Question
Lesson 6 : Part A: (The Concepts): True/False: Answer each question given below by answering if the question is true or false. Include your explanation
Lesson 6 : Part A: (The Concepts): True/False: Answer each question given below by answering if the question is true or false. Include your explanation for your choice. Each question is worth two marks: one mark for the explanation and one mark for the correct answer. 1.A good working definition for energy is the capacity to do work. 2. Temperature is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another. 3. Work is defined as the energy transferred to an object by a force applied over a measured distance. 4.For an ideal spring, the force-stretch graph is a curved line 5. The area under a force-stretch graph of an ideal spring represents the spring's force constant. Part A (Using the Concepts): Multiple Choice: Each question is worth different marks according to the strategy used. If calculations are required, the mark for the strategy will worth more marks and the final answer will be worth one mark. 6. Which of the following energy-transformation equations best describes the operation of a wind generator that is used to power an electric can opener. a. thermal energy -> electrical energy -> kinetic energy b. wind energy -> thermal energy -> kinetic energy c. Kinetic energy -> electrical energy > kinetic energy d. electrical energy -> kinetic energy > thermal energy 7. The energy-transformation equation gravitational potential energy > kinetic energy gravitational potential energy could represent which of the following events? a. a roller coaster gliding up and over a hill b. an arrow shot into the air C. a bouncing ball d. a car accelerating along a level road 8. In which of the following cases is no work being done? a. a child pushes against a wall that does not move b. a child pulls a wagon across a horizontal surface C. a child pulls a wagon up a hill d. a wagon runs down a hill on its own 9. How much work is done by a person who exerts a force of 8.0 N to push a 2.0-kg object horizontally over a distance of 3.0 m? a.48 T b.24 J c. 16J d.12 J 10.How far does a 5.0-N force have to move a 2.0-kg object to accomplish 24 J of work? a.48 m b.3.4 m c.24 m d.0.42 m 11. If a toy car loses 8.4 J of kinetic energy by rolling across the floor for 1.5 m, the force of kinetic friction acting on the car has a magnitude of a. much greater than 5.6 N b. slightly greater than 5.6 N c. exactly 5.6 N d. slightly more than 5.6 N
12.(A person exerts a force of 16 N against 4.0 N of kinetic friction and moves an object a distance of 2.5 m. How much useful work is accomplished?
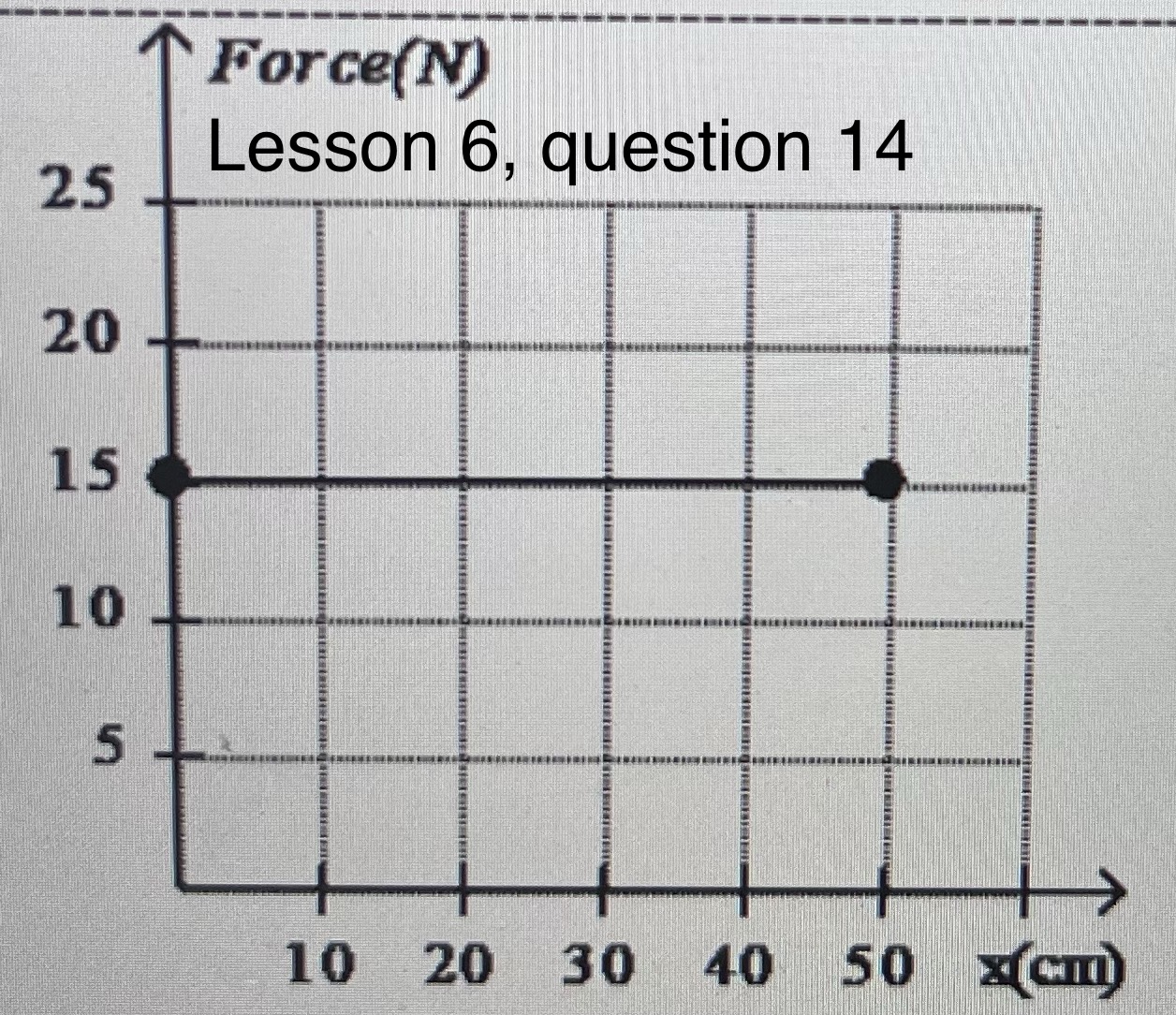
a.50.0 J b.40.0 T C.30.0 J d. It is not possible to say without knowing the mass of the object. 13. A horizontal force of 24 N causes a 2.0-kg object to slide along a shelf at a constant velocity. How far does the object slide if 7.2 J of work is done by the force? a. 1.7 m b. 0.60 m d. 0.40 m c. 0.30 m 14. Using the force-displacement graph, determine the work done to move the object 50 cm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


