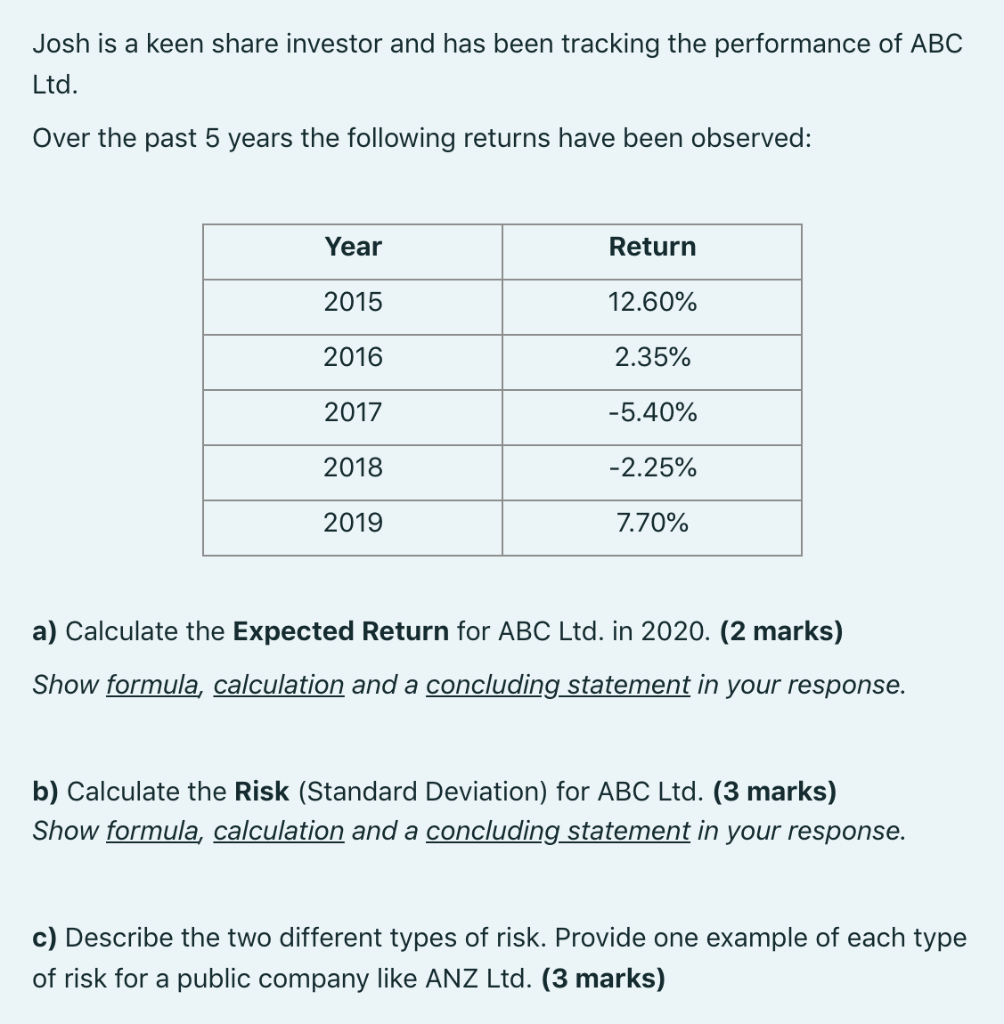

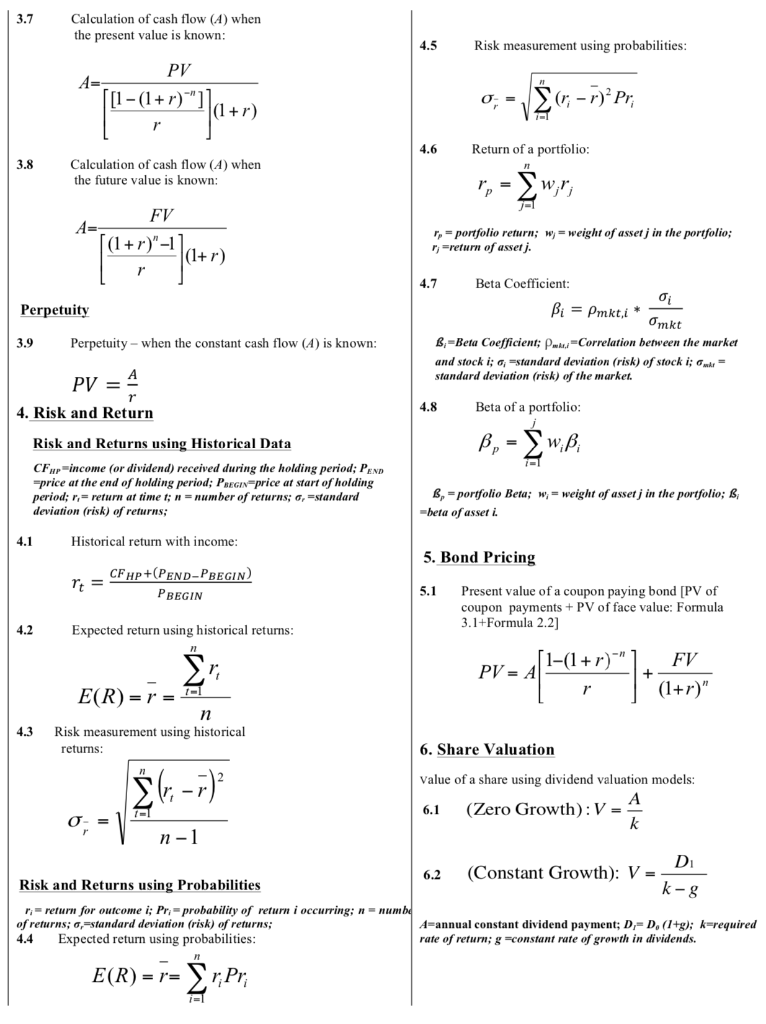
Josh is a keen share investor and has been tracking the performance of ABC Ltd. Over the past 5 years the following returns have been observed: Year Return 2015 12.60% 2016 2.35% 2017 -5.40% 2018 -2.25% 2019 7.70% a) Calculate the Expected Return for ABC Ltd. in 2020. (2 marks) Show formula, calculation and a concluding statement in your response. b) Calculate the Risk (Standard Deviation) for ABC Ltd. (3 marks) Show formula, calculation and a concluding statement in your response. c) Describe the two different types of risk. Provide one example of each type of risk for a public company like ANZ Ltd. (3 marks) 1. Simple interest 2.6 Number of time periods at compound interest I= simple interest; P = principal;r=interest rate p.a.; 1 = time in terms of a year; FV = future value; PV = present value; FV Ln( PV Ln(1+r) 1.1 Calculation of simple interest: n= I= Pxrxt Future value of principal at simple interest: 1.2 FV-PV (1+rxt)) Present value at simple interest: 3. Annuities 4= cash flow received paid; FV-future walue; PV=present value; r=interest rate per compounding period n-number of periods; 1.3 Ordinary Annuities FV PV=FV(1+(rxt) 'or PV=- (1+(rxt)) Yield at simple interest: 3.1 1.4 Present value of n payments of A at interest rate : FV r=-X - PV Number of time periods at simple interest: 1-(1+r) PV = A - [] 1.5 3.2 Future value of n payments of A at interest rater FV t = -X PV --- (1+r)"-1 FV = A / 1 3.3 2. Compound interest FV=future value; PV=present value; r=interest rate per compounding period; n=number of periods; m=number of compounding periods in one year; is =effective rute p.a.; now = nominal rate p.a. Calculation of cash flow (A) when the present value is known: PV A= 2.1 Future value of principal at compound interest: [1-(1+r)" FV=PV (1+r)" 3.4 1 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the future value is known: 2.2 Present value at compound interest: A= FV PV = FV (1+r)" or PV = (1+r)" Effective annual interest rate when nominal interest rate is known: FV [(1 + r)" -1 4712) 2.3 Annuity Due 3.5 Present