LEA is a direct laborer on a furniture manufacturing company in Cebu. Given the following independent cases, compute for her gross pay for the day
- LEA is a direct laborer on a furniture manufacturing company in Cebu. Given the following independent cases, compute for her gross pay for the day assuming her hourly rate is P80.00 and the overtime premium is provided equal to 25% of her regular 8 hour work/day:
REQUIRED:
a. She worked for 12 hours in a regular working day.
b. She worked for 8 hours, in a special holiday in the province of Cebu. This was true even though it was her rest day at that day at the same time.
c. She worked for 10 hours on January 1, New Years Day, a national regular holiday, even though it was her rest day.
d. he worked for 7 hours on a regular working day yesterday. Today she worked for total of 10 hours (regular working day). This is to offset her under-time yesterday. (Gross pay is?)
2.) Based on the following information about RED Co. which uses activity-based costing:
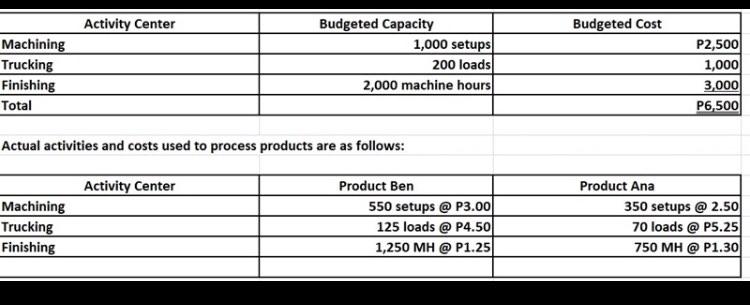
REQUIRED:
a. The amount of actual overhead of BEN
b. The amount of over- / under-applied overhead products to Ana is
3.) In 2020, a manufacturing company instituted a total quality management (TQM) program producing the following report:
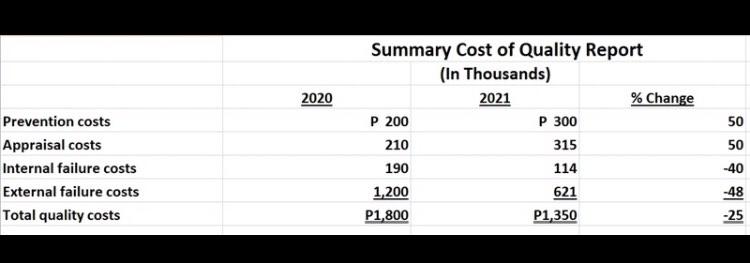
On the basis of this report, which of the following statements is most likely correct?
a. An increase in conformance costs resulted in a higher-quality product and a decrease in nonconformance costs.
b. An increase in inspection costs was solely responsible for the decrease in quality costs.
c. Quality costs such as scrap and rework decreased by 48%.
d. Quality costs such as returns and repairs under warranty decrease by 40%.
4.) AUDI Company is preparing to bid on the production of seven additional racer cars for forthcoming formula 1 event. Under a special contract, the company has already produced one racer car with the following costs:
Materials 800,000
Labor (60,000 hrs.) 750,000
Variable overhead:
50% of direct labor cost 375,000
On the basis of materials used150,000
Total 2,075,000
Variable overhead based on materials used represents materials storage cost. For seven cars, this cost would be P1,050,000. The company was informed that the maximum acceptable bid is P2,000,000 per unit. However, EBONY will not place a bid unless it can recover its costs plus a P600,000 gross profit per car. An 80% learning curve is in effect.
REQUIRED:
a. What is the total direct labor hours required for all eight racer cars?
b. How much is the total cost for the seven cars covered by the new bid?
c. How much is the profit (loss) per unit if a bid of P2,000,000 per racer car if offered?
5.) Color Design Inc. received an order for 25 tables . Because of the order's exacting specifications, it is anticipated that defective and spoiled work will exceed the normal rate. The material cost per unit is P80; labor cost P194; and factory overhead for this order is to be applied at 100% of the labor cost. During production, 5 units were found defective and required the following total additional costs: materials, P97 labor P125 and factory overhead at the rate of 100%. On the final inspection, 2 units were classified as seconds and sold for P400 each, the proceeds being credited to the order. The purchaser has agreed to accept the 23 tables, although the acceptable units were fewer than the number ordered.
How much is the unit cost of completed tables?
