Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
its all one question! need help solving it. thank you! During the fourth quarter of 2018, Stream, Inc. generated excess cash, which the company invested
its all one question!
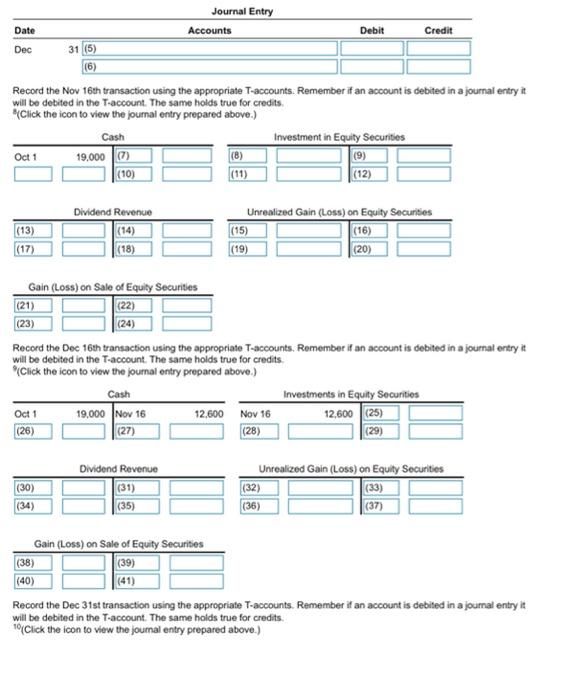
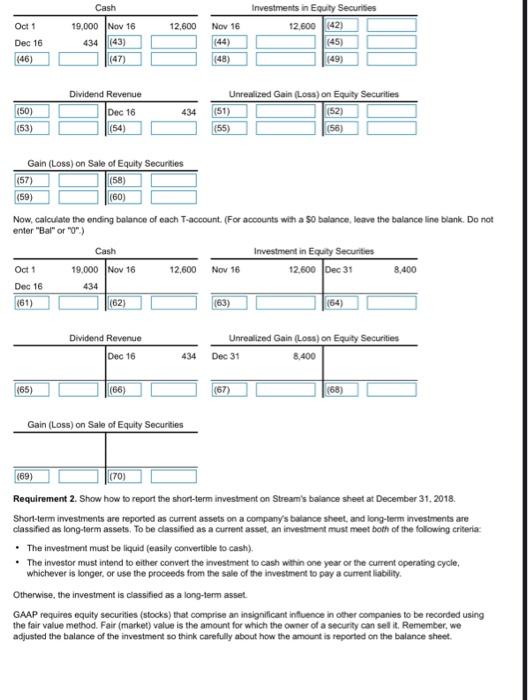
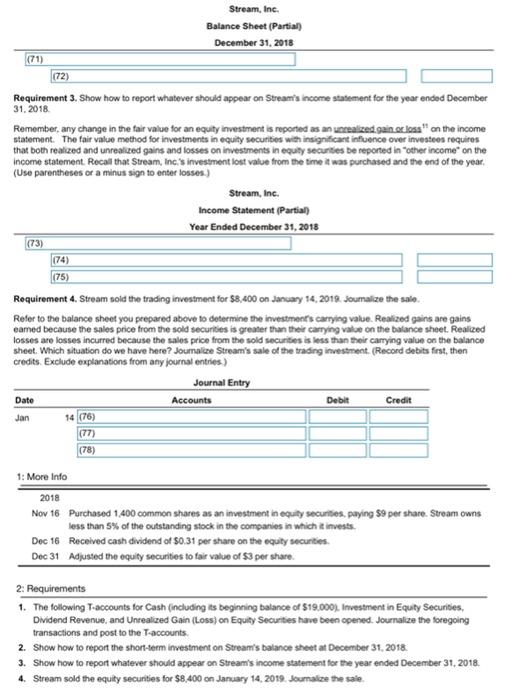
During the fourth quarter of 2018, Stream, Inc. generated excess cash, which the company invested in equity securities as follows: Click on the icon to view the equity securities transactions) Read the requirements? Equity securities are investments in capital stock. According to GAAP, the proper way to account for equity investments depends on the percentage of the voting stock the investor owns, and hence, the degree of influence the investor has over the company in which it invested (the investee). If an investor owns less than 20% of the voting stock of the investee, the investor is presumed to have insignificant influence, and the fair valve method of reporting the investment must be used. Investments in equity securities (stock) can be classified as either current or long-term assets, depending on the company's ability and intent to hold or sell them. GAAP requires equity securities (stocks) that comprise an insignificant influence in other companies to be recorded using the fair value method-regardless of whether they are classified as current or long-term assets. The fair value method for investments in equity securities with insignificant influence over investees requires that both realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments in equity securities be reported in other income on the income statement Requirement 1. The following T-accounts for Cash (including its beginning balance of $19,000), Investment in Equity Securities Dividend Revenue and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities have been opened Journalize the foregoing transactions and post to the T-accounts On November 16th, Stream purchased 1,400 shares of common shares at a per share price of $9Stream owns less than 5% of the outstanding stock in the companies in which it invests The purchase of the stock for cash will increase Stream's asset account, Investment in Equity Securities, and decrease its Cash account by the purchase price of the investment. Go ahead and prepare the journal entry for the purchase of the stock. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Joumal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Nov 16 (1) (2) On December 16th, the company received a cash dividend on their investment of $0.31 per share. The company received cash and must record the dividend as revenue. Think carefully about which accounts would be affected by this transaction-the book value of an investment is not affected by the dividends declared. Recall the normal balance of the accounts. Will they increase or decrease as a result of the transaction? You will need to compute the total dividend received". Go ahead and record the entry Joumal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Dec 16 (3) (4) On December 31st, the company adjusted the equity securities to fair value of $3 per share. Since equity investments with insignificant influence over investees are reported on the balance sheet at their fair value, we must make an adjustment for the change in fair value at year-end. Unrealized gains are gains that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value exceeds their cost Unrealized losses are losses that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value drops below their cost. Let's calculate the unrealized gain or loss of Stream, Inc.'s equity investment at December 31. You will have to calculate the total fair value of the investment on this date. Fair (market value ve at December 31 Purchase price Unrealized gain(108) 12.600 Now record the unrealized loss. Think carefully about whether the investment's value is increasing or decreasing Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts Dec 31 (5) (6) Record the Nov 16th transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits (Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Investment in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 (7) (9) (10) (12) Cash (13) (17) Dividend Revenue (14) (18) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (15) (16) (19) (20) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (21) (22) (23) (24) Record the Dec 16th transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Cash Investments in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 Nov 16 12,600 Nov 16 12,600 (25) (26) (27) (28) (29) (30) (34) Dividend Revenue (31) (35) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (32) (33) (36) (37) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (38) (39) (40) Record the Dec 31st transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Oct 1 12,600 Cash 19,000 Nov 16 434 (43) (47) Investments in Equity Securities 12,600 (42) (45) (49) Nov 16 (44) (48) Dec 16 (46) Dividend Revenue Dec 16 434 (50) (53) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (51) (52) (55) (56) (54) (58) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (57) (59) (60) Now, calculate the ending balance of each T-account. (For accounts with a 50 balance, leave the balance line blank. Do not enter"Bal" or "0") Cash Investment in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 Nov 16 12,600 Nov 16 12.600 Dec 31 8,400 Dec 16 434 (61) (62) (63) (64) Dividend Revenue Dec 16 Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dec 31 8.400 434 (65) (66) (67) (68) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (70) (69) Requirement 2. Show how to report the short-term investment on Stream's balance sheet at December 31, 2018. Short-term investments are reported as current assets on a company's balance sheet, and long-term investments are classified as long-term assets. To be classified as a current asset an investment must meet both of the following criteria: . The investment must be liquid (easily convertible to cash) The investor must intend to either convert the investment to cash within one year or the current operating cycle, whichever is longer, or use the proceeds from the sale of the investment to pay a current liability Otherwise, the investment is classified as a long-term asset. GAAP requires equity securities (stocks) that comprise an insignificant influence in other companies to be recorded using the fair value method. Fair (market) value is the amount for which the owner of a security can selit. Remember, we adjusted the balance of the investment so think carefully about how the amount is reported on the balance sheet. Stream, Inc. Balance Sheet (Partial December 31, 2018 (71) (72) Requirement 3. Show how to report whatever should appear on Stream's income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 Remember, any change in the fair value for an equity investment is reported as an unrealized gain closs" on the income statement. The fair value method for investments in equity securities with insignificant influence over investees requires that both realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments in equity Securities be reported in other income on the Income statement. Recall that Stream, Inc. investment lost value from the time it was purchased and the end of the year, (Use parentheses or a minus sign to enter losses.) Stream, Inc. Income Statement (Partial) Year Ended December 31, 2018 (73) (74) (75) Requirement 4. Stream sold the trading investment for $8,400 on January 14, 2019. Soumalize the sale. Refer to the balance sheet you prepared above to determine the investment's carrying value. Realized gains are gains eamed because the sales price from the sold securities is greater than their carrying value on the balance sheet. Realized losses are losses incurred because the sales price from the sold securities is less than their carrying value on the balance sheet. Which situation do we have here? Journalize Stream's sale of the trading investment. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Jan 14 (76) (77) (78) 1: More Info 2018 Nov 16 Purchased 1400 common shares as an investment in equity securities, paying 99 per share. Stream owns less than 5% of the outstanding stock in the companies in which it invests. Dec 16 Received cash dividend of $0.31 per share on the equity securities Dec 31 Adjusted the equity securities to fair value of 53 per share. 2: Requirements 1. The following T-accounts for Cash (including its beginning balance of $19.000). Investment in Equity Securities, Dividend Revenue, and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities have been opened Journalize the foregoing transactions and post to the T-accounts 2. Show how to report the short-term investment on Stream's balance sheet at December 31, 2018 3. Show how to report whatever should appear on Stream's income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 4. Stream sold the equity securities for $8,400 on January 14, 2019. Journalice the sale 3: Definition Fair (market value is the amount for which the owner of a security can sell it 4: Definition Purchase price Number of shares x Cost per share 1,400 X $ ? 