Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 3 4 5 In adjusting the accounts on December 31, the company estimated that 1.20% of accounts receivable
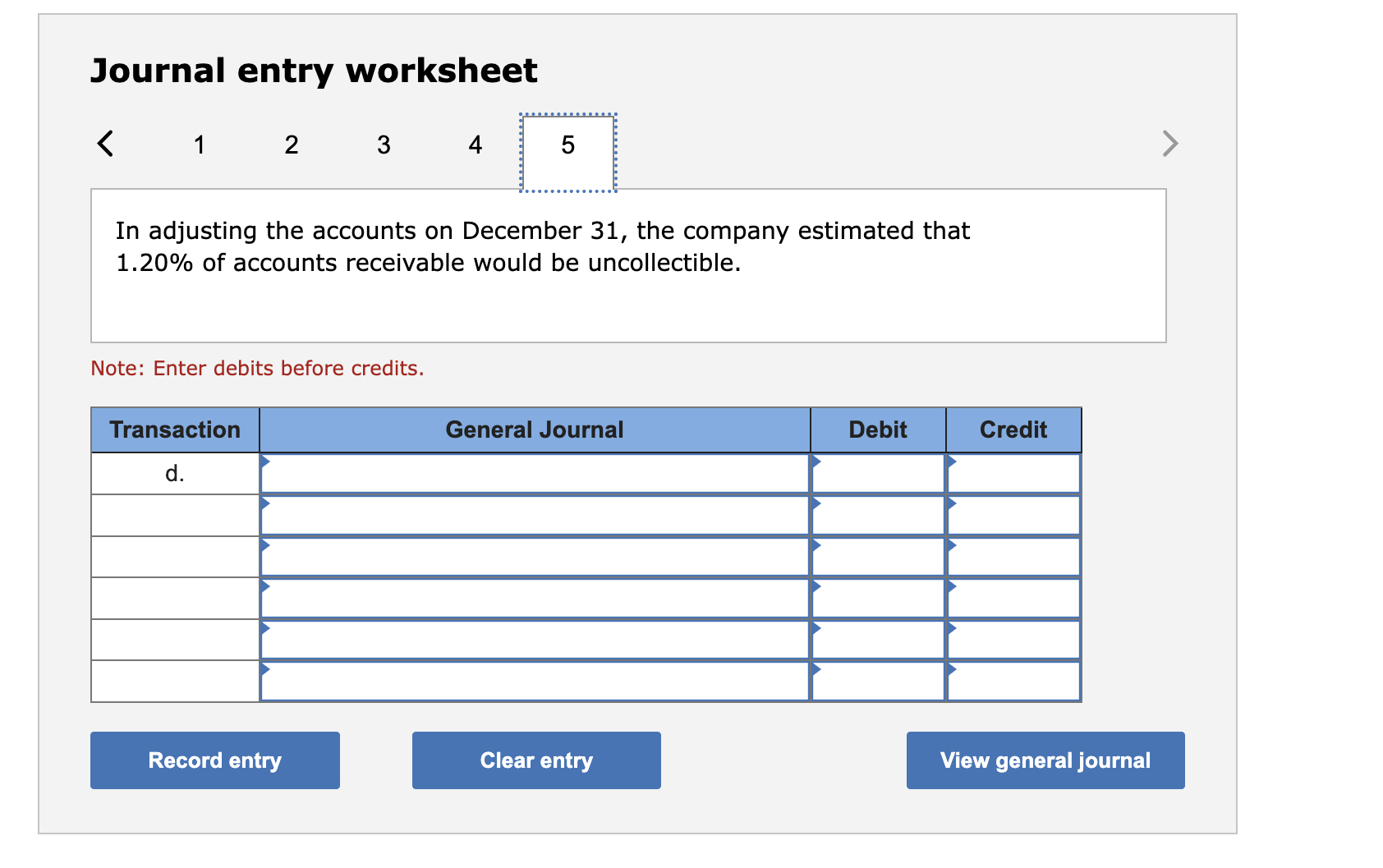
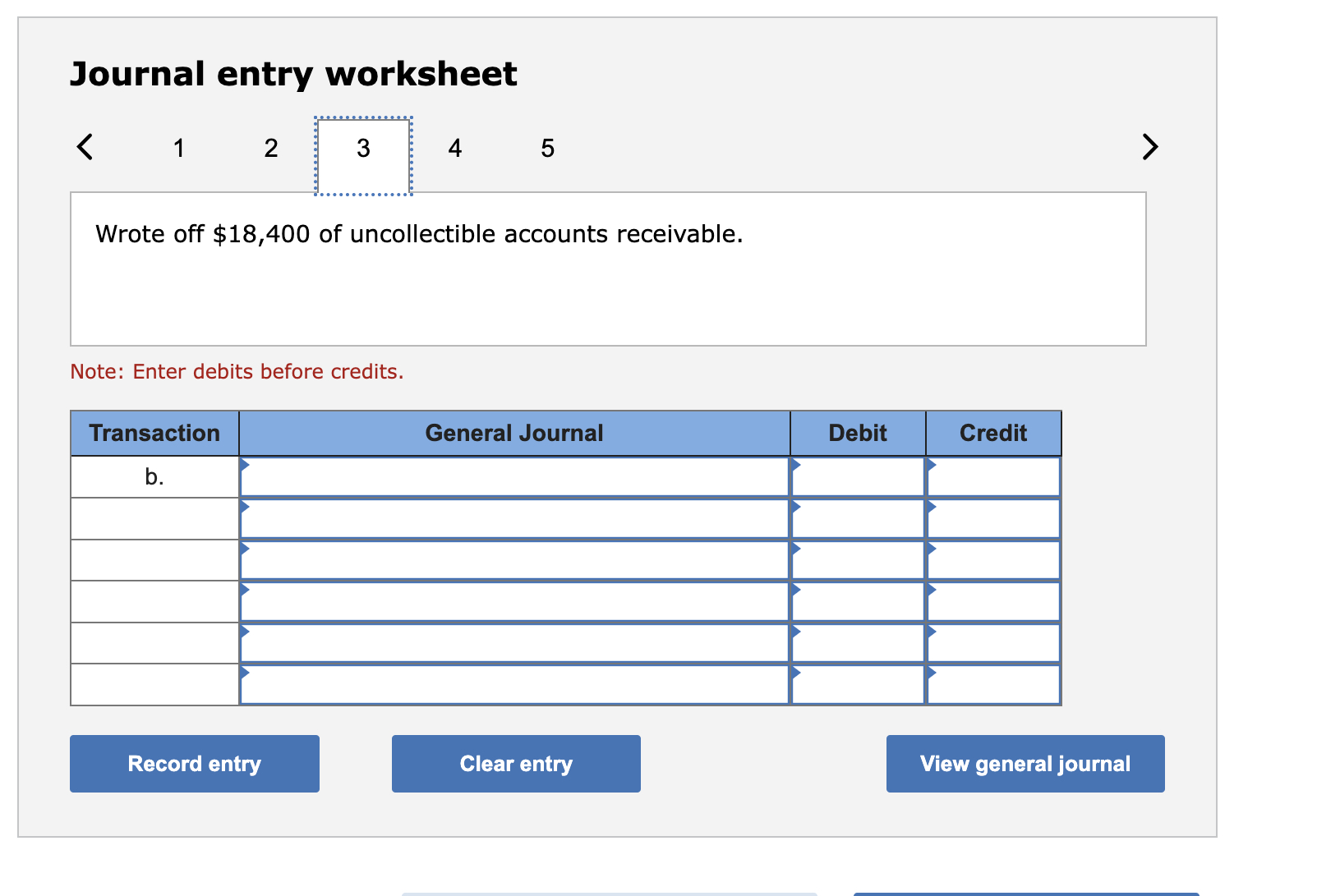
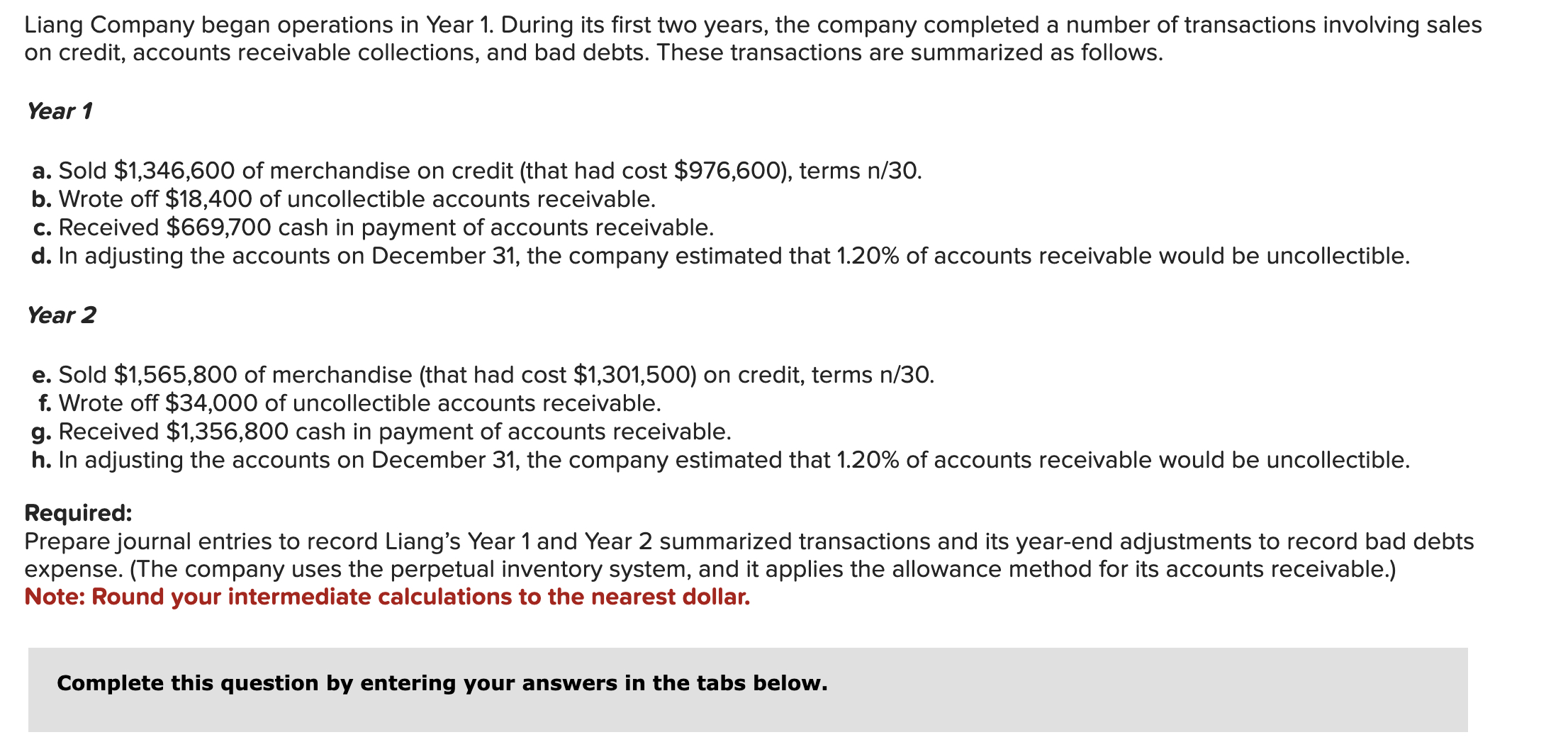
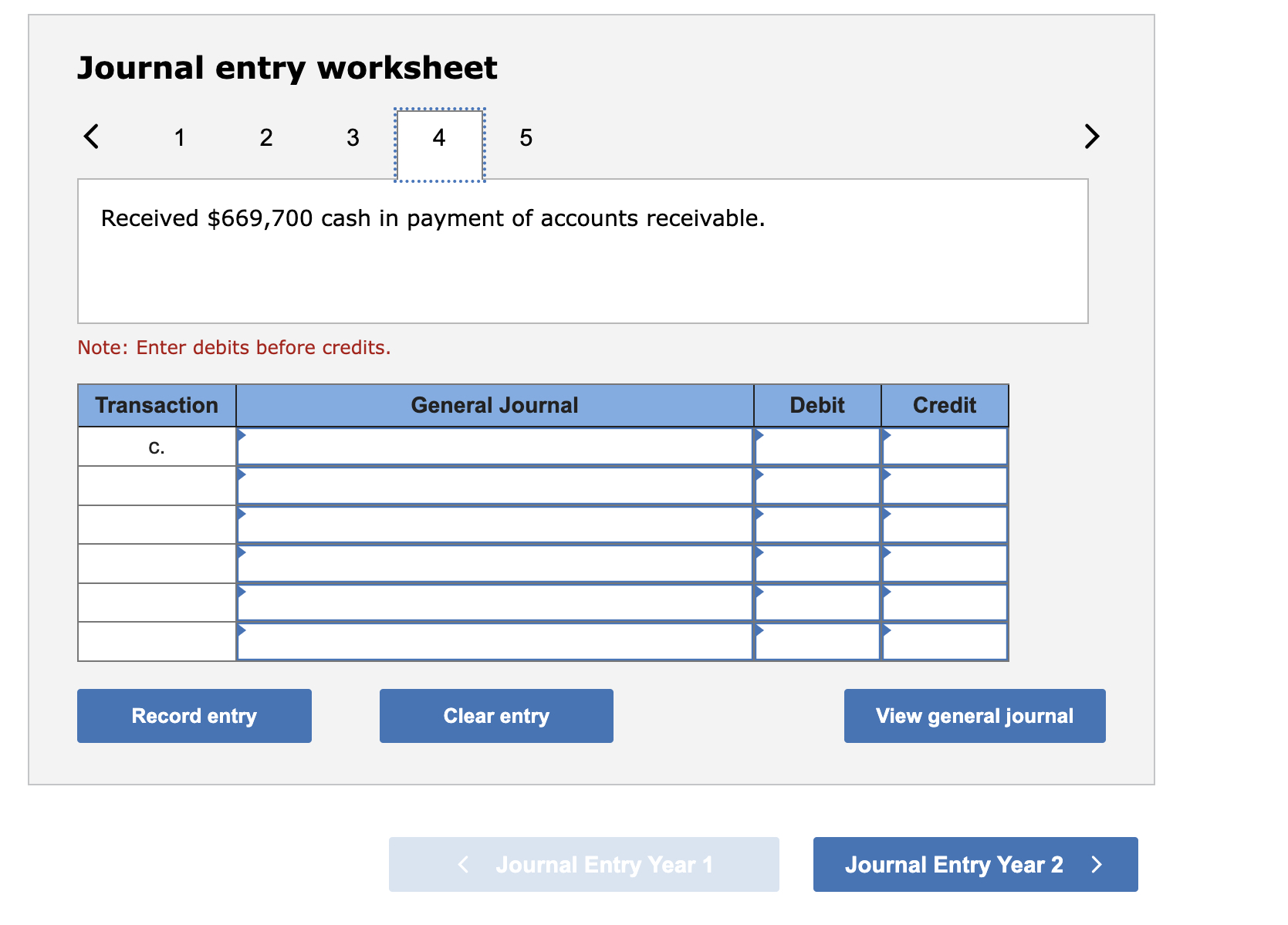
Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 3 4 5 In adjusting the accounts on December 31, the company estimated that 1.20% of accounts receivable would be uncollectible. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction d. General Journal Debit Credit View general journal Record entry Clear entry > Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 3 4 5 Wrote off $18,400 of uncollectible accounts receivable. