Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Let O be a Bernoulli random variable that indicates which one of two hypotheses is true, and let P(O = 1) = p. Under
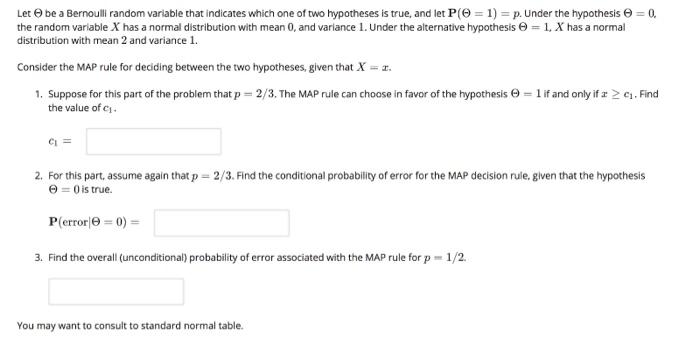
Let O be a Bernoulli random variable that indicates which one of two hypotheses is true, and let P(O = 1) = p. Under the hypothesis e = 0, the random variable X has a normal distribution with mean 0, and variance 1. Under the alternative hypothesis e = 1, X has a normal distribution with mean 2 and variance 1. Consider the MAP rule for deciding between the two hypotheses, given that X = r. 1. Suppose for this part of the problem that p = 2/3, The MAP rule can choose in favor of the hypothesis e = l if and only if z > e1. Find the value of c. CI = 2. For this part, assume again that p = 2/3. Find the conditional probability of error for the MAP decision rule, glven that the hypothesis e = 0 is true. P(error|e = 0) = 3. Find the overall (unconditional) probability of error associated with the MAP rule for p= 1/2. You may want to consult to standard normal table.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.43 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Document Format ( 2 attachments)
6360fe61168a6_235240.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
6360fe61168a6_235240.docx
120 KBs Word File
Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


