Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Lab 3: Density Purpose: To determine the density of objects. Introduction: All matter has mass and volume. Mass and volume are physical properties of

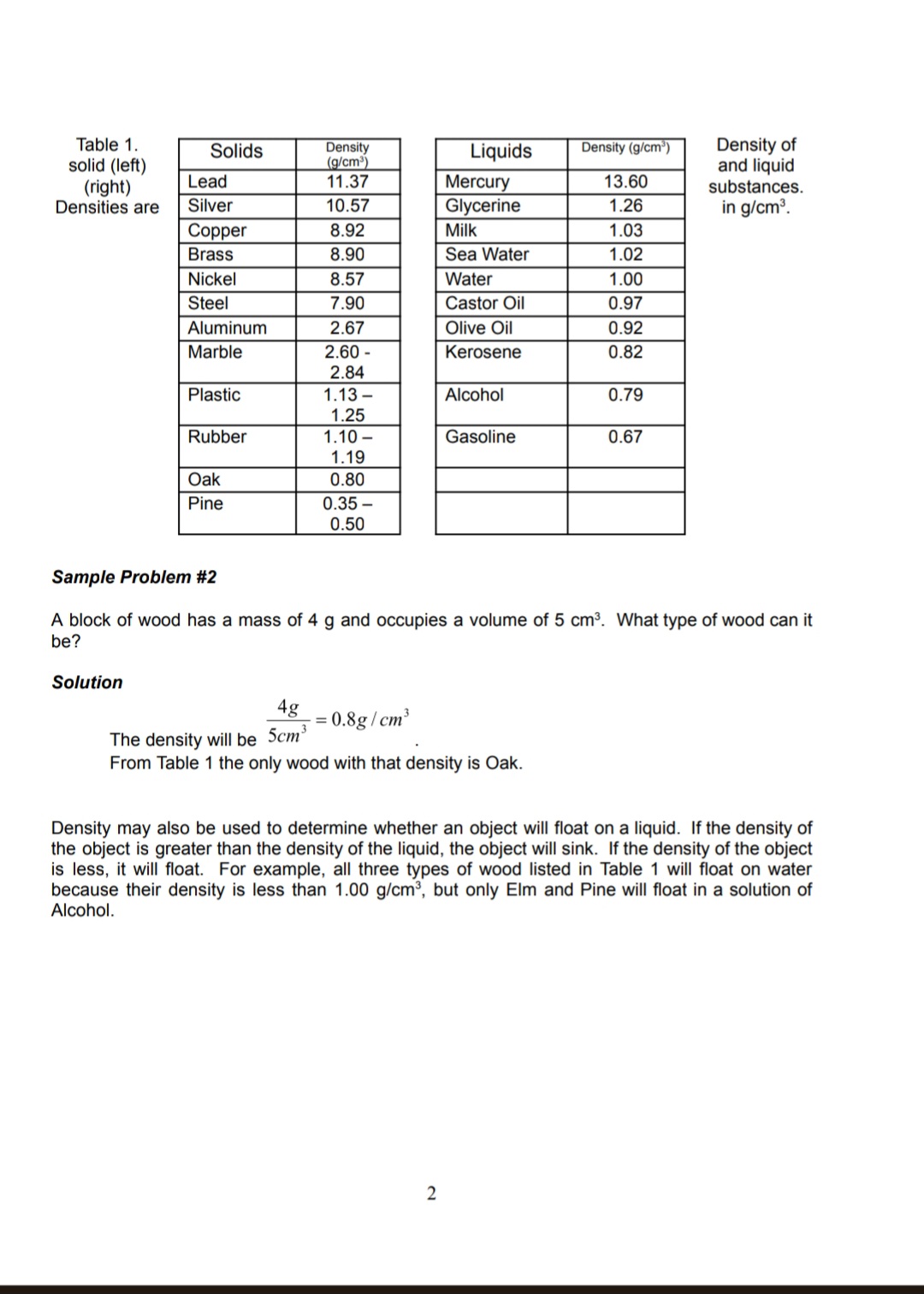
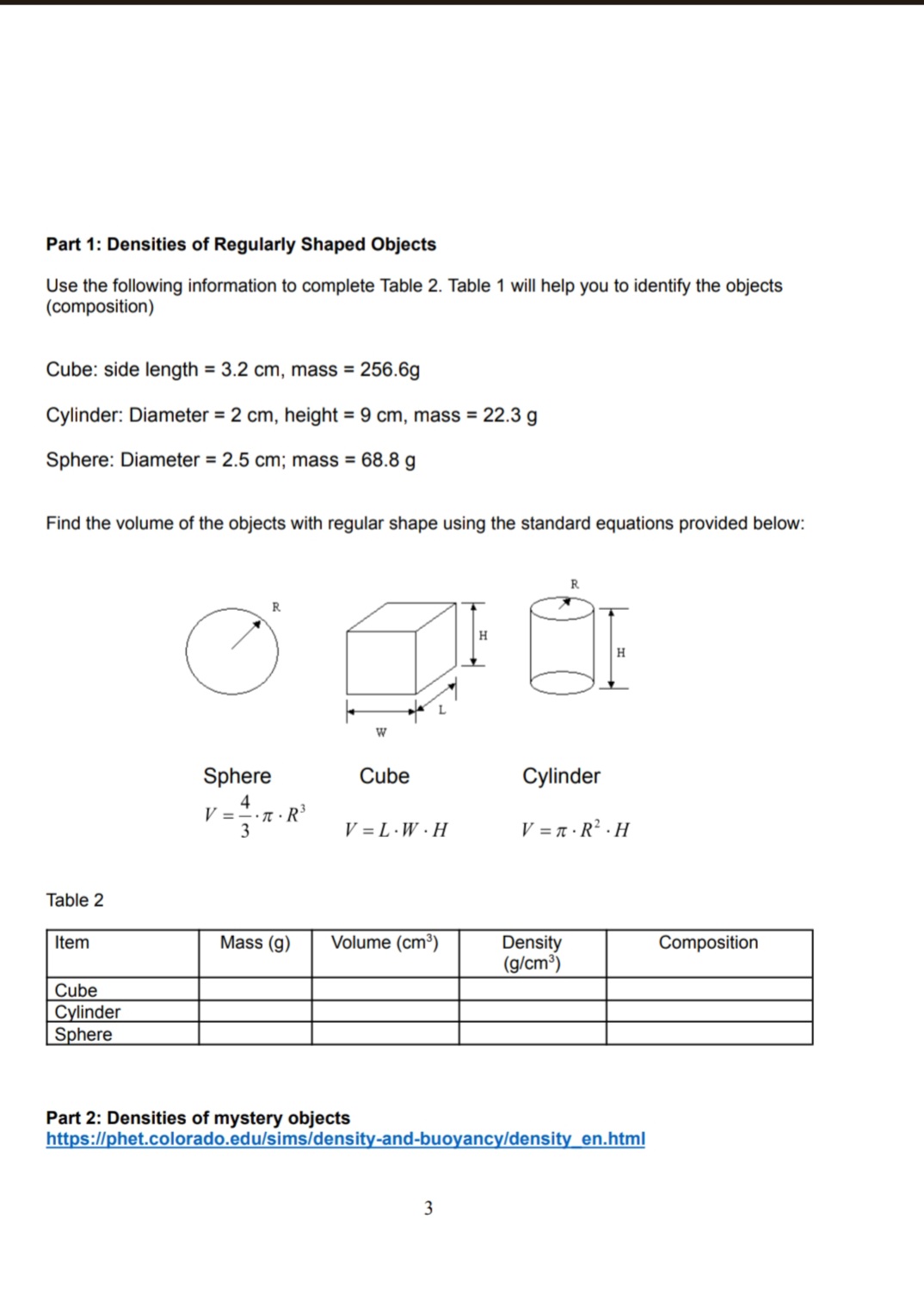
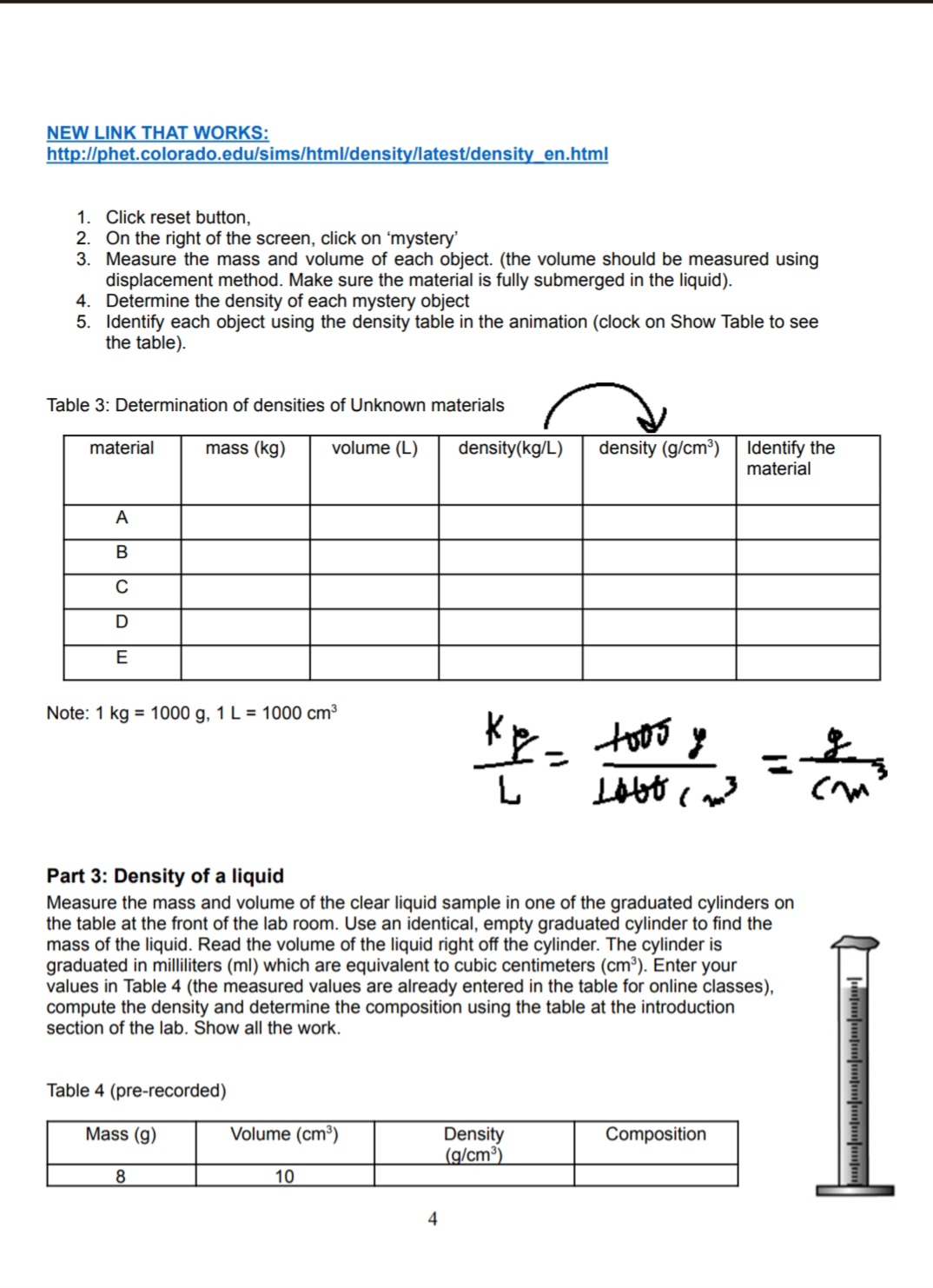

Lab 3: Density Purpose: To determine the density of objects. Introduction: All matter has mass and volume. Mass and volume are physical properties of matter and may vary with different objects. For example, it is possible for two pieces of metal to be made out of the same material yet for one piece to be bigger than the other. If the first piece of metal is twice as large as the second, then you would expect that this piece is also twice as heavy (or have twice the mass) as the first. If both pieces of metal are made of the same material the ratio of the mass and volume will be the same. We define density (p) as the ratio of the mass of an object to the volume it occupies. The equation is given by: M p = V here the symbol M stands for the mass of the object, and V for the volume. Density has the units of mass divided by volume such as grams per centimeters cube (g/cm) or kilograms per liter (kg/l). Sample Problem #1 A block of wood has a mass of 8 g and occupies a