


Just answer
1
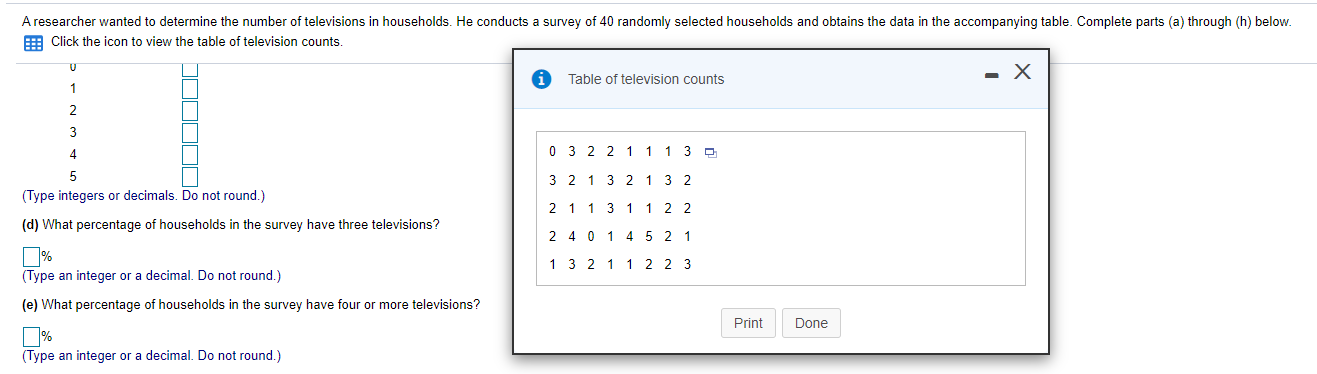
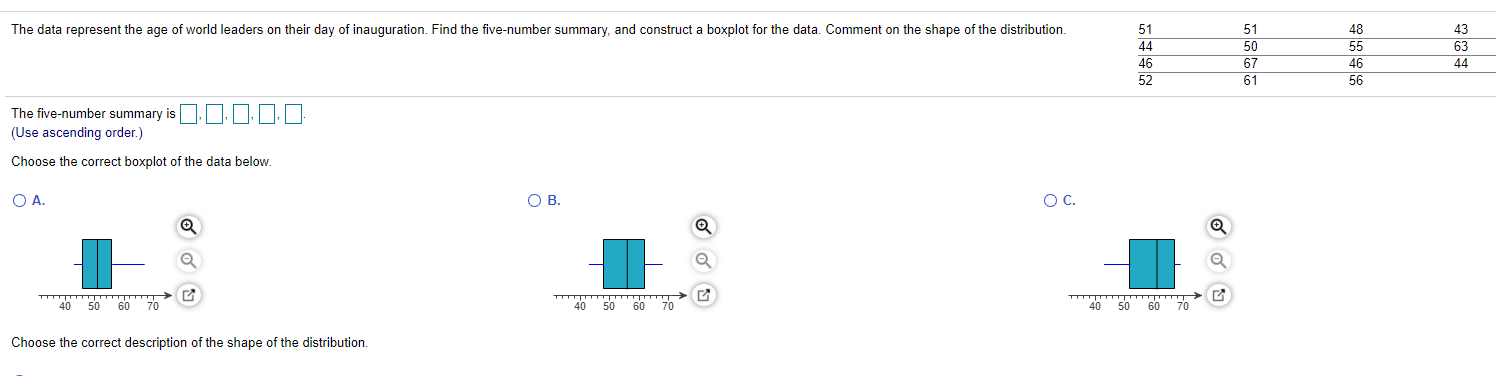
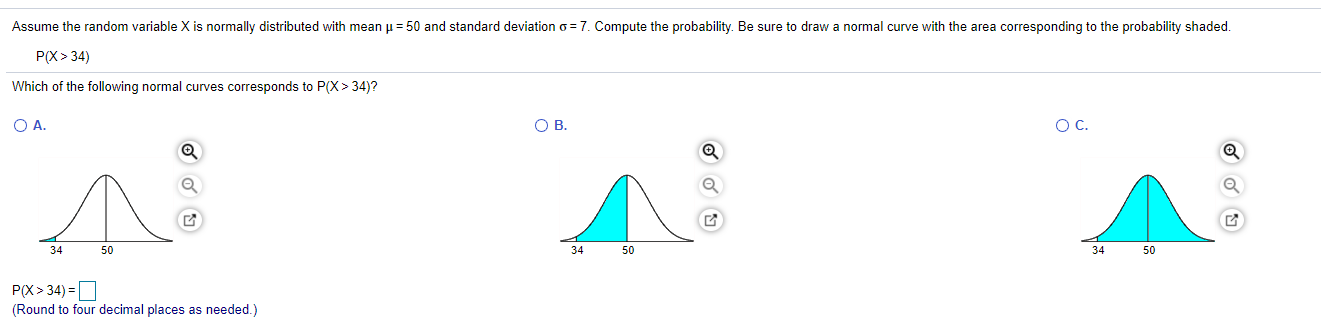
A researcher wanted to determine the number of televisions in households. He conducts a survey of 40 randomly selected households and obtains the data in the accompanying table. Complete parts (a) through (h) below. Click the icon to view the table of television counts. (b) Construct a frequency distribution of the data. Televisions Frequency i Table of television counts - X 0 N - 03 2 2 1 1 1 3 0 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 21 13 1 1 2 2 (c) Construct a relative frequency distribution of the data. 2 4 0 1 4 5 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 2 2 3 Televisions Relative Frequency Print DoneA researcher wanted to determine the number of televisions in households. He conducts a survey of 40 randomly selected households and obtains the data in the accompanying table. Complete parts (a) through (h) below. Click the icon to view the table of television counts. i Table of television counts - X A w 0 3 2 2 1 1 1 3 0 5 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 2 (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) 2 1 1 3 1 1 2 2 (d) What percentage of households in the survey have three televisions? 2 4 0 1 4 5 2 1 % 1 3 2 1 1 2 2 3 (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) (e) What percentage of households in the survey have four or more televisions? Print Done % (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)51 51 48 43 The data represent the age of world leaders on their day of inauguration. Find the five-number summary, and construct a boxplot for the data. Comment on the shape of the distribution. 44 50 55 63 46 67 46 44 52 61 56 The five-number summary is . . 0. 0.0 (Use ascending order.) Choose the correct boxplot of the data below. O A. O B. O C. TITTTTTTTTTTTTTT 40 50 60 70 50 60 70 40 50 60 70 40 Choose the correct description of the shape of the distribution.Assume the random variable X is normally distributed with mean u = 50 and standard deviation o = 7. Compute the probability. Be sure to draw a normal curve with the area corresponding to the probability shaded. P(X > 34) Which of the following normal curves corresponds to P(X > 34)? O A. O B. O C. 34 50 34 50 34 50 P(X > 34) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)Let dj = X; - Yj. Write the hypotheses for the test. Ho: H1: Calculate the test statistic. to = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) are shorter than Calculate the P-value. are taller than P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) are the same height as Should the null hypothesis be rejected? are not the same height as Ho because the P-value is the level of significance. There sufficient evidence to conclude that sons their fathers at the 0.10 level of significance.Construct a confidence interval of the population proportion at the given level of confidence. x = 120, n= 1200, 98% confidence Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1). Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2). The lower bound of the confidence interval is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The upper bound of the confidence interval is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)Assume the random variable X is normally distributed with mean u = 50 and standard deviation o = 7. Compute the probability. Be sure to draw a normal curve with the area corresponding to the probability shaded. P(35



















