Lets define leverage defined as L = 10/E (asset-to-equity ratio).
You may find leverage ratio defined in other ways, such as the leverage/equity ratio (rather than asset/equity ratio, as we do here). Ignore those alternative definitions.
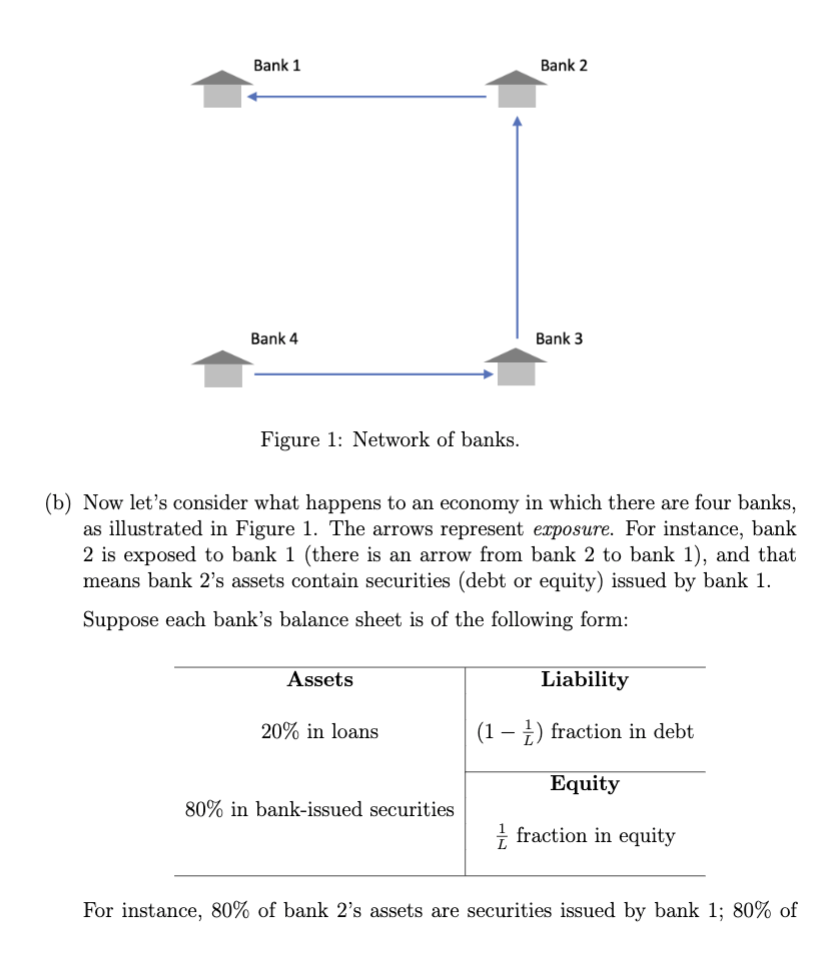

Bank 1 Bank 2 Bank 4 Bank 3 Figure 1: Network of banks. (b) Now let's consider what happens to an economy in which there are four banks, as illustrated in Figure 1. The arrows represent exposure. For instance, bank 2 is exposed to bank 1 (there is an arrow from bank 2 to bank 1), and that means bank 2's assets contain securities (debt or equity) issued by bank 1. Suppose each bank's balance sheet is of the following form: Assets Liability 20% in loans (1 - 1) fraction in debt Equity 80% in bank-issued securities fraction in equity For instance, 80% of bank 2's assets are securities issued by bank 1; 80% of 90% bank 3's assets are securities issued by bank 2, and etc. (follow the arrows in Figure 1). The loans held by different banks are all separate from each other. Throughout this question, you don't need to think in dollar values, but only need to think about values in proportional terms (e.g. loans are 20% of total asset value in the balance sheet above). Recall how investors are paid in bankruptcy: if a bank goes bankrupt, then its equity becomes worthless, and its debt holders get all remaining asset value with a haircut. For instance, suppose L = 10 (so equity is 10% of total assets), and suppose the asset value of a bank declines by 30%. Then, it goes bankrupt, and its equity becomes worthless. Its debt is now worth 1-30% as much as before. So the holders of its equity suffer a loss of 100% (worthless now), and the holders of its debt suffer a proportional loss of 15 = ~ 22.2%. In all sub-questions below, we want to figure out what happens if bank 1 suffers a negative shock: the value of its loans suddenly becomes zero. (The "bank-issued securities on bank 1 balance sheet is not affected, and the loans held by other banks are also not affected.) For simplicity, suppose all four banks have the same leverage ratio of L before the negative shocked happened. Please answer the questions below. i. How high can the leverage ratio L be for there to be no bankruptcy among all four banks in response to this negative shock?3 ii. Now suppose banks hold debt securities issued by other banks. Sup- pose all banks have a leverage ratio of L = 15. How many banks will go bankrupt? Please be specific in your answer which banks are bankrupt and why. Support your answer with calculations. Hint: there is a "chain reaction". When bank 1 gets the negative shock, the value of its equity and its ability to pay back debt may be affected. That will impact the asset values of bank 2, because bank 2 holds securities issued by bank 1. And then that impacts bank 3, and so on... iii. Still assume that L = 15 for all banks. Now suppose banks hold equity securities issued by other banks. How many banks will go bankrupt? iv. What do you