Question
Review the steps of an action potential and the events at synapses, and then fill in the following blanks, as you trace the events in
Review the steps of an action potential and the events at synapses, and then fill in the following blanks, as you trace the events in a 3-neuron sequence, including the generation and propagation of the action potentials, and the synaptic events between the neurons.
Neuronal action potential reaches the axon terminal of neuron 1, which causes _______________ to open, leading to an influx of calcium into the axon terminal of Neuron # 1. This causes the exocytosis of vesicles filled with _________________ that leave the ______________ of neuron # 1 and diffuse across the synaptic cleft to Neuron # 2. At Neuron # 2, neurotransmitters bind to the postsynaptic membrane of neuron #2 and generate an excitatory/depolarizing local potential by opening_____________. This excitatory depolarization spreads through neuron # 2 from the ____________________to the________________ and finally to the _______________, where the axon hillock is depolarized to threshold by the summation of the local potentials. Depolarization of the axon hillock causes ________________ to open, which allows _______________ to rush into the axon, causing an ___________________. The action potential is propagated down the axon of neuron # 2 via ____________________ because neuron # 2 is a myelinated motor neuron. After the action potential passes, ______________________open and ___________________ exits the neuron, causing repolarization of that part of the neuronal membrane. The action potential continues to propogate down the axon of neuron # 2 until it reaches the ______________________ of neuron # 2 and causes the opening of _____________________. Calcium influxes into the axon terminal and causes the release of __________________, which diffuse across the _______________________ between neuron # 2, which is the ____________________neuron, and neuron # 3, which is the ________________ neuron. Neurotransmitters cause excitatory/depolarizing or inhibitory/hyperpolarizing local potentials in the postsynaptic membrane of neuron # 3.
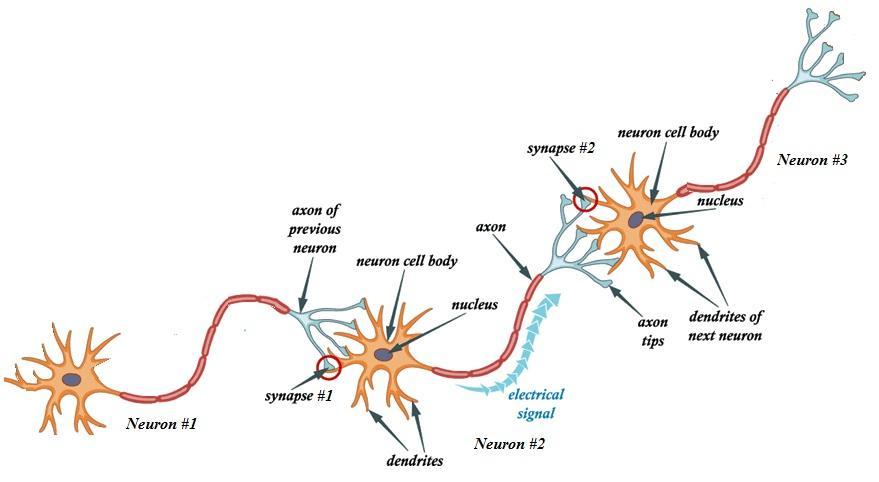
Choose from the following possible terms – not all may be used and some may be used more than once:
Axon terminal, sodium voltage-gated channels, calcium voltage-gated channels, potassium voltage-gated channels, axon hillock, neurotransmitters, sodium, calcium, potassium, dendrites, soma, action potential, saltatory conduction, continuous conduction, synaptic cleft, postsynaptic, presynaptic.
n cell body synapse #2 Neuron #3 nucleus axon of previous neuron neuron cell body cleus dendrites of axon next neuron tips electrical signal synpse #1 Neuron #1 Neuron #2 dendrites
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Neuronal action potential reaches the axon terminal of neuron 1 which causes Calcium voltage channel ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


