Question
Iterative hanoi javascript Move method: Move class: //Method needed to be done public static void iterativeHanoi(int disc, int from, int aux, int to) { Move
Iterative hanoi javascript
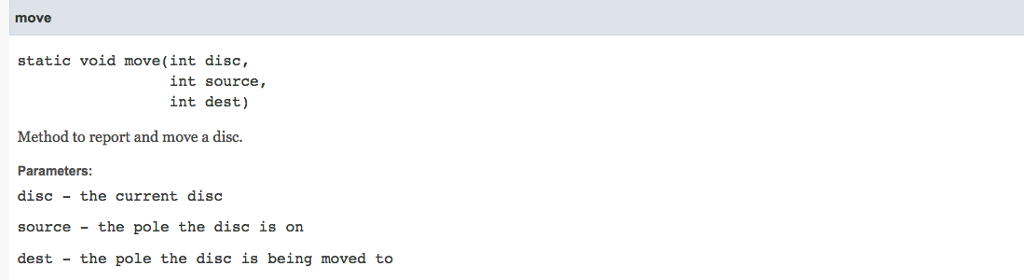
Move method:
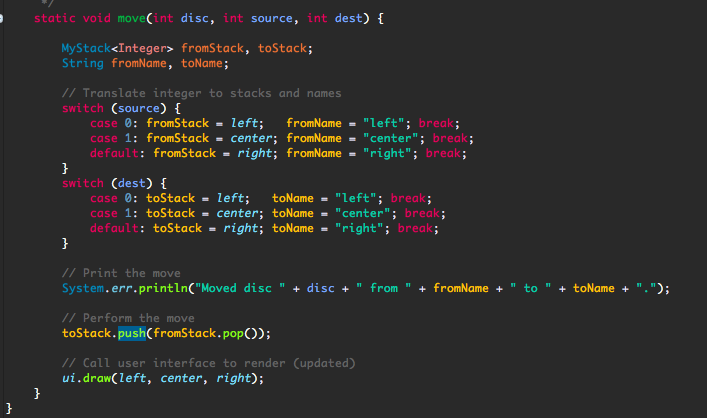
Move class:
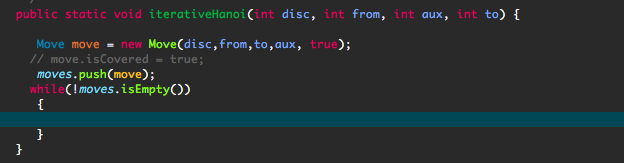
//Method needed to be done
public static void iterativeHanoi(int disc, int from, int aux, int to) {
Move move = new Move(disc,from,to,aux, true);
// move.isCovered = true;
moves.push(move);
while(!moves.isEmpty())
{
//code here
}
}
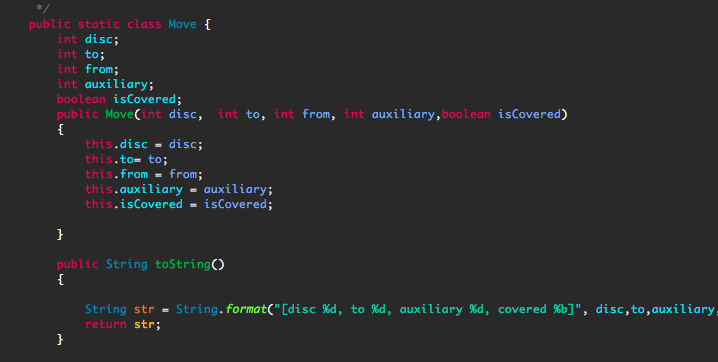
//move Class
public static class Move {
int disc;
int to;
int from;
int auxiliary;
boolean isCovered;
public Move(int disc, int to, int from, int auxiliary,boolean isCovered)
{
this.disc = disc;
this.to= to;
this.from = from;
this.auxiliary = auxiliary;
this.isCovered = isCovered;
}
public String toString()
{
String str = String.format("[disc %d, to %d, auxiliary %d, covered %b]", disc,to,auxiliary,isCovered);
return str;
}
}
/**
* Stack used for the iterative method solution
*/
private static MyStack moves = new MyStack();
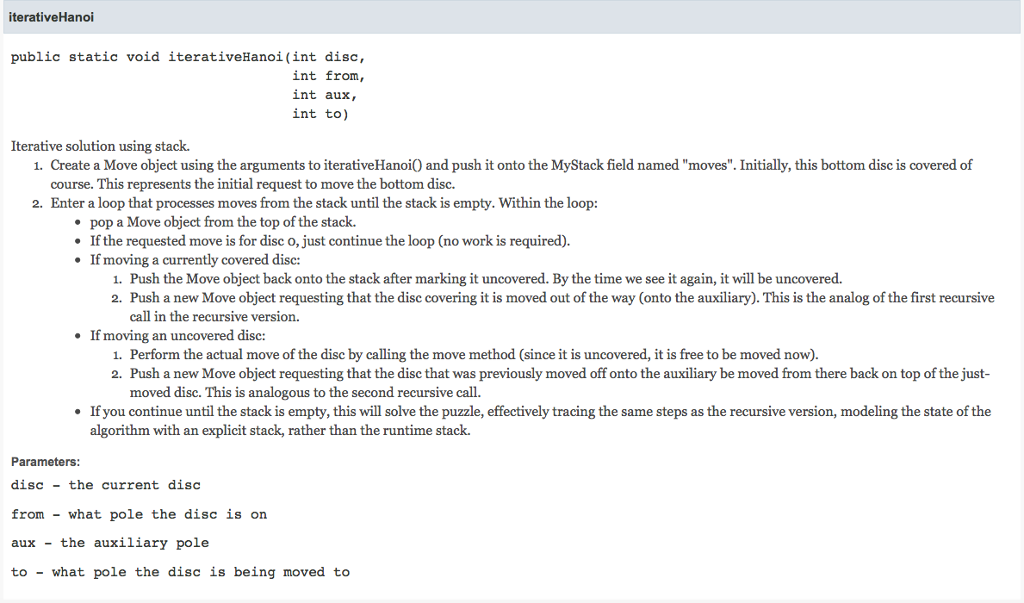
iterativeHanoi public static void iterativeHanoi (int disc, int from, int aux, int to) Iterative solution using stack. 1. Create a Move object using the arguments to iterativeHanoiO and push it onto the MyStack field named "moves". Initially, this bottom disc is covered of course. This represents the initial request to move the bottom disc. 2. Enter a loop that processes moves from the stack until the stack is empty. Within the loop: pop a Move object from the top of the stack. If the requested move is for disc o, just continue the loop (no work is required) If moving a currently covered disc: 1. Push the Move object back onto the stack after marking it uncovered. By the time we see it again, it will be uncovered. 