Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
IS THIS RIGHT?/??????????????? Problem 1. 40 pts Last year, a major east-coast insurance company contracted with Qwest Diagnostics (QD), to provide laboratory services for its

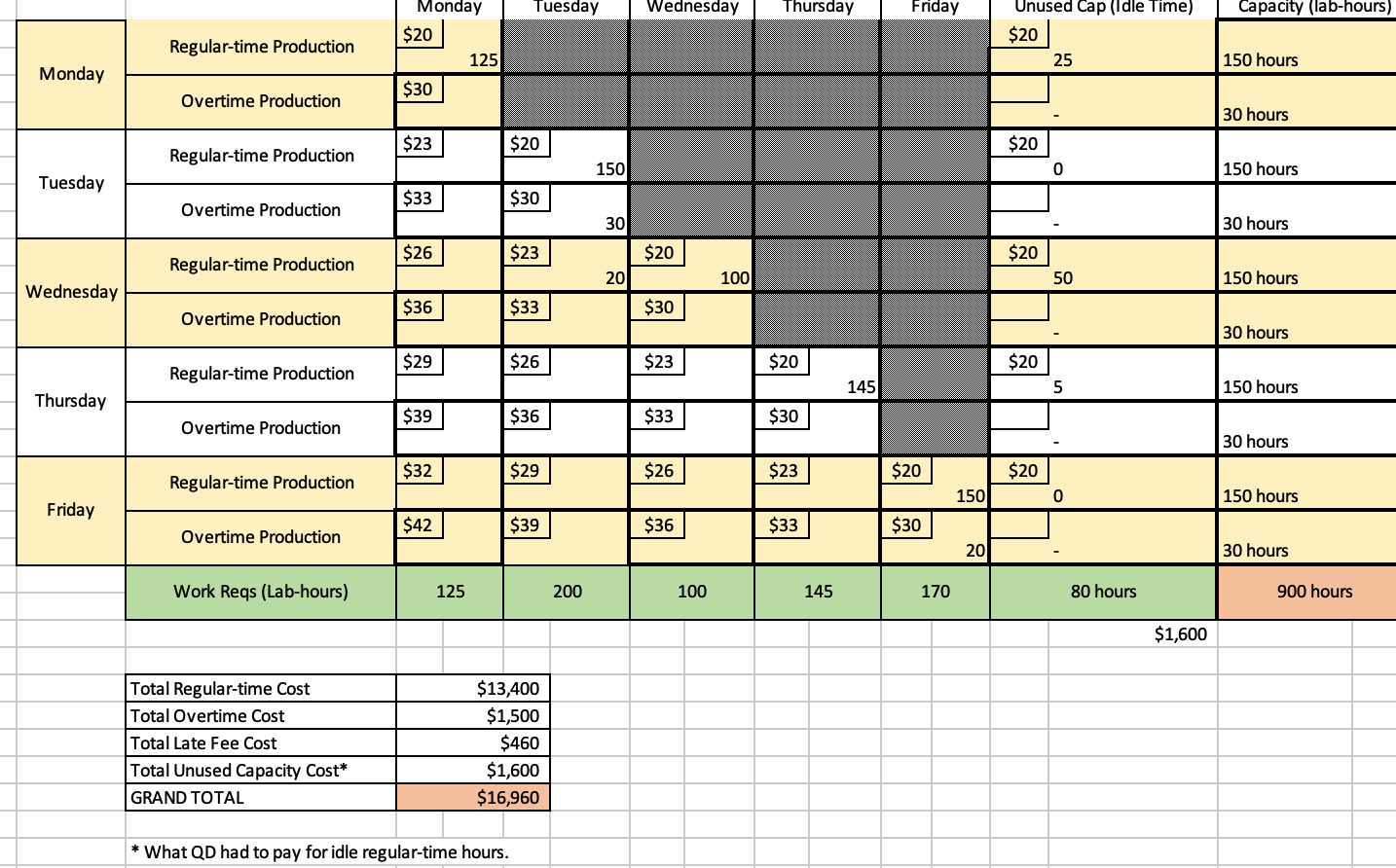
IS THIS RIGHT?/???????????????
