Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Let X be a random variable and a, b be constants. 1. Show that E(aX+b) : = aE(X)+b 2. Show that V(ax + b)
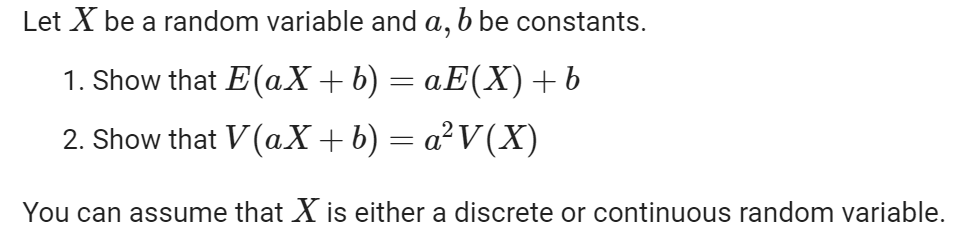
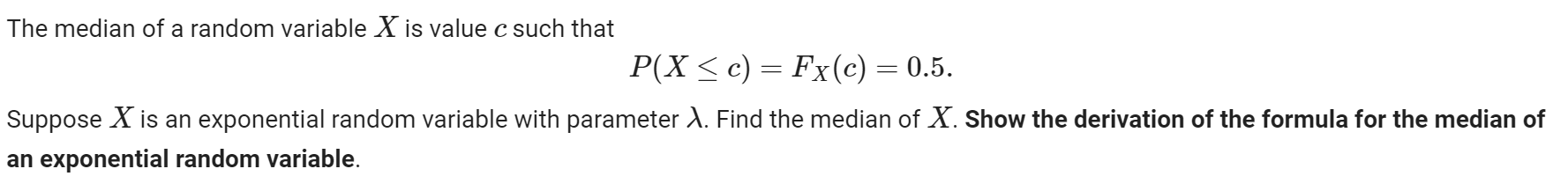
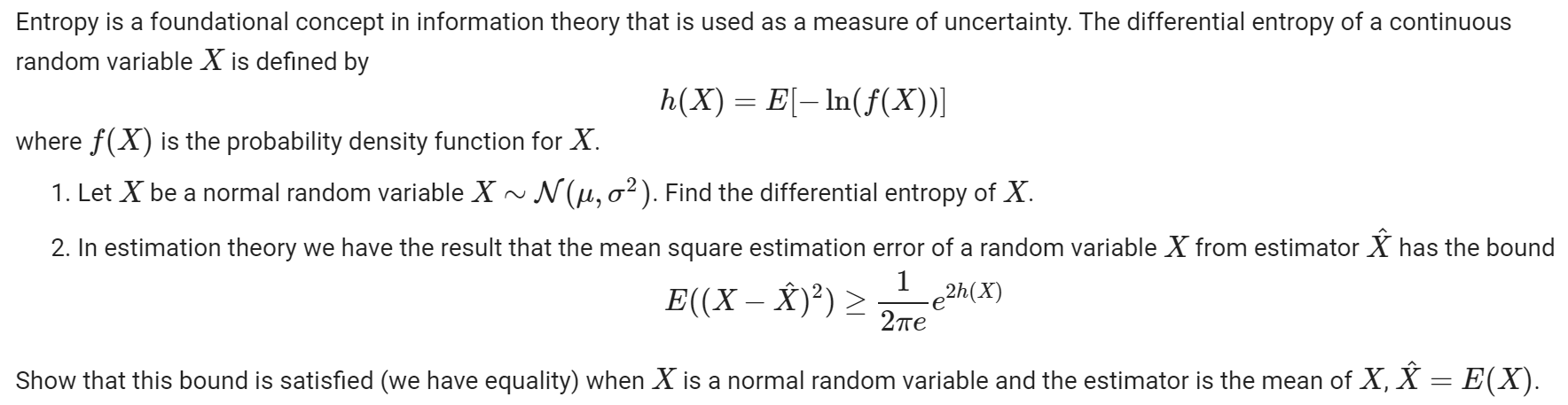
Let X be a random variable and a, b be constants. 1. Show that E(aX+b) : = aE(X)+b 2. Show that V(ax + b) = aV(X) You can assume that X is either a discrete or continuous random variable. The median of a random variable X is value c such that P(X c) = Fx(c) = 0.5. Suppose X is an exponential random variable with parameter A. Find the median of X. Show the derivation of the formula for the median of an exponential random variable. Entropy is a foundational concept in information theory that is used as a measure of uncertainty. The differential entropy of a continuous random variable X is defined by where (X) is the probability density function for X. h(X) = E[ ln((X))] 1. Let X be a normal random variable X ~ N(u, o). Find the differential entropy of X. 2. In estimation theory we have the result that the mean square estimation error of a random variable X from estimator has the bound E((X )) > -e2h (X) 1 2 Show that this bound is satisfied (we have equality) when X is a normal random variable and the estimator is the mean of X, = E(X).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