5: Definition Assets Liabilities Common Stockholders' equity Retained carnings + Revenues - Expenses - DR CR DR CR DR CA stock TTTTTTT Assets Liabilities DR CR DR CR Dividends DR CA DR CR 6: Definition Number of shares 1.400 x Dividend per share X$ Total dividend received 0.31 7. Definition Number of shares Fair value per share Total tair value 1.400 8: More Info Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts 16 Investment in Equity Securities Cash Nov 12.600 12,600 9: More Info Journal Entry Accounts Credit Date Dec Debit 434 16 Cash Dividend Revenue 10: More Info Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts 31 Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Dec 8.400 8.400 11: Definition Unrealized gains are gains that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value exceeds their cost. Unrealized losses are losses that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value drops below their cost. Oo OOOO investment in Equity Securities Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Cash Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities OOOO (3) 0 000 OO 0 000 (2) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities O Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (5) O Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (8) (9) (10) (11) Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 O Dec 31 Dec 31 Dec 31 Dec 31 OO OOOO 0 000 OOOO OOOO 0000 (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) OOOO Nov 16 Dec 16 O Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 O Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (17) (18) (19) (20) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (21) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Dec 31 (22) (23) (24) (25) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (26) Dec 31 (27) D Dec 31 (28) Dec 31 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 0 0 0 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (29) Dec 31 (30) Dec 31 O Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 o Dec 31 (3) Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 o Dec 31 34) Oct 1 Nov 16 ODec 16 (32) Dec 31 (33) Dec 31 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (36) ODec 31 Dec 31 (35) Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 O Dec 31 (39) ODec 31 (40) o Dec 31 (38) OOct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (41) ODec 31 (42) ) (43) (44) 0 000 OOct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (45) O Nov 16 ODec 16 Dec 31 (46) (47) (48) (49) (50) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (51) (52) 53) (55) Nov 16 ODec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 154) O No 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (56) (57) (58) (59) (60) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 ODec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 ONov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (61) (62) 163) (64) (66) (67) (65) Bal ) 0 0 Bal Bal Bal Bal Bal Bal (68) (69) (700 Bal Bal o Bal OOOO OOOO OOOO 0 000 0 0 (71) O Other revenue and expense Current assets: Long-term assets: Operating expenses (72) Long-term investments Dividend revenue Unrealized gain foss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (73) Other revenue expense Current assets: Service revenue Long-term assets: Stockholders' equity Operating expenses: (74) Long-term investments, at fair value Dividend revenue Unrealized gain lioss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (75) Long-term investments, at fair value Dividend revenue Unrealized gain loss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (76) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities (77) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gein (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities (78) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities OOOO OOOO During the fourth quarter of 2018, Stream, Inc. generated excess cash, which the company invested in equity securities as follows: Click on the icon to view the equity securities transactions) Read the requirements? Equity securities are investments in capital