Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
JUST TWO QUESTIONS, PLS HELP HW05 Q10. Why do branch instructions slow the execution of programs compared to instructions that are always followed by the

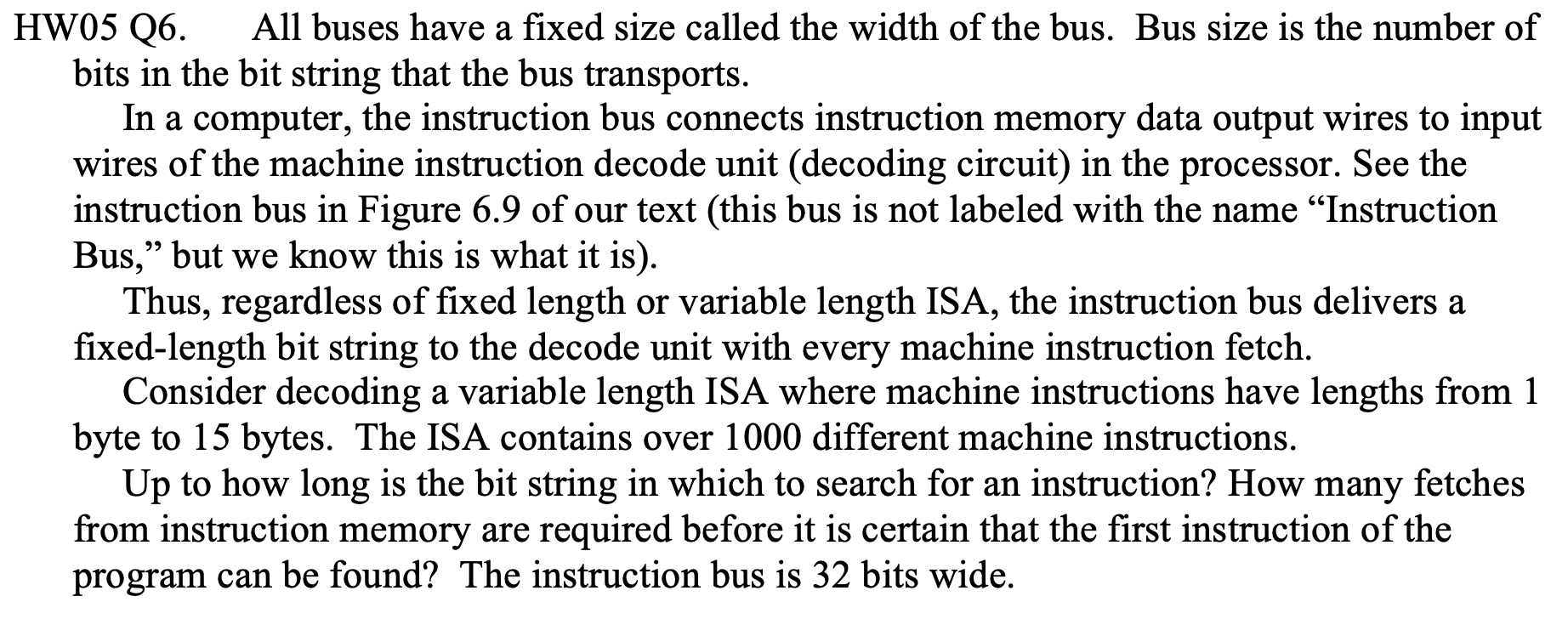
JUST TWO QUESTIONS, PLS HELP
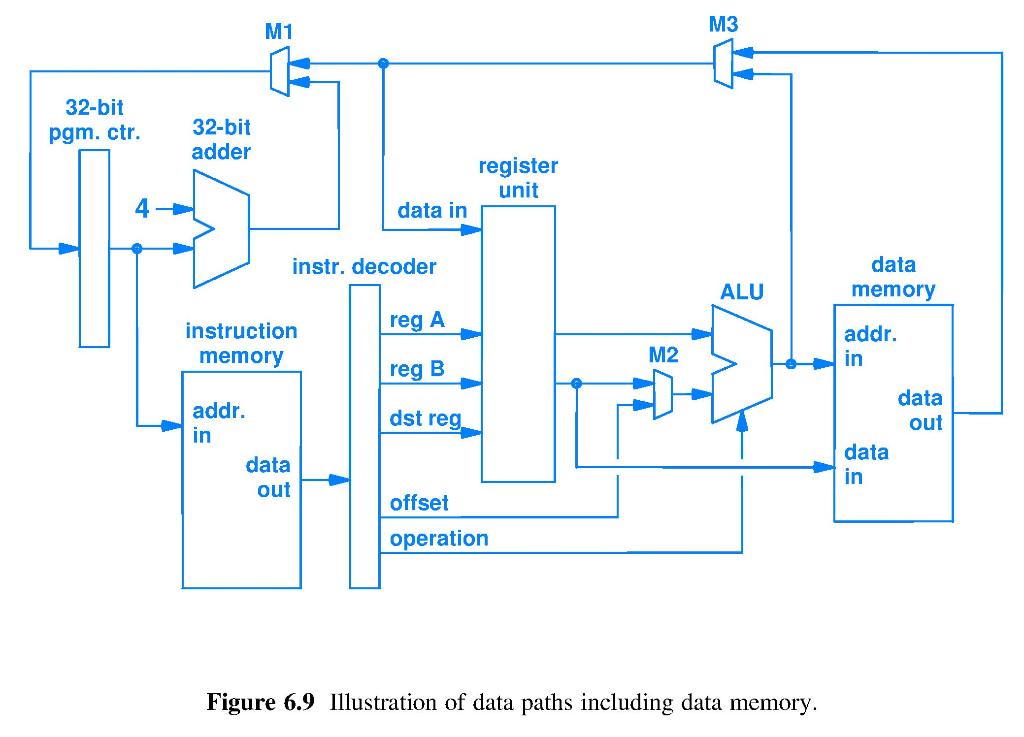
HW05 Q10. Why do branch instructions slow the execution of programs compared to instructions that are always followed by the instruction at the default next memory location? HW05 Q6. All buses have a fixed size called the width of the bus. Bus size is the number of bits in the bit string that the bus transports. In a computer, the instruction bus connects instruction memory data output wires to input wires of the machine instruction decode unit (decoding circuit) in the processor. See the instruction bus in Figure 6.9 of our text (this bus is not labeled with the name "Instruction Bus, but we know this is what it is). Thus, regardless of fixed length or variable length ISA, the instruction bus delivers a fixed-length bit string to the decode unit with every machine instruction fetch. Consider decoding a variable length ISA where machine instructions have lengths from 1 byte to 15 bytes. The ISA contains over 1000 different machine instructions. Up to how long is the bit string in which to search for an instruction? How many fetches from instruction memory are required before it is certain that the first instruction of the program can be found? The instruction bus is 32 bits wide. M1 M3 32-bit pgm. ctr. 32-bit adder register unit data in instr. decoder data memory ALU reg A instruction memory M2 