Problem 1. 40 pts Last year, a major east-coast insurance company contracted with Qwest Diagnostics (QD), to provide laboratory services for its subscribers. QD must plan weekly service rates at one of its lab sites. Daily work requirements can be performed on either regular or overtime. Daily capacity for regular-time work is 150 lab-hours. Daily capacity for overtime work is 30 lab-hours. QD incurs a labor cost of $20 per lab-hour of work done on regular time; overtime labor cost is 50% more than regular time labor cost. Regular time labor cost must be paid even if workers are idle; however, such is not the case with overtime labor cost. QD agreed to pay the insurance company a late fee of $3/lab-hour for each day that services are performed after the due date. Daily work requirements (in lab-hours) are given below: Work Requirements (lab-hrs) 125 Day Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 200 100 145 170 No work will be carried over from the end of the current week to the Monday of the upcoming week. a) Set up the problem in a transportation tableau format. Use the template in the posted Excel file. Fill in all cost cells, capacities and work requirements. Note that many cost cells are blacked out. You can't allocate capacity to the blacked-out cells because these cells imply that you can hold inventory. In this case, you can't hold inventory. b) Generate a feasible solution. You can't use the Northwest Corner Rule due to the structure of the tableau being that cells are blacked out. Just generate a feasible solution using any method that you wish. Each group could potentially show a different solution. . c) Compute the grand total cost associated with your solution by computing each of the following cost components Regular-time labor cost Overtime labor cost Late fee cost Unused capacity cost Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Capacity (lab-hours) Monday $20 125 Unused Cap (Idle Time) $20 25 Regular-time Production 150 hours Monday $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 150 0 150 hours Tuesday $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 30 hours $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 20 100 50 150 hours Wednesday $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $29 $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 145 5 150 hours Thursday $39 $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $32 $29 $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 150 0 150 hours Friday $42 $39 $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 20 30 hours Work Reqs (Lab-hours) 125 200 100 145 170 80 hours 900 hours $1,600 Total Regular-time Cost Total Overtime Cost Total Late Fee Cost Total Unused Capacity Cost* GRAND TOTAL $13,400 $1,500 $460 $1,600 $16,960 * What QD had to pay for idle regular-time hours. Problem 1. 40 pts Last year, a major east-coast insurance company contracted with Qwest Diagnostics (QD), to provide laboratory services for its subscribers. QD must plan weekly service rates at one of its lab sites. Daily work requirements can be performed on either regular or overtime. Daily capacity for regular-time work is 150 lab-hours. Daily capacity for overtime work is 30 lab-hours. QD incurs a labor cost of $20 per lab-hour of work done on regular time; overtime labor cost is 50% more than regular time labor cost. Regular time labor cost must be paid even if workers are idle; however, such is not the case with overtime labor cost. QD agreed to pay the insurance company a late fee of $3/lab-hour for each day that services are performed after the due date. Daily work requirements (in lab-hours) are given below: Work Requirements (lab-hrs) 125 Day Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 200 100 145 170 No work will be carried over from the end of the current week to the Monday of the upcoming week. a) Set up the problem in a transportation tableau format. Use the template in the posted Excel file. Fill in all cost cells, capacities and work requirements. Note that many cost cells are blacked out. You can't allocate capacity to the blacked-out cells because these cells imply that you can hold inventory. In this case, you can't hold inventory. b) Generate a feasible solution. You can't use the Northwest Corner Rule due to the structure of the tableau being that cells are blacked out. Just generate a feasible solution using any method that you wish. Each group could potentially show a different solution. . c) Compute the grand total cost associated with your solution by computing each of the following cost components Regular-time labor cost Overtime labor cost Late fee cost Unused capacity cost Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Capacity (lab-hours) Monday $20 125 Unused Cap (Idle Time) $20 25 Regular-time Production 150 hours Monday $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 150 0 150 hours Tuesday $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 30 hours $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 20 100 50 150 hours Wednesday $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $29 $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 145 5 150 hours Thursday $39 $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 30 hours $32 $29 $26 $23 $20 $20 Regular-time Production 150 0 150 hours Friday $42 $39 $36 $33 $30 Overtime Production 20 30 hours Work Reqs (Lab-hours) 125 200 100 145 170 80 hours 900 hours $1,600 Total Regular-time Cost Total Overtime Cost Total Late Fee Cost Total Unused Capacity Cost* GRAND TOTAL $13,400 $1,500 $460 $1,600 $16,960 * What QD had to pay for idle regular-time hoursStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