2. Push a new Move object requesting that the disc covering it is moved out of the way (onto the auxiliary). This is the analog of the first recursive call in the recursive version If moving an uncovered disc: 1. Perform the actual move of the disc by calling the move method (since it is uncovered, it is free to be moved now) 2. Push a new Move object requesting that the disc that was previously moved off onto the auxiliary be moved from there back on top of the just- moved disc. This is analogous to the second recursive call. If you continue until the stack is empty, this will solve the puzzle, effectively tracing the same steps as the recursive version, modeling the state of the algorithm with an explicit stack, rather than the runtime stack. Parameters: disc-the current disc from - what pole the disc is on aux the auxiliary pole to - what pole the disc is being moved to iterativeHanoi public static void iterativeHanoi (int disc, int from, int aux, int to) Iterative solution using stack. 1. Create a Move object using the arguments to iterativeHanoiO and push it onto the MyStack field named "moves". Initially, this bottom disc is covered of course. This represents the initial request to move the bottom disc. 2. Enter a loop that processes moves from the stack until the stack is empty. Within the loop: pop a Move object from the top of the stack. If the requested move is for disc o, just continue the loop (no work is required) If moving a currently covered disc: 1. Push the Move object back onto the stack after marking it uncovered. By the time we see it again, it will be uncovered. 2. Push a new Move object requesting that the disc covering it is moved out of the way (onto the auxiliary). This is the analog of the first recursive call in the recursive version If moving an uncovered disc: 1. Perform the actual move of the disc by calling the move method (since it is uncovered, it is free to be moved now) 2. Push a new Move object requesting that the disc that was previously moved off onto the auxiliary be moved from there back on top of the just- moved disc. This is analogous to the second recursive call. If you continue until the stack is empty, this will solve the puzzle, effectively tracing the same steps as the recursive version, modeling the state of the algorithm with an explicit stack, rather than the runtime stack. Parameters: disc-the current disc from - what pole the disc is on aux the auxiliary pole to - what pole the disc is being moved toStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