stock. According to GAAP, the proper way to account for equity investments depends on the percentage of the voting stock the investor owns, and hence, the degree of influence the investor has over the company in which it invested (the investee). If an investor owns less than 20% of the voting stock of the investee, the investor is presumed to have insignificant influence, and the fair valve method of reporting the investment must be used. Investments in equity securities (stock) can be classified as either current or long-term assets, depending on the company's ability and intent to hold or sell them. GAAP requires equity securities (stocks) that comprise an insignificant influence in other companies to be recorded using the fair value method-regardless of whether they are classified as current or long-term assets. The fair value method for investments in equity securities with insignificant influence over investees requires that both realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments in equity securities be reported in other income on the income statement Requirement 1. The following T-accounts for Cash (including its beginning balance of $19,000), Investment in Equity Securities Dividend Revenue and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities have been opened Journalize the foregoing transactions and post to the T-accounts On November 16th, Stream purchased 1,400 shares of common shares at a per share price of $9Stream owns less than 5% of the outstanding stock in the companies in which it invests The purchase of the stock for cash will increase Stream's asset account, Investment in Equity Securities, and decrease its Cash account by the purchase price of the investment. Go ahead and prepare the journal entry for the purchase of the stock. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Joumal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Nov 16 (1) (2) On December 16th, the company received a cash dividend on their investment of $0.31 per share. The company received cash and must record the dividend as revenue. Think carefully about which accounts would be affected by this transaction-the book value of an investment is not affected by the dividends declared. Recall the normal balance of the accounts. Will they increase or decrease as a result of the transaction? You will need to compute the total dividend received". Go ahead and record the entry Joumal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Dec 16 (3) (4) On December 31st, the company adjusted the equity securities to fair value of $3 per share. Since equity investments with insignificant influence over investees are reported on the balance sheet at their fair value, we must make an adjustment for the change in fair value at year-end. Unrealized gains are gains that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value exceeds their cost Unrealized losses are losses that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value drops below their cost. Let's calculate the unrealized gain or loss of Stream, Inc.'s equity investment at December 31. You will have to calculate the total fair value of the investment on this date. Fair (market value ve at December 31 Purchase price Unrealized gain(108) 12.600 Now record the unrealized loss. Think carefully about whether the investment's value is increasing or decreasing Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts Dec 31 (5) (6) Record the Nov 16th transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits (Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Investment in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 (7) (9) (10) (12) Cash (13) (17) Dividend Revenue (14) (18) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (15) (16) (19) (20) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (21) (22) (23) (24) Record the Dec 16th transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Cash Investments in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 Nov 16 12,600 Nov 16 12,600 (25) (26) (27) (28) (29) (30) (34) Dividend Revenue (31) (35) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (32) (33) (36) (37) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (38) (39) (40) Record the Dec 31st transaction using the appropriate T-accounts. Remember if an account is debited in a journal entry it will be debited in the T-account. The same holds true for credits Click the icon to view the journal entry prepared above.) Oct 