addr. in reg B dst reg addr. in data out data out data in offset operation Figure 6.9 Illustration of data paths including data memory. HW05 Q10. Why do branch instructions slow the execution of programs compared to instructions that are always followed by the instruction at the default next memory location? HW05 Q6. All buses have a fixed size called the width of the bus. Bus size is the number of bits in the bit string that the bus transports. In a computer, the instruction bus connects instruction memory data output wires to input wires of the machine instruction decode unit (decoding circuit) in the processor. See the instruction bus in Figure 6.9 of our text (this bus is not labeled with the name "Instruction Bus, but we know this is what it is). Thus, regardless of fixed length or variable length ISA, the instruction bus delivers a fixed-length bit string to the decode unit with every machine instruction fetch. Consider decoding a variable length ISA where machine instructions have lengths from 1 byte to 15 bytes. The ISA contains over 1000 different machine instructions. Up to how long is the bit string in which to search for an instruction? How many fetches from instruction memory are required before it is certain that the first instruction of the program can be found? The instruction bus is 32 bits wide. M1 M3 32-bit pgm. ctr. 32-bit adder register unit data in instr. decoder data memory ALU reg A instruction memory M2 addr. in reg B dst reg addr. in data out data out data in offset operation Figure 6.9 Illustration of data paths including data memoryStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


