Question: Lab lesson 9 has two parts. Part 2 be making use of functions, pass by reference, and files Part 2 is worth 65 points (55
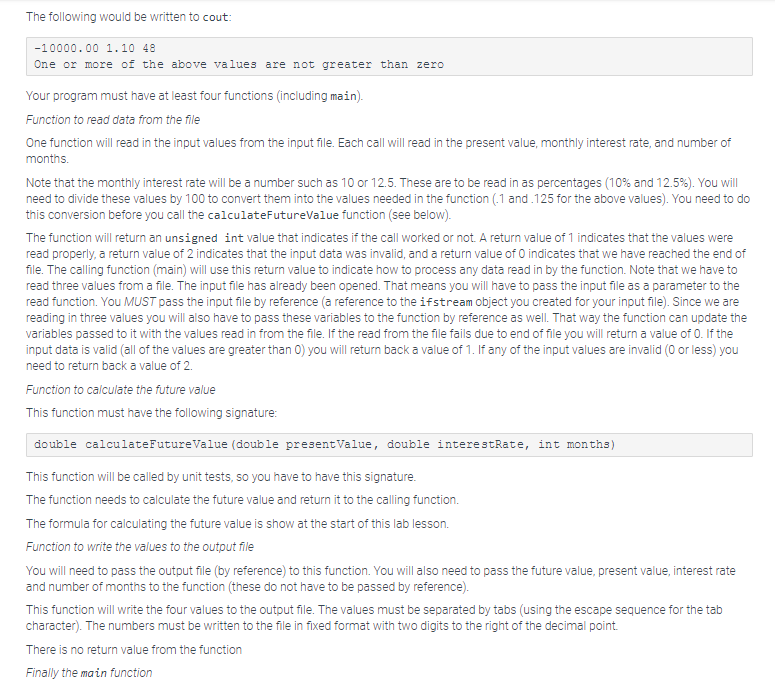
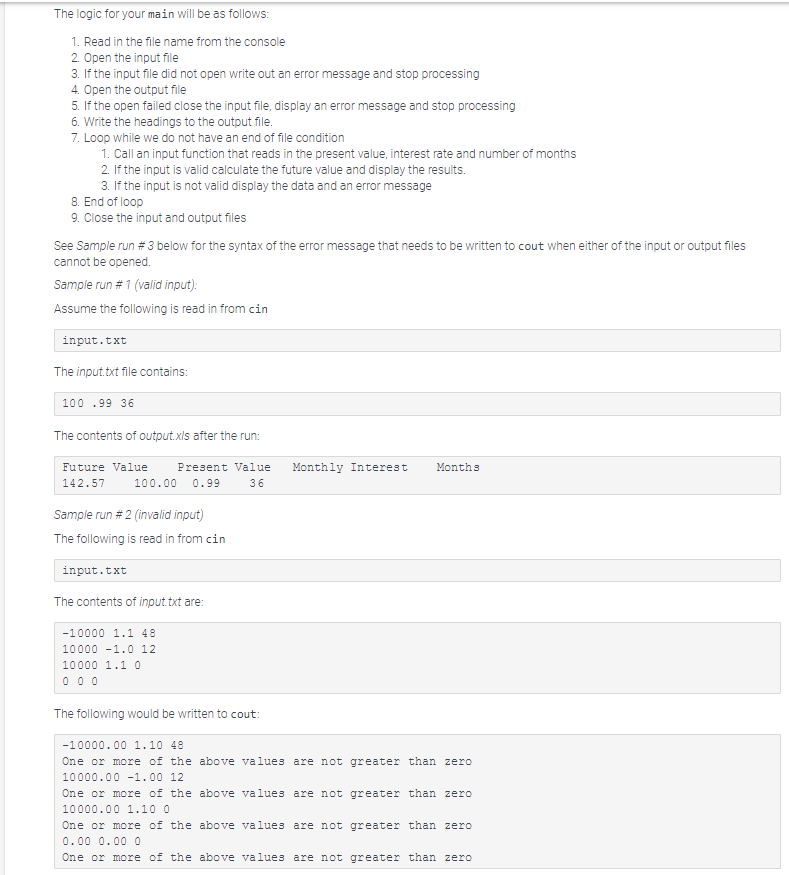
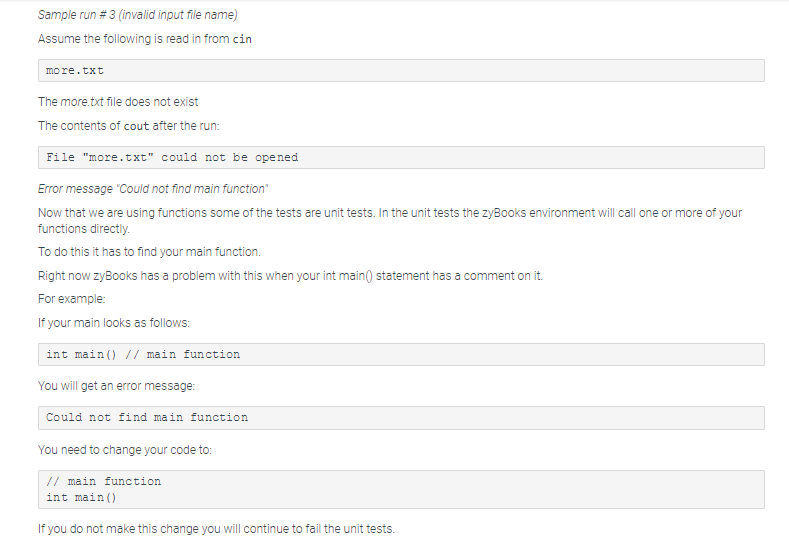
Lab lesson 9 has two parts. Part 2 be making use of functions, pass by reference, and files Part 2 is worth 65 points (55 points for passing the tests and 10 for your code). Failure to meet the requirements could result in loss of points beyond the 10 for the code formatting, variable names, and so on. In lab lesson 8 part 2 you calculated the present value. In this lab we are going to be calculating the future value. You will need to read in the present value, the monthly interest rate and the number of months for the investment. The formula is going to compute compounded interest (by month). There are a number of required functions that you will be writing, so do not start programming before you have read all of the instructions You must use function prototypes for all of the functions (except main) Here is the formula F=P*((1+1)*) Where F is the future value, P is the present value, i is the monthly interest rate and t is the number of months. Note that the formula above is (1 i to the power oft. On some older browsers the superscript for t does not display properly. The above expression can be written as F P ((1+it) Your program will need to make sure of better variable names that those used above The input for the program will be read in from a file. You will read in the file name from cin You will then read in the present value, monthly interest rate, and the number of months from the input file There may be multiple sets of these values. You need to process them all The program should end when you reach the end of file on the input file The output from the program will be written to two different places Any error messages will be written to cout. You will also be writing out to a file called output.xis The first thing you will write out are four "headings' separated by tabs (using the It escape sequence) Here is an output statement (this example is using cout). Your program will instead write to the output file cout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


