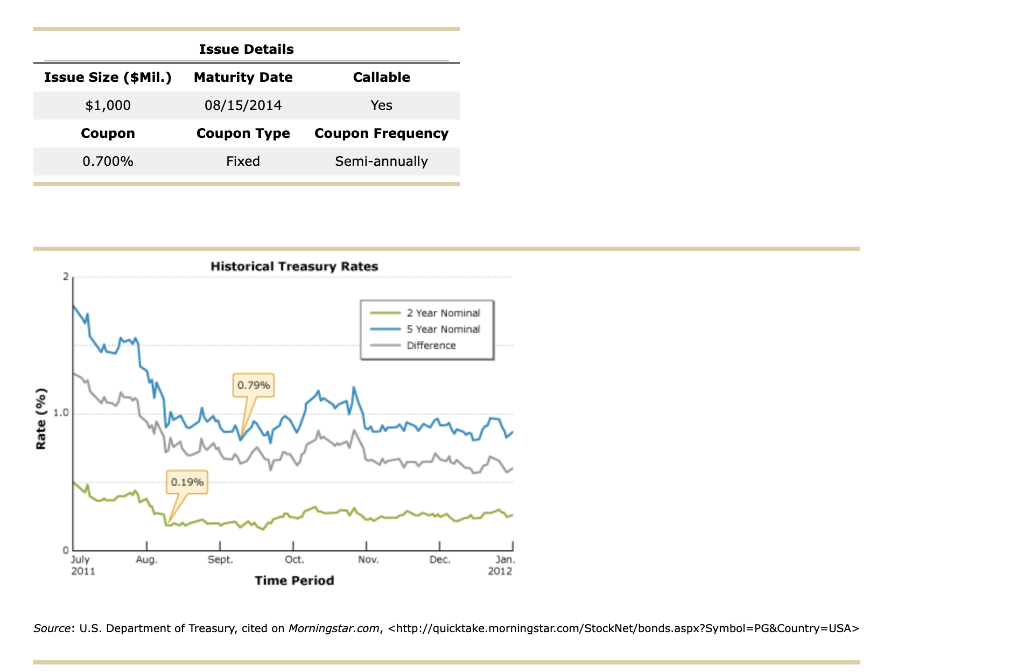

Issue Details Maturity Date Callable Issue Size ($Mil.) $1,000 08/15/2014 Yes Coupon Coupon Type Fixed Coupon Frequency Semi-annually 0.700% Historical Treasury Rates 2 Year Nominal 5 Year Nominal Difference 0.79% 1.0 Rate(%) 0.19% Aug Sept. Oct. Nov. July 2011 Dec. Jan 2012 Time Period Source: U.S. Department of Treasury, cited on Morningstar.com,
Proctor and Gamble's total amount of debt increased from 31.9% in March 2011 to 34.2% in December 2011, mainly due to its net debt issuances to fund general corporate purposes. What was the annual cost of the funds raised from the $1.0 billion bonds that mature in 2014 to P&G? 100.10 basis points. If the bond sold at $100.10 at the time of issue, investors' required annual yield would be 0.67% Looking at the comparable U.S. Treasury yield, these bonds were issued at a spread of basis points. Because the coupon rate is the yield required by the market, the bond sold at at the time of issue. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal If the new observed yield of the bond is 1.3%, the bond is likely to be trading at a price of $ places.) If the current yield is higher than the coupon rate, investors would want a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is less than the yield required by the market, the price of the bond is most likely to be the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at . Thus, when the yield As interest rates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, and the price of the bond is likely to increases to 1.3%, the bond's price by %. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) Understanding yield to call and when bonds are called Suppose the bond had a call structure that allowed the company to call its bonds after one year. The call structure of the bonds states that the bonds would be callable at par. What would be the yield to call? 2.498% 1.785% 1.598% 1.054% In what situation would the company call the bond? When interest rates fall When interest rates rise When the bond's price rises When current yield on the bonds falls From an investor's perspective, if the investor holds these P&G bonds in their portfolio and market interest rates rise, the bonds' value in the fixed- income asset class in the portfolio will most likely decline ; but if market interest rates fall, the value of bonds in the portfolio will increase Issue Details Maturity Date Callable Issue Size ($Mil.) $1,000 08/15/2014 Yes Coupon Coupon Type Fixed Coupon Frequency Semi-annually 0.700% Historical Treasury Rates 2 Year Nominal 5 Year Nominal Difference 0.79% 1.0 Rate(%) 0.19% Aug Sept. Oct. Nov. July 2011 Dec. Jan 2012 Time Period Source: U.S. Department of Treasury, cited on Morningstar.com, Proctor and Gamble's total amount of debt increased from 31.9% in March 2011 to 34.2% in December 2011, mainly due to its net debt issuances to fund general corporate purposes. What was the annual cost of the funds raised from the $1.0 billion bonds that mature in 2014 to P&G? 100.10 basis points. If the bond sold at $100.10 at the time of issue, investors' required annual yield would be 0.67% Looking at the comparable U.S. Treasury yield, these bonds were issued at a spread of basis points. Because the coupon rate is the yield required by the market, the bond sold at at the time of issue. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal If the new observed yield of the bond is 1.3%, the bond is likely to be trading at a price of $ places.) If the current yield is higher than the coupon rate, investors would want a higher return on their investment. If the coupon rate is less than the yield required by the market, the price of the bond is most likely to be the par value of the bond, and the bond will sell at . Thus, when the yield As interest rates increase, the yield required by the market will increase, and the price of the bond is likely to increases to 1.3%, the bond's price by %. (Note: Round your answer to two decimal places.) Understanding yield to call and when bonds are called Suppose the bond had a call structure that allowed the company to call its bonds after one year. The call structure of the bonds states that the bonds would be callable at par. What would be the yield to call? 2.498% 1.785% 1.598% 1.054% In what situation would the company call the bond? When interest rates fall When interest rates rise When the bond's price rises When current yield on the bonds falls From an investor's perspective, if the investor holds these P&G bonds in their portfolio and market interest rates rise, the bonds' value in the fixed- income asset class in the portfolio will most likely decline ; but if market interest rates fall, the value of bonds in the portfolio will increase









