Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Learning Objectives List sources of parallelization overhead Distinguish between task vs. data parallelism Apply Foster's methodology for parallel program design to produce a design that

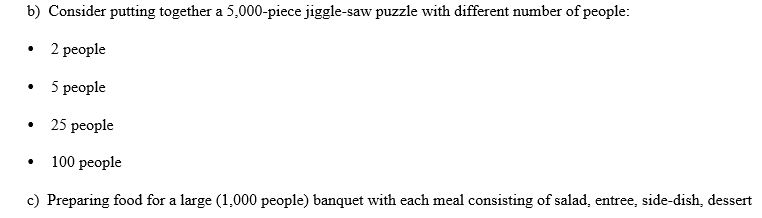

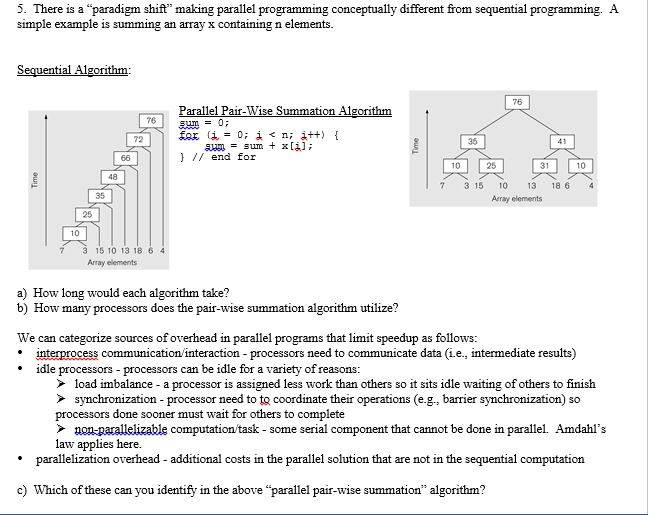
Learning Objectives List sources of parallelization overhead Distinguish between task vs. data parallelism Apply Foster's methodology for parallel program design to produce a design that minimizes parallel overhead. Apply Amdalh's law to calculate the maximum speedup given a fraction of serial processing. Calculate parallel performance metrics: speedup and efficiency 1. Two types of parallelism: task parallelism - split program into major tasks and solve as many tasks in parallel as possible data parallelism - partition the data across the processors with each processor doing the same type of calculations on their own chuck of data a) Which of the above approaches is more scalable (can utilize more processors) as the problems get large (i.e., lots of data)? b) How might a combination of the two be used? 2. Let's think about parallelism, but with real-world examples. Here think of each person as a processor. For each example, determine the "majo" sequence of tasks/steps, but also explain what tasks can be "data parallelized" assuming we had many people? a) Building a house Learning Objectives List sources of parallelization overhead Distinguish between task vs. data parallelism Apply Foster's methodology for parallel program design to produce a design that minimizes parallel overhead. Apply Amdalh's law to calculate the maximum speedup given a fraction of serial processing. Calculate parallel performance metrics: speedup and efficiency 1. Two types of parallelism: task parallelism - split program into major tasks and solve as many tasks in parallel as possible data parallelism - partition the data across the processors with each processor doing the same type of calculations on their own chuck of data a) Which of the above approaches is more scalable (can utilize more processors) as the problems get large (i.e., lots of data)? b) How might a combination of the two be used? 2. Let's think about parallelism, but with real-world examples. Here think of each person as a processor. For each example, determine the "majo" sequence of tasks/steps, but also explain what tasks can be "data parallelized" assuming we had many people? a) Building a house
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