1 12,600 Cash 19,000 Nov 16 434 (43) (47) Investments in Equity Securities 12,600 (42) (45) (49) Nov 16 (44) (48) Dec 16 (46) Dividend Revenue Dec 16 434 (50) (53) Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities (51) (52) (55) (56) (54) (58) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (57) (59) (60) Now, calculate the ending balance of each T-account. (For accounts with a 50 balance, leave the balance line blank. Do not enter"Bal" or "0") Cash Investment in Equity Securities Oct 1 19,000 Nov 16 12,600 Nov 16 12.600 Dec 31 8,400 Dec 16 434 (61) (62) (63) (64) Dividend Revenue Dec 16 Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dec 31 8.400 434 (65) (66) (67) (68) Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (70) (69) Requirement 2. Show how to report the short-term investment on Stream's balance sheet at December 31, 2018. Short-term investments are reported as current assets on a company's balance sheet, and long-term investments are classified as long-term assets. To be classified as a current asset an investment must meet both of the following criteria: . The investment must be liquid (easily convertible to cash) The investor must intend to either convert the investment to cash within one year or the current operating cycle, whichever is longer, or use the proceeds from the sale of the investment to pay a current liability Otherwise, the investment is classified as a long-term asset. GAAP requires equity securities (stocks) that comprise an insignificant influence in other companies to be recorded using the fair value method. Fair (market) value is the amount for which the owner of a security can selit. Remember, we adjusted the balance of the investment so think carefully about how the amount is reported on the balance sheet. Stream, Inc. Balance Sheet (Partial December 31, 2018 (71) (72) Requirement 3. Show how to report whatever should appear on Stream's income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 Remember, any change in the fair value for an equity investment is reported as an unrealized gain closs" on the income statement. The fair value method for investments in equity securities with insignificant influence over investees requires that both realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments in equity Securities be reported in other income on the Income statement. Recall that Stream, Inc. investment lost value from the time it was purchased and the end of the year, (Use parentheses or a minus sign to enter losses.) Stream, Inc. Income Statement (Partial) Year Ended December 31, 2018 (73) (74) (75) Requirement 4. Stream sold the trading investment for $8,400 on January 14, 2019. Soumalize the sale. Refer to the balance sheet you prepared above to determine the investment's carrying value. Realized gains are gains eamed because the sales price from the sold securities is greater than their carrying value on the balance sheet. Realized losses are losses incurred because the sales price from the sold securities is less than their carrying value on the balance sheet. Which situation do we have here? Journalize Stream's sale of the trading investment. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries) Journal Entry Date Accounts Debit Credit Jan 14 (76) (77) (78) 1: More Info 2018 Nov 16 Purchased 1400 common shares as an investment in equity securities, paying 99 per share. Stream owns less than 5% of the outstanding stock in the companies in which it invests. Dec 16 Received cash dividend of $0.31 per share on the equity securities Dec 31 Adjusted the equity securities to fair value of 53 per share. 2: Requirements 1. The following T-accounts for Cash (including its beginning balance of $19.000). Investment in Equity Securities, Dividend Revenue, and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities have been opened Journalize the foregoing transactions and post to the T-accounts 2. Show how to report the short-term investment on Stream's balance sheet at December 31, 2018 3. Show how to report whatever should appear on Stream's income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018 4. Stream sold the equity securities for $8,400 on January 14, 2019. Journalice the sale 3: Definition Fair (market value is the amount for which the owner of a security can sell it 4: Definition Purchase price Number of shares x Cost per share 1,400 X $ ? 