it would be great if i could get a strp by step
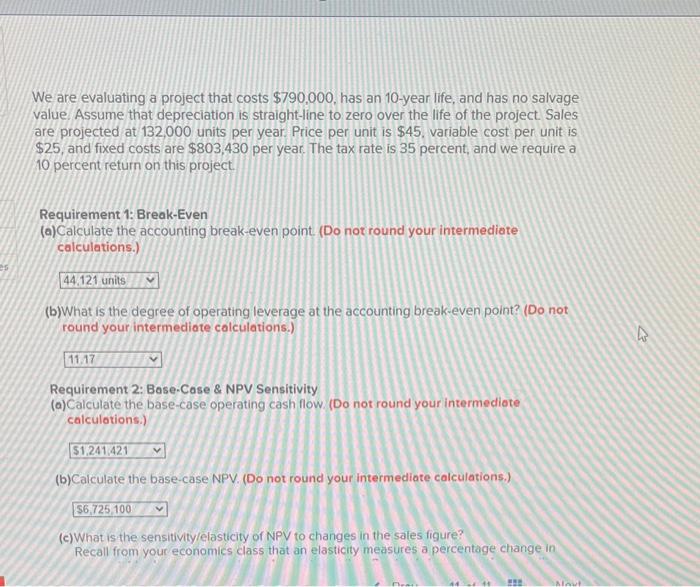
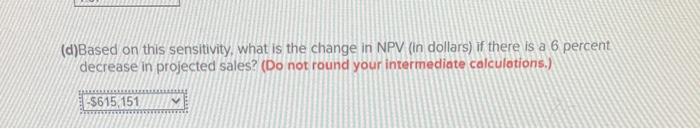
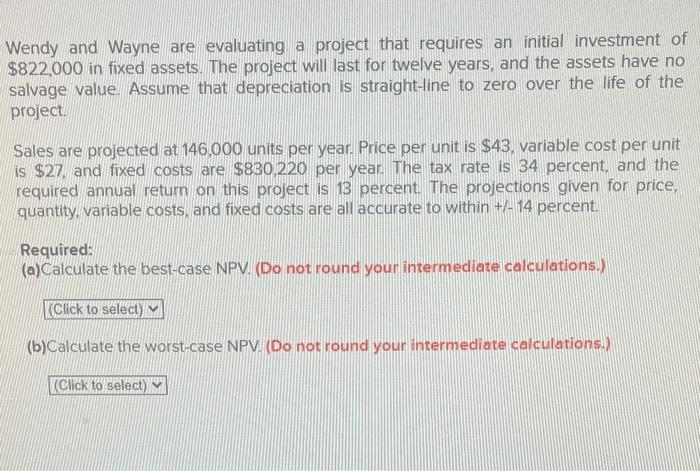
Wendy and Wayne are evaluating a project that requires an initial investment of $822.000 in fixed assets. The project will last for twelve years, and the assets have no salvage value. Assume that depreciation is straight-line to zero over the life of the project. Sales are projected at 146,000 units per year. Price per unit is $43, variable cost per unit is \$27, and fixed costs are $830.220 per year. The tax rate is 34 percent, and the required annual return on this project is 13 percent. The projections given for price, quantity, variable costs, and fixed costs are all accurate to within +114 percent Required: (a)Calculate the best-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (b) Calculate the worst-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) We are evaluating a project that costs $790,000, has an 10 -year life, and has no salvage value. Assume that depreciation is straight-line to zero over the life of the project. Sales are projected at 132,000 units per year. Price per unit is $45. variable cost per unit is $25, and fixed costs are $803,430 per year. The tax rate is 35 percent, and we require a 10 percent return on this project. Requirement 1: Break-Even (a)Calculate the accounting break-even point (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (b) What is the degree of operating leverage at the accounting break-even point? (Do not round your intermediote colculations.) Requirement 2: Base.Case \& NPV Sensitivity (a) Calculate the base-case operating cash flow. (Do not round your intermediote calculotions.) (b) Calculate the base-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (c) What is the sensitivitylelasticity of NPV to changes in the sales figure? Recall from your economics class that an elasticity measures a percentage change in (d)Based on this sensitivity, what is the change in NPV (in dollars) if there is a 6 percent decrease in projected sales? (Do not round your intermediate calculotions.) Wendy and Wayne are evaluating a project that requires an initial investment of $822.000 in fixed assets. The project will last for twelve years, and the assets have no salvage value. Assume that depreciation is straight-line to zero over the life of the project. Sales are projected at 146,000 units per year. Price per unit is $43, variable cost per unit is \$27, and fixed costs are $830.220 per year. The tax rate is 34 percent, and the required annual return on this project is 13 percent. The projections given for price, quantity, variable costs, and fixed costs are all accurate to within +114 percent Required: (a)Calculate the best-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (b) Calculate the worst-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) We are evaluating a project that costs $790,000, has an 10 -year life, and has no salvage value. Assume that depreciation is straight-line to zero over the life of the project. Sales are projected at 132,000 units per year. Price per unit is $45. variable cost per unit is $25, and fixed costs are $803,430 per year. The tax rate is 35 percent, and we require a 10 percent return on this project. Requirement 1: Break-Even (a)Calculate the accounting break-even point (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (b) What is the degree of operating leverage at the accounting break-even point? (Do not round your intermediote colculations.) Requirement 2: Base.Case \& NPV Sensitivity (a) Calculate the base-case operating cash flow. (Do not round your intermediote calculotions.) (b) Calculate the base-case NPV. (Do not round your intermediate calculations.) (c) What is the sensitivitylelasticity of NPV to changes in the sales figure? Recall from your economics class that an elasticity measures a percentage change in (d)Based on this sensitivity, what is the change in NPV (in dollars) if there is a 6 percent decrease in projected sales? (Do not round your intermediate calculotions.)