC employee is paid per hour (including fringe benefits). e. Calculate the total annual savings that would result from implementation of the final layout solution. f. Calculate the total cost to implement the final solution layout. (Hint: Compare the initial solution layout to the final solution layout and see how many QHC sections need to be remodeled/moved.) g. Determine whether it would be worthwhile to change the layout of the QHC. If so, how many years would it take to recover the cost of layout changes? 5.10 The Clinic Manager of Quick Heal Clinic (QHC) became concerned about increasing hallway traffic, which prompted him to begin looking into possible problems with the current layout. 1. Entrance 2. Waiting Room 3. Patient Care 1 600 4. Patient Care 2 5. Radiology 6. Lab/EKG feet 7. Operating Room 8. Recovery Room 9. Orthopedics 900 feet Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout. Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Table EX 5.10.2 Distance Matrix. Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 - 500 700 300 500 700 600 600 800 2 500 500 300 500 600 600 600 3 700 500 300 800 600 600 4 500 700 300 500 700 5 500 500 300 500 6 700 500 300 7 500 700 8 500 9 1 - - - - - - - - - 1 1 - 1 1 1 1 1 - - - - - 1 11 - - 1 - 8 1 1 - - 1 - QHC was able to bring in a consultant to perform a work sampling study to analyze the movement of QHC patients and staff between departments. Study results, averaged per month, are presented in the from-to chart in Table EX 5.10.3. Table EX 5.10.3 From-To Chart: Monthly Traffic between Departments (Number of People in Motion). Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Entrance 2 Waiting Area 2,350 - 3 Patient Care 1 1,600 575 - 4 Patient Care 2 1,720 325 600 5 Radiology 850 500 750 1,195 6 Lab/EKG 960 680 1,105 890 465 7 Operating Room 525 0 405 520 395 825 - 8 Recovery Room 0 0 0 0 0 0 1,520 9 Orthopedics 0 0 0 0 1,210 755 0 0 - - - - 1 1 - -- - - - - - - - - 1 - 1 - 1 A consultant provided the clinic manager with estimates of how much pay is going toward inefficient operations (i.e., how much time and money are wasted on unnecessary walking due to an inefficient layout). The manager was then able to gather the following additional information. A typical QHC worker on a normal phase can walk a distance of two miles in one hour. The median expected salary for a typical QHC employee is $45,680; with roughly 25 percent fringe benefits, the annual cost of such employee is thus $57,100. Each full-time employee is budgeted for 2,080 hours of work. Given this information, the clinic manager would like to minimize unnecessary walking by changing the department locations on the basis of traffic data. The costs to move each department are listed in Table EX 5.10.4. Table EX 5.10.4 Cost of Moving Departments. Department Cost of Move ($) Entrance 16,000 Waiting Area 8,000 Exam Room 1 32,000 Exam Room 2 18,000 X-Ray 135,000 Lab/EKG 90,000 Operating Room 195,000 Recovery Room 20,000 Cast Setting Room 13,000 a. Using the Layout template, enter the distance and transactions data, and using weight of "1" determine how many feet of walking take place in a month. This is the initial solution. b. Change the locations of QHC departments to find the lowest "Total Cost" solution, trying many variations until cost can no longer be reduced. This is the final solution. C. Compare the final solution to the initial solution and calculate the difference in "Total Cost." Annualize the difference and convert this to miles (one mile has 5,280 feet). This shows how many extra miles of walking by employees can be saved by implementing the final solution layout d. Calculate how much an average QHC employee is paid per hour (including fringe benefits). e. Calculate the total annual savings that would result from implementation of the final layout solution. f. Calculate the total cost to implement the final solution layout. (Hint: Compare the initial solution layout to the final solution layout and see how many QHC sections need to be remodeled/moved.) g. Determine whether it would be worthwhile to change the layout of the QHC. If so, how many years would it take to recover the cost of layout changes? 