Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
LEAST SQUARE DUMMY VARIABLE = LSVD OLS = ORDINARY LEAST SQUARE 2.8 From the results above, which model between Pooled OLS in (2.2) and
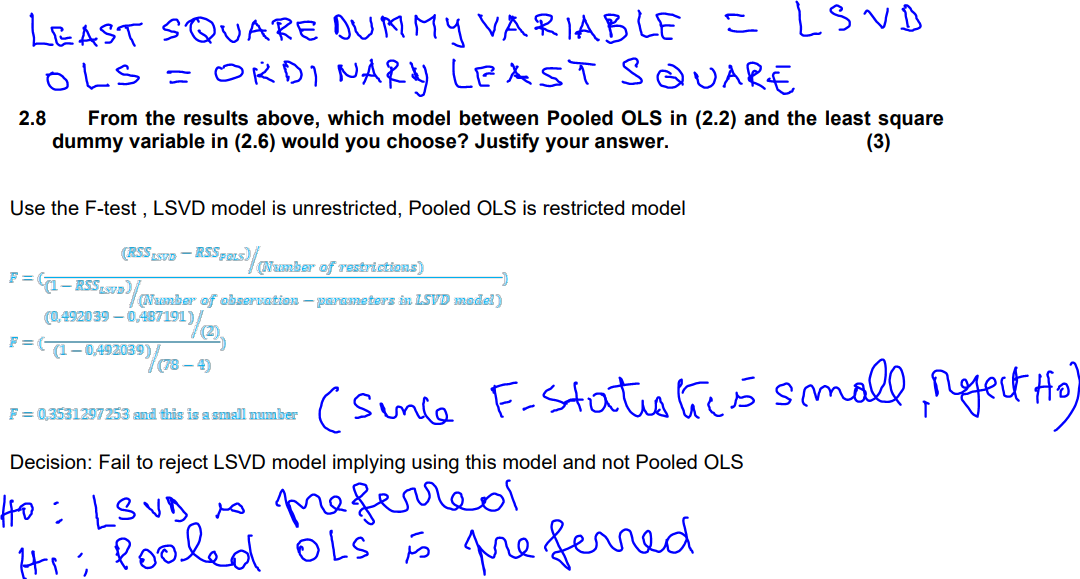

LEAST SQUARE DUMMY VARIABLE = LSVD OLS = ORDINARY LEAST SQUARE 2.8 From the results above, which model between Pooled OLS in (2.2) and the least square dummy variable in (2.6) would you choose? Justify your answer. (3) Use the F-test, LSVD model is unrestricted, Pooled OLS is restricted model F = F= (RSS LSVD-RSS POLS) (Number of restrictions) (Number of observation-parameters in LSVD model) (1-RSS SVD) (0.492039-0,487191) (1 0,492039)/ 39)/(78- 11/1277 (78-4) F = 0,3531297253 and this is a small number (Since F-statistics small, nget Ho Decision: Fail to reject LSVD model implying using this model and not Pooled OLS Ho: LSVD is preferred Hi; Pooled OLS is preferred 3.12 Random effects versus pooled OLS How to choose between the RE and pooled OLS approaches? Breusch and Pagan developed a Lagrange Multiplier test, which can be used to make a choice between RE and pooled OLS. However, it has been criticised due to number of factors: - - - - Null hypothesis: = 0, thus, there are no unobserved effects. Failure to reject the null hypothesis favours the OLS estimation. Rejection of null hypothesis implies that the OLS estimation is inefficient and RE should be used, but on the condition that the assumptions are satisfied. Weakness of the test The usefulness of the test is limited. The outcome of the test says nothing about whether pooled OLS is consistent. >0 has nothing to do with whether a; is correlated with explanatory variables. Both pooled OLS and RE are inconsistent if a, is correlated with explanatory variables. It is a test of positive serial correlation in the composite error terms. The test assumes that all unobservable are normally distributed and maintains the homoscedasticity. Neither of these assumptions are necessary for either RE or pooled OLS to be consistent. Reasons to prefer random effects over pooled OLS RE removes a fraction of the error term - so there is less bias compared to the pooled OLS estimate. RE estimator is a bit more efficient than the pooled OLS estimator. RE estimator partly removes some of the serial correlation.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