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction b. General Journal Debit Credit View general journal Record entry Clear entry > Liang Company began operations in Year 1. During its first two years, the company completed a number of transactions involving sales on credit, accounts receivable collections, and bad debts. These transactions are summarized as follows. Year 1 a. Sold $1,346,600 of merchandise on credit (that had cost $976,600), terms n/30. b. Wrote off $18,400 of uncollectible accounts receivable. c. Received $669,700 cash in payment of accounts receivable. d. In adjusting the accounts on December 31, the company estimated that 1.20% of accounts receivable would be uncollectible. Year 2 e. Sold $1,565,800 of merchandise (that had cost $1,301,500) on credit, terms n/30. f. Wrote off $34,000 of uncollectible accounts receivable. g. Received $1,356,800 cash in payment of accounts receivable. h. In adjusting the accounts on December 31, the company estimated that 1.20% of accounts receivable would be uncollectible. Required: Prepare journal entries to record Liang's Year 1 and Year 2 summarized transactions and its year-end adjustments to record bad debts expense. (The company uses the perpetual inventory system, and it applies the allowance method for its accounts receivable.) Note: Round your intermediate calculations to the nearest dollar. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Journal entry worksheet 1 2 3 4 5 Received $669,700 cash in payment of accounts receivable. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction C. General Journal Debit Credit Clear entry Record entry View general journal > < Journal Entry Year 1 Journal Entry Year 2 > Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 3 4 5 Record cost of goods sold, $976,600. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction a(2) General Journal Debit Credit > View general journal Record entry Clear entry Journal entry worksheet 1 2 3 4 5 Sold $1,346,600 of merchandise on credit, terms n/30. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction a(1) General Journal Debit Credit View general journal Record entry Clear entry >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