5.10 The Clinic Manager of Healin OHC) become comedor alwaytric which prominenten your 12. W Z. Operating Room 5 SEXS1 Layout Careery petored in 00 deprimera 300 fot hemden 1. Die Department 1 2 3 4 500 70000 700 500 200 000 500 DHC miring consomwoning movement of Opensando en department ed intromechan303 Department. 21 1 Wine 2 Patient Care 1800 595- Patient Car? 1120 325 800 5 2007 - LADENO 90 SO 1.10500 5 Operating Rooms 4000- Recomery Room Ortopedie DOO Acomat provided the image with you Nie persone chimneymary to recent tous The manager when there omation AOC wonenaroma powstanom The media expected story to CSS betor 2.000 ord work with the heto minimize saying by changing the deteriores traille du The com to move ahead Twingo Depen Cost of Em 6.000 WA000 Em 32.000 En 2000 KRay 5.000 LG 000 Dom. com 20.000 Car Sting Room 13.000 the Laurence and determine how my foot of wing Change the color of the Cong Compare the one them and Co At the end of the vows & Cote how muchos perto de - Caulir the en Call the other.Com solution tayout to the layout and um Determine whether would be the change the theo 5.10 The Clinic Manager of Quick Heal Clinic (QHC) became concerned about increasing hallway traffic, which prompted him to begin looking into possible problems with the current layout. 1. Entrance 2. Waiting Room 3. Patient Care 1 600 4. Patient Care 2 5. Radiology 6. Lab/EKG feet 7. Operating Room 8. Recovery Room 9. Orthopedics 900 feet Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout. Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Table EX 5.10.2 Distance Matrix. Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 - 500 700 300 500 700 600 600 800 2 500 500 300 500 600 600 600 3 700 500 300 800 600 600 4 500 700 300 500 700 5 500 500 300 500 6 700 500 300 7 500 700 8 500 9 1 - - - - - - - - - 1 1 - 1 1 1 1 1 - - - - - 1 11 - - 1 - 8 1 1 - - 1 - QHC was able to bring in a consultant to perform a work sampling study to analyze the movement of QHC patients and staff between departments. Study results, averaged per month, are presented in the from-to chart in Table EX 5.10.3. Table EX 5.10.3 From-To Chart: Monthly Traffic between Departments (Number of People in Motion). Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Entrance 2 Waiting Area 2,350 - 3 Patient Care 1 1,600 575 - 4 Patient Care 2 1,720 325 600 5 Radiology 850 500 750 1,195 6 Lab/EKG 960 680 1,105 890 465 7 Operating Room 525 0 405 520 395 825 - 8 Recovery Room 0 0 0 0 0 0 1,520 9 Orthopedics 0 0 0 0 1,210 755 0 0 - - - - 1 1 - -- - - - - - - - - 1 - 1 - 1 A consultant provided the clinic manager with estimates of how much pay is going toward inefficient operations (i.e., how much time and money are wasted on unnecessary walking due to an inefficient layout). The manager was then able to gather the following additional information. A typical QHC worker on a normal phase can walk a distance of two miles in one hour. The median expected salary for a typical QHC employee is $45,680; with roughly 25 percent fringe benefits, the annual cost of such employee is thus $57,100. Each full-time employee is budgeted for 2,080 hours of work. Given this information, the clinic manager would like to minimize unnecessary walking by changing the department locations on the basis of traffic data. The costs to move each department are listed in Table EX 5.10.4. Table EX 5.10.4 Cost of Moving Departments. Department Cost of Move ($) Entrance 16,000 Waiting Area 8,000 Exam Room 1 32,000 Exam Room 2 18,000 X-Ray 135,000 Lab/EKG 90,000 Operating Room 195,000 Recovery Room 20,000 Cast Setting Room 13,000 a. Using the Layout template, enter the distance and transactions data, and using weight of "1" determine how many feet of walking take place in a month. This is the initial solution. b. Change the locations of QHC departments to find the lowest "Total Cost" solution, trying many variations until cost can no longer be reduced. This is the final solution. C. Compare the final solution to the initial solution and calculate the difference in "Total Cost." Annualize the difference and convert this to miles (one mile has 5,280 feet). This shows how many extra miles of walking by employees can be saved by implementing the final solution layout d. Calculate how much an average QHC employee is paid per hour (including fringe benefits). e. Calculate the total annual savings that would result from implementation of the final layout solution. f. Calculate the total cost to implement the final solution layout. (Hint: Compare the initial solution layout to the final solution layout and see how many QHC sections need to be remodeled/moved.) g. Determine whether it would be worthwhile to change the layout of the QHC. If so, how many years would it take to recover the cost of layout changes? 