Question
Jasper Junction Corporation (JJC) is an accrual basis, calendar-year entity that was created by Chao, Iris, and Nolan in 20X1. JJC furnishes the original incorporation
Jasper Junction Corporation (JJC) is an accrual basis, calendar-year entity that was created by Chao, Iris, and Nolan in 20X1. JJC furnishes the original incorporation agreement. The shareholders' bases in the assets contributed are as follows:
- Cash $150,000
- Equipment $245,000
- Inventory $380,000
- Land and Building $375,000
The first five years of business have been lean years. Nolan had to loan the corporation $75,000 to ensure that JJC had enough cash to pay its bills and its Accumulated Earnings and Profits only amounts to $23,000 at the end of 20X5. JJC has its first year of substantial income in 20X6. It also sells some of its land for $100,000 cash, but the sale results in a capital loss. The Board of Directors decides to pay $250,000 in dividends to its shareholders. This is in addition to the $3,500 of interest it pays on the bonds and the $1,500 it pays to Nolan on the money he loaned JJC. The income and expenses of JJC for 20X6, taxable income, and current E&P are provided in the Table below. Corporate Agreement
| Amount | Taxable Income | Current E&P | ||||
| Income | ||||||
| Taxable Income | 176,500 | |||||
| Sales | 412,000 | 412,000 | ||||
| COGS | 150,000 | (150,000 | ) | |||
| Dividends (own 5%) | 133,000 | 133,000 | ||||
| Muni Bond Interest | 1,000 | 1,000 | ||||
| Expenses | ||||||
| Capital loss | 32,935 | (32,935 | ) | |||
| Interest Expense | 5,000 | (5,000 | ) | |||
| Operating Expenses | 120,000 | (120,000 | ) | |||
| Key Life Insurance Premiums | 6,000 | - | (6,000 | ) | ||
| Taxable income before Special Deductions | 270,000 | |||||
| Charitable Contributions | 30,000 | (27,000 | ) | (3,000 | ) | |
| Dividend Receivable Deduction | (66,500 | ) | 66,500 | |||
| Taxable Income | 176,500 | |||||
| Federal Income Tax | 37,065 | (37,065 | ) | |||
| Current E&P | 165,000 | |||||
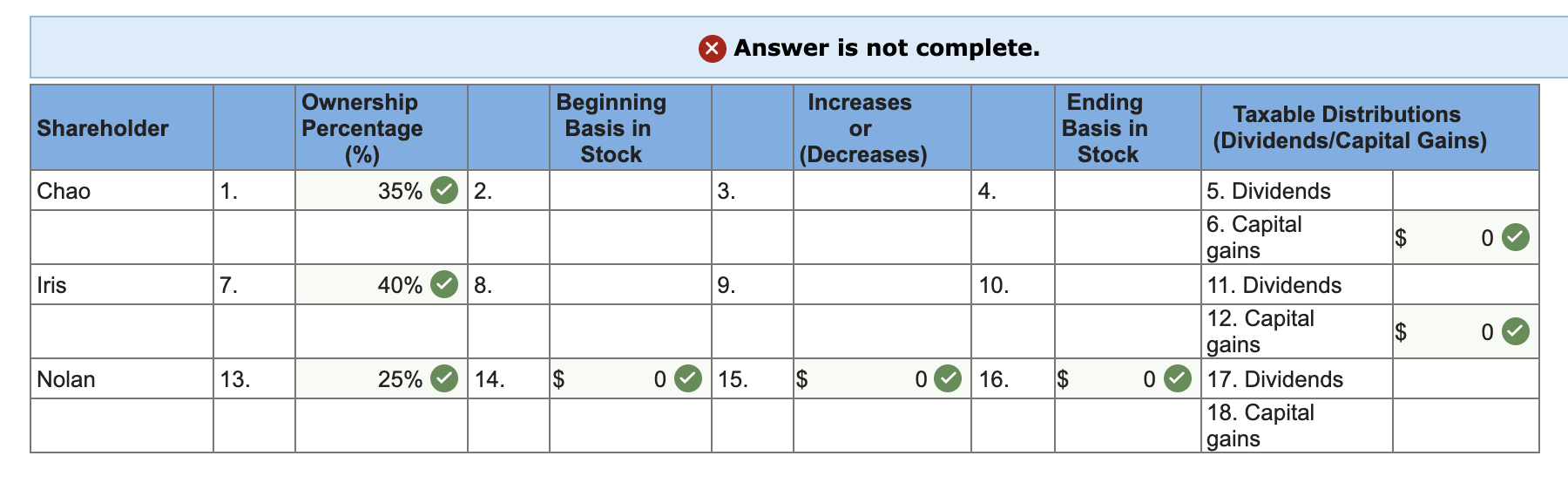
Analyze the information provided to reconcile the shareholders' beginning and ending bases in their stock to determine the federal tax consequences of JJC's corporate distributions. (Decreases should be entered with a minus sign.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