5: Definition Assets Liabilities Common Stockholders' equity Retained carnings + Revenues - Expenses - DR CR DR CR DR CA stock TTTTTTT Assets Liabilities DR CR DR CR Dividends DR CA DR CR 6: Definition Number of shares 1.400 x Dividend per share X$ Total dividend received 0.31 7. Definition Number of shares Fair value per share Total tair value 1.400 8: More Info Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts 16 Investment in Equity Securities Cash Nov 12.600 12,600 9: More Info Journal Entry Accounts Credit Date Dec Debit 434 16 Cash Dividend Revenue 10: More Info Date Debit Credit Journal Entry Accounts 31 Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Dec 8.400 8.400 11: Definition Unrealized gains are gains that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value exceeds their cost. Unrealized losses are losses that arise before securities are sold, because their fair market value drops below their cost. Oo OOOO investment in Equity Securities Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Cash Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities OOOO (3) 0 000 OO 0 000 (2) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities O Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (5) O Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities Investment in Equity Securities Cash Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Gain (Loss) on Sale of Equity Securities (8) (9) (10) (11) Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 O Dec 31 Dec 31 Dec 31 Dec 31 OO OOOO 0 000 OOOO OOOO 0000 (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) OOOO Nov 16 Dec 16 O Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 O Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (17) (18) (19) (20) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (21) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Dec 31 (22) (23) (24) (25) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (26) Dec 31 (27) D Dec 31 (28) Dec 31 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 0 0 0 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (29) Dec 31 (30) Dec 31 O Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 o Dec 31 (3) Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 o Dec 31 34) Oct 1 Nov 16 ODec 16 (32) Dec 31 (33) Dec 31 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (36) ODec 31 Dec 31 (35) Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 O Dec 31 (39) ODec 31 (40) o Dec 31 (38) OOct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 Oct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 (41) ODec 31 (42) ) (43) (44) 0 000 OOct 1 Nov 16 Dec 16 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 000 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (45) O Nov 16 ODec 16 Dec 31 (46) (47) (48) (49) (50) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 0 0 0 0 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (51) (52) 53) (55) Nov 16 ODec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 154) O No 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (56) (57) (58) (59) (60) Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 ODec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 ONov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 Nov 16 Dec 16 Dec 31 (61) (62) 163) (64) (66) (67) (65) Bal ) 0 0 Bal Bal Bal Bal Bal Bal (68) (69) (700 Bal Bal o Bal OOOO OOOO OOOO 0 000 0 0 (71) O Other revenue and expense Current assets: Long-term assets: Operating expenses (72) Long-term investments Dividend revenue Unrealized gain foss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (73) Other revenue expense Current assets: Service revenue Long-term assets: Stockholders' equity Operating expenses: (74) Long-term investments, at fair value Dividend revenue Unrealized gain lioss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (75) Long-term investments, at fair value Dividend revenue Unrealized gain loss) on equity securities Gain (loss) on sale of equity securities Investment in equity securities (76) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities (77) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gein (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities (78) Investment in Equity Securities Cash Loss on Sale of Equity Securities Dividend Revenue Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Equity Securities Gain on Sale of Equity Securities OOOO OOOO need help solving it. thank you! 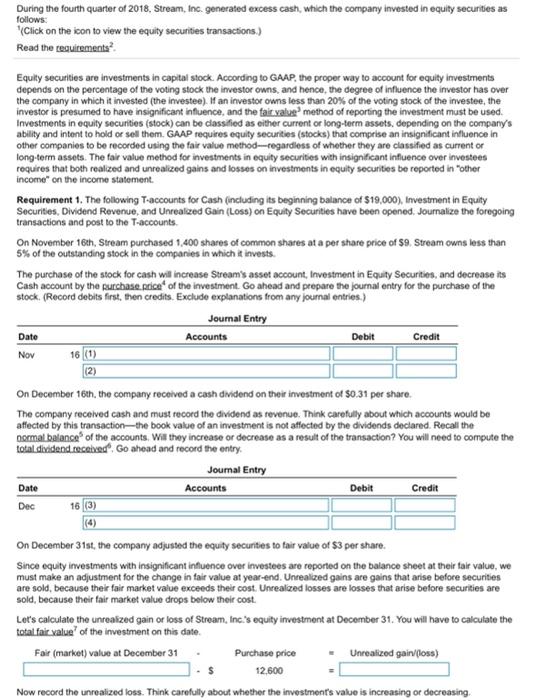












Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