value of an annuity due: 1 m Nominal annual interest rate when effective interest rate is known: 2.4 [[1-(1+r)"] PV = A - 0-1772" 1+r) 1 3.6 m = m Future value of an annuity due: m[{1+1,3% -1)] 2.5 Yield at compound interest: (1+r)"-1 FV=1[+/-1300 =A 1 FV r = PV -- -1 3.7 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the present value is known: 4.5 Risk measurement using probabilities: PV A- [1-(1+r)"] 0 = * (r; - 1)? Pr; (1+r) 1 4.6 Return of a portfolio: 3.8 Calculation of cash flow (A) when the future value is known: - 2wr A * Talep'4]=> FV (1+r)"-1 r, = portfolio return; w = weight of assetj in the portfolio; -return of asset. (1+r) Perpetuity 4.7 Beta Coefficient: 0 Bi = Pmkt, i * Omkt B-Beta Coefficient; PwCorrelation between the marker and stock i; ; Estandard deviation (risk) of stock i;= standard deviation (risk) of the market. 3.9 Perpetuity - when the constant cash flow (A) is known: PV = 4 r 4.8 4. Risk and Return Beta of a portfolio: , -, Risk and Returns using Historical Data CFwp-income (or dividend) received during the holding period; PEND =price at the end of holding period; Peegin=price at start of holding period; r;=return at time t; n = number of returns; 6, Estandard deviation (risk) of returns, B, - portfolio Beta; w;= weight of assetj in the portfolio: B beta of asseri 4.1 Historical return with income: 5. Bond Pricing rt CFHp+(PEND-PBEGIN) PBEGIN 5.1 Present value of a coupon paying bond [PV of coupon payments + PV of face value: Formula 3.1+Formula 2.2] 4.2 Expected return using historical returns: (1-(1+r)" = A FV PV-11-1***) + (1+r)" E(R) = r = n Risk measurement using historical returns: 4.3 6. Share Valuation (; -,) ri- Value of a share using dividend valuation models: A 6.1 (Zero Growth): V = k II 0 = n-1 D 6.2 (Constant Growth): V = k-g Risk and Returns using Probabilities r;=return for outcome i; Pr, probability of return i occurring; n-numbe of returns; 6,=standard deviation (risk) of returns; 4.4 Expected return using probabilities: A=annual constant dividend payment; D=D. (1+g); k=required rate of return; g =constant rate of growth in dividends. E(R) = r=