learn from the previous three questions? Please focus on how inter-bank relationships impact the likelihood of wide-spread bank failures. Bank 1 Bank 2 Bank 4 Bank 3 Figure 1: Network of banks. (b) Now let's consider what happens to an economy in which there are four banks, as illustrated in Figure 1. The arrows represent exposure. For instance, bank 2 is exposed to bank 1 (there is an arrow from bank 2 to bank 1), and that means bank 2's assets contain securities (debt or equity) issued by bank 1. Suppose each bank's balance sheet is of the following form: Assets Liability 20% in loans (1 - 1) fraction in debt Equity 80% in bank-issued securities fraction in equity For instance, 80% of bank 2's assets are securities issued by bank 1; 80% of 90% bank 3's assets are securities issued by bank 2, and etc. (follow the arrows in Figure 1). The loans held by different banks are all separate from each other. Throughout this question, you don't need to think in dollar values, but only need to think about values in proportional terms (e.g. loans are 20% of total asset value in the balance sheet above). Recall how investors are paid in bankruptcy: if a bank goes bankrupt, then its equity becomes worthless, and its debt holders get all remaining asset value with a haircut. For instance, suppose L = 10 (so equity is 10% of total assets), and suppose the asset value of a bank declines by 30%. Then, it goes bankrupt, and its equity becomes worthless. Its debt is now worth 1-30% as much as before. So the holders of its equity suffer a loss of 100% (worthless now), and the holders of its debt suffer a proportional loss of 15 = ~ 22.2%. In all sub-questions below, we want to figure out what happens if bank 1 suffers a negative shock: the value of its loans suddenly becomes zero. (The "bank-issued securities on bank 1 balance sheet is not affected, and the loans held by other banks are also not affected.) For simplicity, suppose all four banks have the same leverage ratio of L before the negative shocked happened. Please answer the questions below. i. How high can the leverage ratio L be for there to be no bankruptcy among all four banks in response to this negative shock?3 ii. Now suppose banks hold debt securities issued by other banks. Sup- pose all banks have a leverage ratio of L = 15. How many banks will go bankrupt? Please be specific in your answer which banks are bankrupt and why. Support your answer with calculations. Hint: there is a "chain reaction". When bank 1 gets the negative shock, the value of its equity and its ability to pay back debt may be affected. That will impact the asset values of bank 2, because bank 2 holds securities issued by bank 1. And then that impacts bank 3, and so on... iii. Still assume that L = 15 for all banks. Now suppose banks hold equity securities issued by other banks. How many banks will go bankrupt? iv. What do you learn from the previous three questions? Please focus on how inter-bank relationships impact the likelihood of wide-spread bank failures








