JAVA PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE!!!!!!! DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM! DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM! PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE! PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
JAVA PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE!!!!!!!
DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM!
DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
CHECK THE EXAMPLE DESIGN DIAGRAM BELOW!
EXAMPLE OF DESIGN DIAGRAM:
Do this but for the following:
Bank Account and Savings Account Classes
Design an abstract class named BankAccount to hold the following data for a bank account:
Balance
Number of deposits this month
Number of withdrawals
Annual interest rate
Monthly service charges
The class should have the following methods:
Constructor: The constructor should accept arguments for the balance and annual interest rate.
deposit: A method that accepts an argument for the amount of the deposit The method should add the argument to the account balance. It should also increment the variable holding the number of deposits.
Withdraw: A method that accepts an argument for the amount of the with drawal. The method should subtract the argument from the balance. It should also increment the variable holding the number of withdrawals.
caleInterest: A method that updates the balance by calculating the monthly interest earned by the account, and adding this interest to the balance. This is performed by the following formulas:
Monthly Interest Rate = (Annual Interest Rate /12) Monthly Interest = Balance * Monthly Interest Rate
Balance = Balance + Monthly Interest
monthlyProcess: A method that subtracts the monthly service charges from the balance, calls the calcInterest method, and then sets the variables that hold the number of withdrawals, number of deposits, and monthly service charges to zero.
Next, design a Savings Account class that extends the BankAccount class. The Savings Account class should have a status field to represent an active or inactive account. If the balance of a savings account falls below $25, it becomes inactive. The status field could be a boolean variable.) No more withdrawals may be made until the balance is raised above $25, at which time the account becomes active again. The savings account class should have the following methods:
Withdraw: A method that determines whether the account is inactive before a withdrawal is made. (No withdrawal will be allowed if the account is not active.) A withdrawal is then made by calling the superclass version of the method.
Deposit: A method that determines whether the account is inactive before a deposit is made. If the account is inactive and the deposit brings the balance above $25, the account becomes active again. A deposit is then made by calling the superclass version of the method.
monthlyProcess: Before the superclass method is called, this method checks the num ber of withdrawals. If the number of withdrawals for the month is more than 4, a service charge of $1 for each withdrawal above 4 is added to the superclass field that holds the monthly service charges. (Don't forget to check the account balance after the service charge is taken. If the balance falls below $25, the account becomes inactive.)
ALSO INCLUDE THE FOLLOWING CLASSES
BANK.java BankAccount.java SavingsAccount.java
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
PLEASE MAKE A DESIGN DIAGRAM PLEASE!
DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM!
DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM!
DO NOT DO THE PROGRAM!
AND DO NOT WRITE IN CURSIVE.
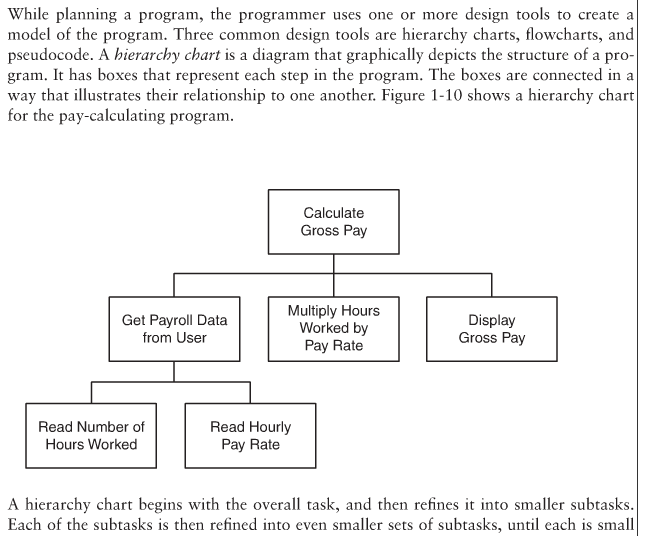
While planning a program, the programmer uses one or more design tools to create a model of the program. Three common design tools are hierarchy charts, flowcharts, and pseudocode. A hierarchy chart is a diagram that graphically depicts the structure of a pro- gram. It has boxes that represent each step in the program. The boxes are connected in a way that illustrates their relationship to one another. Figure 1-10 shows a hierarchy chart| for the pay-calculating program. Calculate Gross Pay Get Payroll Data from User Multiply Hours Worked by Pay Rate Display Gross Pay Read Number of Hours Worked Read Hourly Pay Rate A hierarchy chart begins with the overall task, and then refines it into smaller subtasks. Each of the subtasks is then refined into even smaller sets of subtasks, until each is small While planning a program, the programmer uses one or more design tools to create a model of the program. Three common design tools are hierarchy charts, flowcharts, and pseudocode. A hierarchy chart is a diagram that graphically depicts the structure of a pro- gram. It has boxes that represent each step in the program. The boxes are connected in a way that illustrates their relationship to one another. Figure 1-10 shows a hierarchy chart| for the pay-calculating program. Calculate Gross Pay Get Payroll Data from User Multiply Hours Worked by Pay Rate Display Gross Pay Read Number of Hours Worked Read Hourly Pay Rate A hierarchy chart begins with the overall task, and then refines it into smaller subtasks. Each of the subtasks is then refined into even smaller sets of subtasks, until each is smallStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


