


KIndly help me solve the following questions below
1.Question:
The outlet stream of a continuous chemical reactor is sampled every thirty minutes and titrated. Extensive records of normal operation show the concentration of component A in this stream is approximately normally distributed with mean 41.2 g/L and standard deviation 0.90 g/L.??
??a) What is the probability that the concentration of component A in this stream will be more than 42.3 g/L????
??b) Five determinations of concentration of component A are made. If the mean of these five concentrations is more than 42.3 g/L, action is taken. What is the level of significance associated with this test????
?
c) State the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis that fit the test described in part (b).??
??
d) The test in part (b) is applied. Now suppose the true mean has changed to 43.5 g/L with no change in standard deviation. What is the probability of a Type II error???
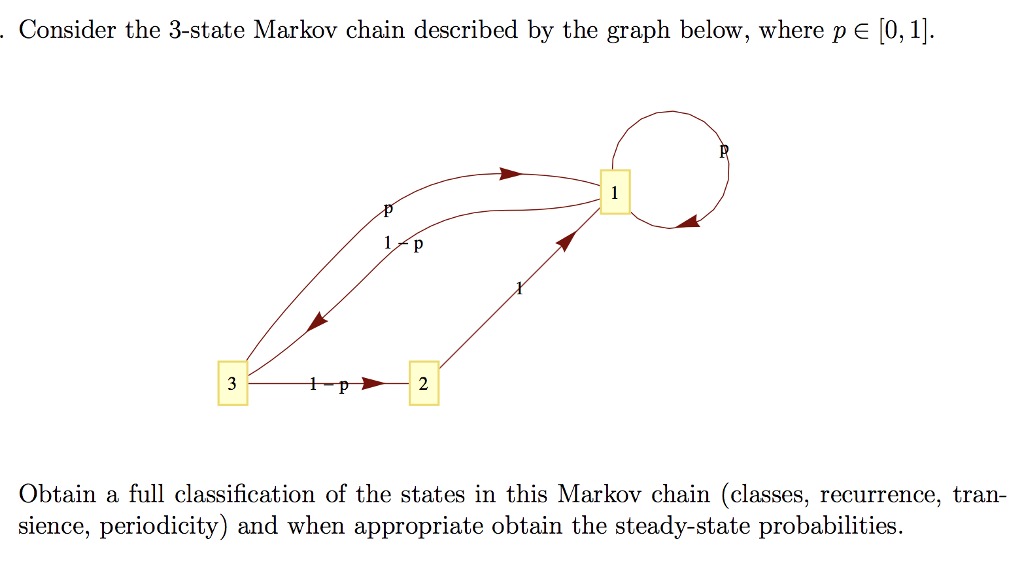
5. [12 marks] Consider the Markov chain with the following transition matrix. 0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0 0.5 0.5 0.5 0 (a) Draw the transition diagram of the Markov chain. (b) Is the Markov chain ergodic? Give a reason for your answer, (c) Compute the two step transition matrix of the Markov chain. (d) What is the state distribution 72 for t = 2 if the initial state distribution for t = 0 is no = (0.1, 0.5, 0.4) ?? (e) What is the average time /1,1 for the chain to return to state 1? Remember: Mij = 1 +) Pikikj .Consider the 3-state Markov chain described by the graph below, where pe [0, 1]. 1 p 3 2 Obtain a full classification of the states in this Markov chain (classes, recurrence, tran- sience, periodicity) and when appropriate obtain the steady-state probabilities.4.1 Two Types of Random Variables 4.2. Probability Distributions for Discrete Random Variables 1. What is a random variable? 2. Give examples for discrete random variable, continuous random variableProblem 2: 2.1) Write down the mathematical definition of each of the following. (Be precise in your definitions. Each definition should be a mathematical statement.) (a) A random variable (b) The pdf of a random variable. (Specify whether the random variable is discrete or continuous.) (c) The pmf of a random variable. (Specify whether the random variable is discrete or continuous.) (d) The cdf of a random variable. (Specify whether there are any restrictions on whether the random variable is discrete or continuous.) (e) the expected value of a random variable. (Give separate expressions for discrete and continuous random variables.) (f) the expected value of a function of a random variable. (Give separate expressions for discrete and continuous random variables.) 2.2) Write down the mathematical definition of each of the following random variables. (Each definition should be a mathematical statement.) For any parameters of the distribution, explain the meaning of each parameter. Specify whether each of these is a discrete or continuous random variable. (a) a Bernoulli random variable (b) a Binomial random variable (c) a geometric random variable (d) a Poisson random variable (e) a uniform random variable (f) an exponential random variable (g) a normal (or Gaussian) random variableDetermine whether the following value is a continuous random variable, discrete random variable, or not a random variable. a. Is the amount of rainfall in a month is a discrete random variable, continuous random variable, or not a random variable? O A. It is a discrete random variable. O B. It is a continuous random variable. O C. It is not a random variable. b. Is the list of books listed for a book club event a discrete random variable, continuous random variable, or not a random variable? O A. It is a discrete random variable. O B. It is a continuous random variable. O C. It is not a random variable. c. Is the number of cars a dealership owns a discrete random variable, continuous random variable, or not a random variable? O A. It is a discrete random variable. O B. It is a continous random variable. O C. It is not a random variable