6.) DAVID Inc. manufactures garden equipment to sell for P280. Last year, the company sold 2,000 of these products realizing a gross profit of 25% of the cost of goods sold. Of this total goods sold, materials accounted for 40% of the total and factory overhead for 15%. During the coming year, it is expected that materials and labor costs will each increase 25% per unit and that factory overhead will increase 12 1/2% per unit. To meet these rising costs, a new sales price must be set.( Round Off to whole numbers)
REQUIRED:
a. What are the number of units to be sold to realize the same gross profit in the coming year as realized last year. If the new selling price is set at 350
b. What are the number of units to be sold to realize the same gross profit in the coming year as realized last year. If the new selling price is set at 395
c. What are the number of units to be sold to realize the same gross profit in the coming year as realized last year. If the new selling price is set at 295
7.) For the simple regression analysis model that is used to estimate the total factory overhead, an internal auditor finds that the line of regression that intersects with the y-axis is P10,000. The slope of the trend line is .20. The independent variable amounts to P850,000 for the month.
What is the estimated amount of factory overhead for the month?
TRUE OR FALSE:
1. Stockless production, lean production and ZIP production are terms used to describe the JIT effort to reduce inventories of work in process and raw materials except backflush production.
2. Incremental cost is a cost that continues to be incurred in the absence of activity.
3. Depreciation based on the number of units produced is classified as Fixed type of cost.
4. When the number of units manufactured increases, the most significant change in average unit cost will be reflected as a decrease in the non-variable element.
5. Advocates of variable costing for internal reporting purposes do not rely on the matching concept.
6. A company experienced a machinery breakdown on one of its production lines. As a consequence of the breakdown, manufacturing fell behind schedule and a decision was made to schedule overtime to return manufacturing schedule. The proper way to account the overtime paid to the direct laborers is overtime hour times the overtime premium would be charged to repair and maintenance expense and overtime hours times the straight-time wages would be treated as direct labor.
7. Absorption costing differs from variable costing in that production influences income under absorption costing, but not under variable costing.
8. The perpetual inventory method differs from the periodic in that the former maintains a continuous record of transactions affecting the inventory balances.
9. The materials control method that is based on physical observation that an order point has been reached is the two-bin method.
10. A company has been ordering more than the economic order quantity. This would result in more frequent order points.
11. An imputed cost is the difference in total costs that results from selecting one choice instead of another.
12. Theoretically, cash discounts permitted on purchased raw materials should be deducted from inventory, whether taken or not.
13. In a job-order cost system, the application of factory overhead is usually reflected in the general ledger as an increase in factory overhead control.
14. The information contained in a cost of goods manufactured budget most directly relates to the materials used, direct labor, overhead applied, work-in-process inventories, and finished goods inventories budgets.
15. The use of variable costing requires knowing the number of units of each product produced during the period.
16. Product-quality-related costs are part of a total quality control program. A product-quality-related cost incurred in detecting individual products that do not conform to specification is an example of a prevention cost.
17. One of the purposes of standard cost is to simplify costing procedures and expedite costs reports.
18. Controllable costs arise from periodic appropriation decisions and have no well-specified function relating inputs to outputs.
19. The difference between variable costs and fixed costs is total variable costs are variable over the relevant range and fixed in the long-term, while fixed costs never change.
20. Within a relevant range, the amount of variable cost per unit moves in the same direction as fixed cost per unit.
21. Internal auditors must often distinguish between product costs and period costs. Product costs are properly assigned to inventory when incurred. Period costs are always expensed in the same period in which they are incurred. Property taxes on a factory is a product cost for a manufacturing company.
22. Inventoriable costs are expensed when the products become part of finished goods inventory.
23. Normal costing is not a type of absorption costing.
24. An accounting system that collects financial and operating data on the basis of the underlying nature and extent of the cost drivers is target costing.
25. Joint costs are those costs of products that must be processed further to be salable.
26. The purchase requisition may originate with a materials record clerk.
27. A direct labor overtime premium should be charged to specific job when the overtime is caused by the increased overall level of activity.
28. Correlation is a term frequently used in conjunction with regression analysis and is measured by the value of the coefficient of correlation, r. The best explanation of the value r is that it is a measure of the relative relative relationship between two variables.
29. The method that gives the lowest inventory cost per unit is the absorption costing using practical capacity to set the standard fixed cost.
30. The slope of the line regression is the rate at which the independent variable varies.
Machining Trucking Finishing Total Activity Center Budgeted Capacity Budgeted Cost 1,000 setups 200 loads P2,500 1,000 2,000 machine hours 3,000 P6,500 Actual activities and costs used to process products are as follows: Activity Center Machining Trucking Finishing Product Ben Product Ana 550 setups @P3.00 125 loads @P4.50 1,250 MH @ P1.25 350 setups @ 2.50 70 loads @P5.25 750 MH @ P1.30
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


