Question
Jones Electrical Case Study - What is the EFN is sales grew the same in 2007 as in 2006? Assume the following: After several years
Jones Electrical Case Study - What is the EFN is sales grew the same in 2007 as in 2006? Assume the following:
After several years of rapid growth, in the spring of 2007 Jones Electrical Distribution anticipated a further substantial increase in sales. Despite good profits, the company had experienced a shortage of cash and had found it necessary to increase its borrowing from Metropolitan Banka local one- branch bankto $250,000 in 2006. The maximum loan that Metropolitan would make to any one borrower was $250,000, and Jones had been able to stay within the limit only by relying very heavily on trade credit from the manufacturers from whom Jones purchased the electrical products it sold to its customers. Nelson Jones, sole owner and president of the company, was therefore looking elsewhere for a new banking relationship that would allow him to negotiate a larger loan.
Jim Lyons, a homebuilder who was a friend of Jones, introduced Jones to Rachel Montrose, Lyonss relationship officer at the local branch of Southern Bank & Trusta large, regional bank. Southern had a 7-year relationship with Lyons, including a current loan balance of over $3 million. Jones and Montrose tentatively discussed the possibility that Southern might extend a line of credit to Jones up to a maximum amount of $350,000. Jones thought that a loan of this size would more than meet his needs for at least the next year, and he was eager for the flexibility that a line of credit of this size would provide. After discussion, Montrose had arranged for the credit department of Southern Bank & Trust to investigate Nelson Jones and his company.
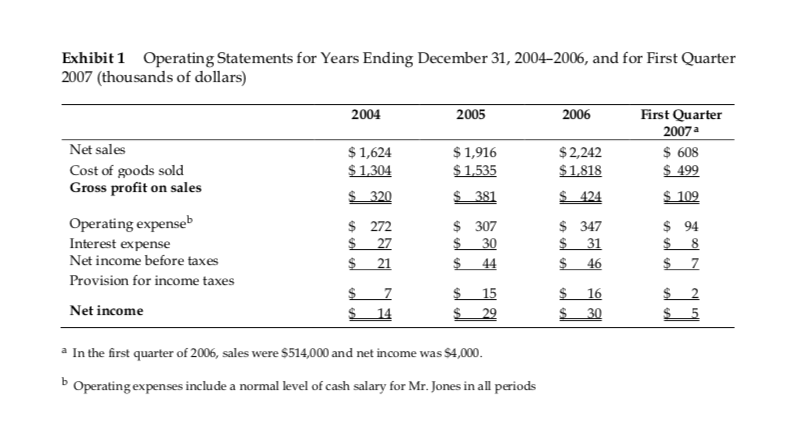
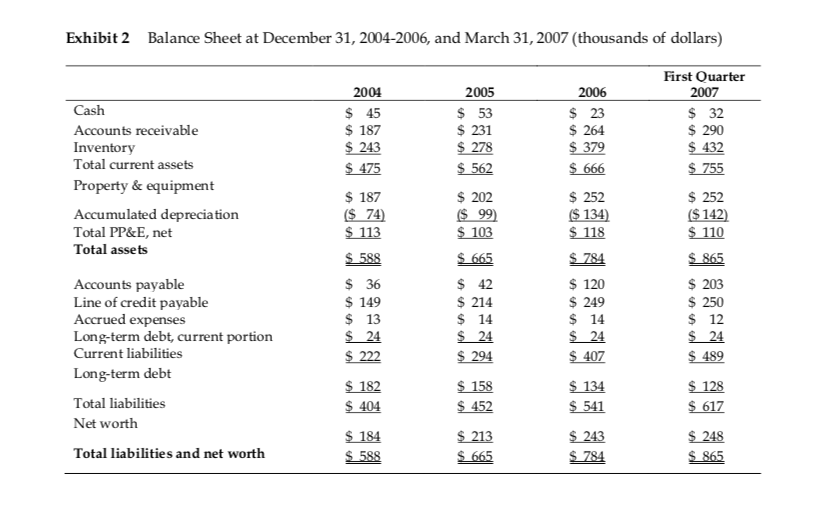
Exhibit 1 Operating Statements for Years Ending December 31, 2004-2006, and for First Quarter 2007 (thousands of dollars) 2004 2005 2006 First Quarter 2007 a Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit on sales $ 1,624 $ 1,304 $_320 $ 1,916 $ 1,535 $_381 $ 2,242 $ 1,818 $424 $ 608 $ 499 $ 109 $ 347 ES $ Operating expenseb Interest expense Net income before taxes Provision for income taxes 31 $_ 15 Net income $ $ 16 30 $_ 29 a In the first quarter of 2006, sales were $514,000 and net income was $4,000. b Operating expenses