volume of 10 cm. What is its density? Solution 8g = 0.8g/cm The density will be 10cm This means that every centimeter cube of this wood will have a mass of 0.8 grams. Unlike the mass and volume that may be different for each specimen, all objects made of the same material will have the same density. Because of this the density is often used to identify unknown substances or to determine the percent composition. The densities of various substances are given in Table 1. Table 1. solid (left) (right) Solids Density Liquids Density (g/cm) (g/cm) Density of and liquid Lead 11.37 Mercury 13.60 substances. Densities are Silver 10.57 Glycerine 1.26 in g/cm. Copper 8.92 Milk 1.03 Brass 8.90 Sea Water 1.02 Nickel 8.57 Water 1.00 Steel 7.90 Castor Oil 0.97 Aluminum 2.67 Olive Oil 0.92 Marble 2.60 - Kerosene 0.82 2.84 Plastic 1.13- Alcohol 0.79 1.25 Rubber 1.10- Gasoline 0.67 1.19 Oak 0.80 Pine 0.35- 0.50 Sample Problem #2 A block of wood has a mass of 4 g and occupies a volume of 5 cm. What type of wood can it be? Solution 4g = 0.8g/cm The density will be 5cm From Table 1 the only wood with that density is Oak. Density may also be used to determine whether an object will float on a liquid. If the density of the object is greater than the density of the liquid, the object will sink. If the density of