5.10 The Clinic Manager of Quick Heal Clinic (QHC) became concerned about increasing hallway traffic, which prompted him to begin looking into possible problems with the current layout. 1. Entrance 2. Waiting Room 3. Patient Care 1 600 4. Patient Care 2 5. Radiology 6. Lab/EKG feet 7. Operating Room 8. Recovery Room 9. Orthopedics 900 feet Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Figure EX 5.10.1 Current Layout. Care delivery is performed in an area 900 by 600 feet, as shown in Figure EX 5.10.1. All departments (areas) measure 300 feet (length) by 200 feet (width). Table EX 5.10.2 summarizes the measured distances among the departments. Table EX 5.10.2 Distance Matrix. Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 - 500 700 300 500 700 600 600 800 2 500 500 300 500 600 600 600 3 700 500 300 800 600 600 4 500 700 300 500 700 5 500 500 300 500 6 700 500 300 7 500 700 8 500 9 1 - - - - - - - - - 1 1 - 1 1 1 1 1 - - - - - 1 11 - - 1 - 8 1 1 - - 1 - QHC was able to bring in a consultant to perform a work sampling study to analyze the movement of QHC patients and staff between departments. Study results, averaged per month, are presented in the from-to chart in Table EX 5.10.3. Table EX 5.10.3 From-To Chart: Monthly Traffic between Departments (Number of People in Motion). Department 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 Entrance 2 Waiting Area 2,350 - 3 Patient Care 1 1,600 575 - 4 Patient Care 2 1,720 325 600 5 Radiology 850 500 750 1,195 6 Lab/EKG 960 680 1,105 890 465 7 Operating Room 525 0 405 520 395 825 - 8 Recovery Room 0 0 0 0 0 0 1,520 9 Orthopedics 0 0 0 0 1,210 755 0 0 - - - - 1 1 - -- - - - - - - - - 1 - 1 - 1 A consultant provided the clinic manager with estimates of how much pay is going toward inefficient operations (i.e., how much time and money are wasted on unnecessary walking due to an inefficient layout). The manager was then able to gather the following additional information. A typical QHC worker on a normal phase can walk a distance of two miles in one hour. The median expected salary for a typical QHC employee is $45,680; with roughly 25 percent fringe benefits, the annual cost of such employee is thus $57,100. Each full-time employee is budgeted for 2,080 hours of work. Given this information, the clinic manager would like to minimize unnecessary walking by changing the department locations on the basis of traffic data. The costs to move each department are listed in Table EX 5.10.4. Table EX 5.10.4 Cost of Moving Departments. Department Cost of Move ($) Entrance 16,000 Waiting Area 8,000 Exam Room 1 32,000 Exam Room 2 18,000 X-Ray 135,000 Lab/EKG 90,000 Operating Room 195,000 Recovery Room 20,000 Cast Setting Room 13,000 a. Using the Layout template, enter the distance and transactions data, and using weight of "1" determine how many feet of walking take place in a month. This is the initial solution. b. Change the locations of QHC departments to find the lowest "Total Cost" solution, trying many variations until cost can no longer be reduced. This is the final solution. C. Compare the final solution to the initial solution and calculate the difference in "Total Cost." Annualize the difference and convert this to miles (one mile has 5,280 feet). This shows how many extra miles of walking by employees can be saved by implementing the final solution layout d. Calculate how much an average QHC employee is paid per hour (including fringe benefits). e. Calculate the total annual savings that would result from implementation of the final layout solution. f. Calculate the total cost to implement the final solution layout. (Hint: Compare the initial solution layout to the final solution layout and see how many QHC sections need to be remodeled/moved.) g. Determine whether it would be worthwhile to change the layout of the QHC. If so, how many years would it take to recover the cost of layout changes 





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