include a normal level of cash salary for Mr. Jones in all periods Exhibit 2 Balance Sheet at December 31, 2004-2006, and March 31, 2007 (thousands of dollars) Cash First Quarter 2007 $ 32 2005 $ 53 $ 231 2004 $ 45 $ 187 $ 243 $ 475 2006 $ 23 $ 264 $ 379 Accounts receivable Inventory Total current assets Property & equipment $ 290 $ 278 $ 562 $ 432 $ 755 $ 666 $ 252 $ 252 ($ 142) Accumulated depreciation Total PP&E, net Total assets $ 187 ($ 74) $ 113 $ 588 $ 36 $ 149 $ 202 ($ 99) $ 103 $ 665 $ 42 $ 110 ($ 134) $ 118 $ 784 $ 120 $ 249 $ 14 $ 24 $ 407 $ 865 $ 203 $ 250 Accounts payable Line of credit payable Accrued expenses Long-term debt, current portion Current liabilities Long-term debt $ 214 $ 12 $ 14 $ 24 $ 294 $ 24 $ 222 $ 182 $ 404 $ 24 $ 489 $ 128 Total liabilities Net worth $ 158 $ 452 $ 134 $ 541 $ 617 $ 243 Total liabilities and net worth $ 184 $ 588 $ 213 $ 665 $ 248 $ 865 $ 784 Exhibit 1 Operating Statements for Years Ending December 31, 2004-2006, and for First Quarter 2007 (thousands of dollars) 2004 2005 2006 First Quarter 2007 a Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit on sales $ 1,624 $ 1,304 $_320 $ 1,916 $ 1,535 $_381 $ 2,242 $ 1,818 $424 $ 608 $ 499 $ 109 $ 347 ES $ Operating expenseb Interest expense Net income before taxes Provision for income taxes 31 $_ 15 Net income $ $ 16 30 $_ 29 a In the first quarter of 2006, sales were $514,000 and net income was $4,000. b Operating expenses include a normal level of cash salary for Mr. Jones in all periods Exhibit 2 Balance Sheet at December 31, 2004-2006, and March 31, 2007 (thousands of dollars) Cash First Quarter 2007 $ 32 2005 $ 53 $ 231 2004 $ 45 $ 187 $ 243 $ 475 2006 $ 23 $ 264 $ 379 Accounts receivable Inventory Total current assets Property & equipment $ 290 $ 278 $ 562 $ 432 $ 755 $ 666 $ 252 $ 252 ($ 142) Accumulated depreciation Total PP&E, net Total assets $ 187 ($ 74) $ 113 $ 588 $ 36 $ 149 $ 202 ($ 99) $ 103 $ 665 $ 42 $ 110 ($ 134) $ 118 $ 784 $ 120 $ 249 $ 14 $ 24 $ 407 $ 865 $ 203 $ 250 Accounts payable Line of credit payable Accrued expenses Long-term debt, current portion Current liabilities Long-term debt $ 214 $ 12 $ 14 $ 24 $ 294 $ 24 $ 222 $ 182 $ 404 $ 24 $ 489 $ 128 Total liabilities Net worth $ 158 $ 452 $ 134 $ 541 $ 617 $ 243 Total liabilities and net worth $ 184 $ 588 $ 213 $ 665 $ 248 $ 865 $ 784Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