the object is less, it will float. For example, all three types of wood listed in Table 1 will float on water because their density is less than 1.00 g/cm, but only Elm and Pine will float in a solution of Alcohol. 2 Part 1: Densities of Regularly Shaped Objects Use the following information to complete Table 2. Table 1 will help you to identify the objects (composition) Cube: side length = 3.2 cm, mass = 256.6g Cylinder: Diameter = 2 cm, height = 9 cm, mass = 22.3 g Sphere: Diameter = 2.5 cm; mass = 68.8 g Find the volume of the objects with regular shape using the standard equations provided below: W H R H Sphere Cube Cylinder 4 V=R 3 V=L.W.H V =.R H Table 2 Item Mass (g) Volume (cm) Density (g/cm) Composition Cube Cylinder Sphere Part 2: Densities of mystery objects https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/density-and-buoyancy/density_en.html 3 NEW LINK THAT WORKS: http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/density/latest/density_en.html 1. Click reset button, 2. On the right of the screen, click on 'mystery' 3. Measure the mass and volume of each object. (the volume should be measured using displacement method. Make sure the material is fully submerged in the liquid). 4. Determine the density of each mystery object 5. Identify each object using the density table in the animation (clock on Show Table to see the table). Table 3: Determination of densities of Unknown materials material A B C D E mass (kg) volume (L) Note: 1 kg 1000 g, 1 L = 1000 cm density(kg/L) density (g/cm) Identify the material 1005 y L Lobo (2m Part 3: Density of a liquid Measure the mass and volume of the clear liquid sample in one of the graduated cylinders on the table at the front of the lab room. Use an identical, empty graduated cylinder to find the mass of the liquid. Read the volume of the liquid right off the cylinder. The cylinder is graduated in milliliters (ml) which are equivalent to cubic centimeters (cm). Enter your values in Table 4 (the measured values are already entered in the table for online classes), compute the density and determine the composition using the table at the introduction section of the lab. Show all the work. Table 4 (pre-recorded) Mass (g) 8 Volume (cm) Density (g/cm) Composition 10 4 Discussion & Conclusions 1. How confident are you in your determination of composition of the materials? Explain. 2. In a real experiment, what could be possible sources of error in carrying out such an experiment? 3. Which of the mystery objects from part 2 will float in the liquid of part 3?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


