Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Learning Goal: To calculate minor head losses and pressure drops for pipe fittings. Minor losses in pipe flow are the result of disruptions to
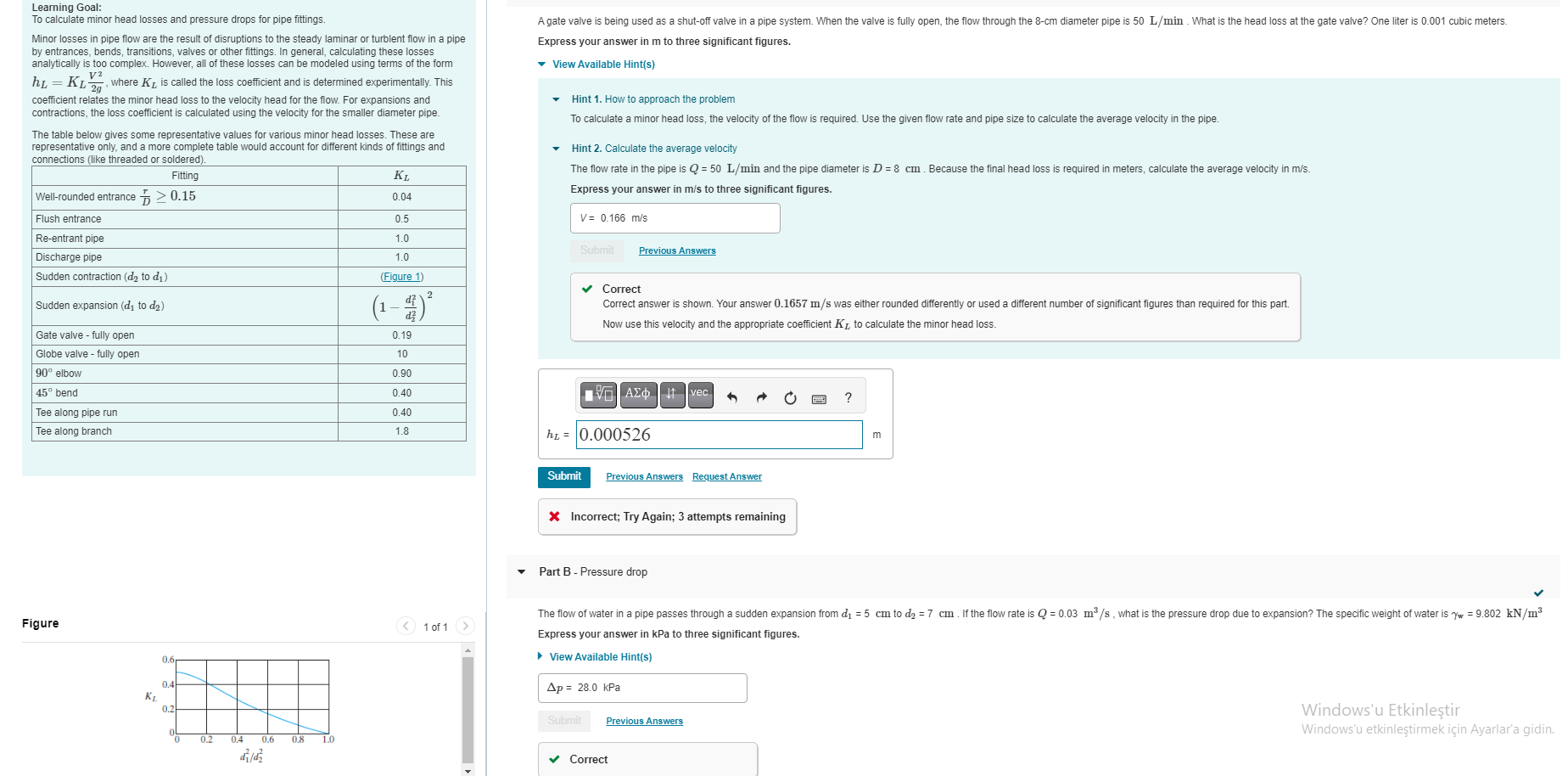
Learning Goal: To calculate minor head losses and pressure drops for pipe fittings. Minor losses in pipe flow are the result of disruptions to the steady laminar or turblent flow in a pipe by entrances, bends, transitions, valves or other fittings. In general, calculating these losses analytically is too complex. However, all of these losses can be modeled using terms of the form V2 hL = KL 2, where K is called the loss coefficient and is determined experimentally. This coefficient relates the minor head loss to the velocity head for the flow. For expansions and contractions, the loss coefficient is calculated using the velocity for the smaller diameter pipe. The table below gives some representative values for various minor head losses. These are representative only, and a more complete table would account for different kinds of fittings and connections (like threaded or soldered). Fitting Well-rounded entrance 0.15 Flush entrance Re-entrant pipe Discharge pipe Sudden contraction (d to d) Sudden expansion (d to d) Gate valve - fully open Globe valve - fully open 90 elbow 45 bend Tee along pipe run Tee along branch A gate valve is being used as a shut-off valve in a pipe system. When the valve is fully open, the flow through the 8-cm diameter pipe is 50 L/min. What is the head loss at the gate valve? One liter is 0.001 cubic meters. Express your answer in m to three significant figures. View Available Hint(s) Hint How approach the problem To calculate a minor head loss, the velocity of the flow is required. Use the given flow rate and pipe size to calculate the average velocity in the pipe. Hint 2. Calculate the average velocity The flow rate in the pipe is Q = 50 L/min and the pipe diameter is D = 8 cm. Because the final head loss is required in meters, calculate the average velocity in m/s. Express your answer in m/s to three significant figures. V = 0.166 m/s Submit Previous Answers KL 0.04 0.5 1.0 1.0 (Figure 1) Correct Correct answer is shown. Your answer 0.1657 m/s was either rounded differently Now use this velocity and the appropriate coefficient K to calculate the minor head loss. used different number of significant figures than required for this part. (1-4) 0.19 10 0.90 0.40 vec 0.40 1.8 hL 0.000526 Figure KL 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 d/d 1 of 1 > Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Part B - Pressure drop The flow of water in a pipe passes through a sudden expansion from d = 5 cm to d = 7 cm. If the flow rate is Q = 0.03 m/s, what is the pressure drop due to expansion? The specific weight of water is yw = 9.802 kN/m Express your answer in kPa to three significant figures. View Available Hint(s) Ap = 28.0 kPa Submit Previous Answers Correct Windows'u Etkinletir Windows'u etkinletirmek iin Ayarlar'a gidin.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


