Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ligands pick either A B or C whichever is the best route to form methanol. explain why you chose it over the other 2 HOH
ligands
pick either A B or C whichever is the best route to form methanol. explain why you chose it over the other 2
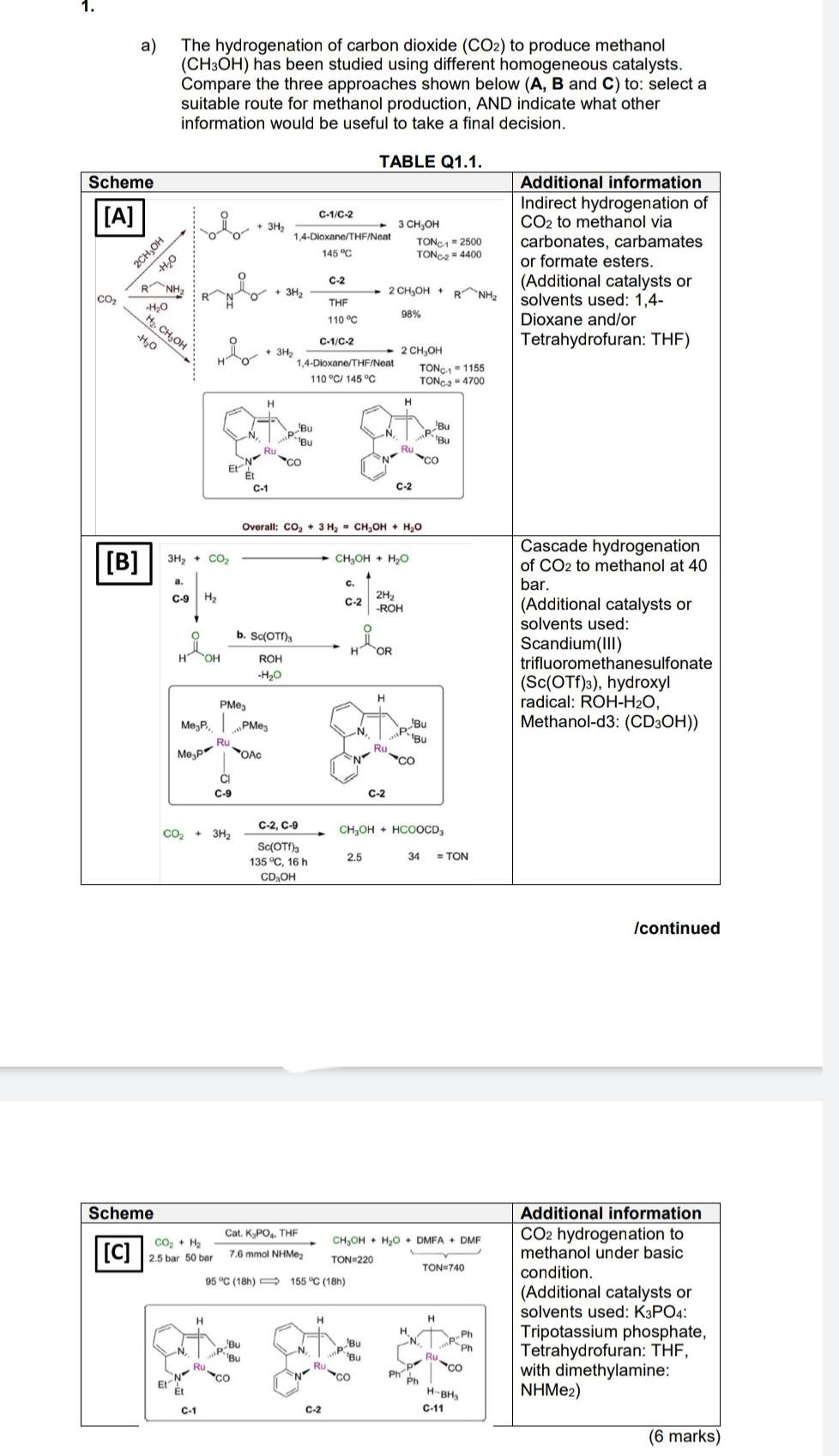
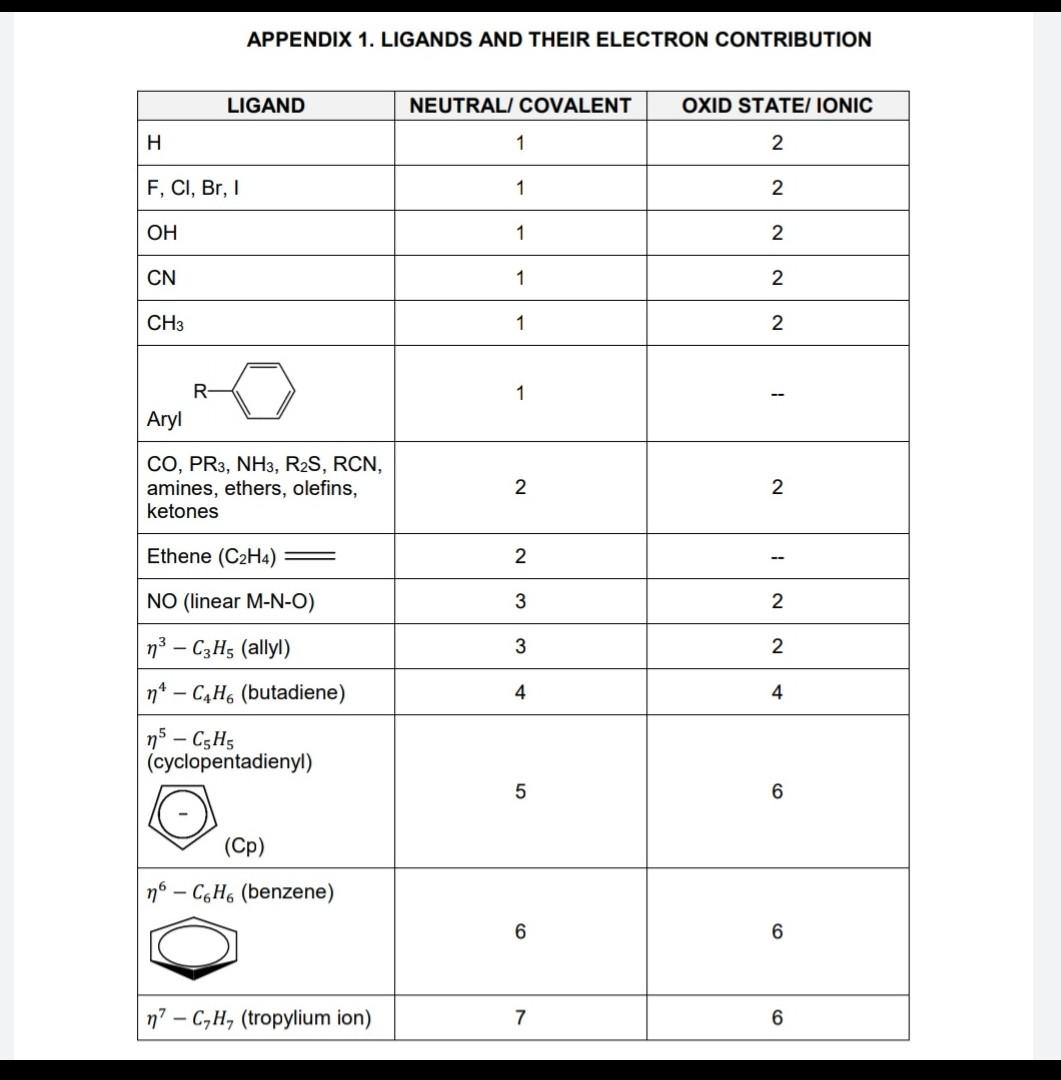
HOH a) The hydrogenation of carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce methanol (CH3OH) has been studied using different homogeneous catalysts. Compare the three approaches shown below (A, B and C) to: select a suitable route for methanol production, AND indicate what other information would be useful to take a final decision. TABLE Q1.1. Scheme [A] C-1/C-2 vio + 3H2 3 CH3OH 2CH OH 1,4-Dioxane/THF/Neat 145 C TONC1 - 2500 TONC2 = 4400 Additional information Indirect hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol via carbonates, carbamates or formate esters. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: 1,4- Dioxane and/or Tetrahydrofuran: THF) H2O C-2 NH -H.0 CO 2 CH,OHRNH2 + 3H2 THF 110 C 98% H2, CH OH -H20 C-1/C-2 + 3H2 1,4-Dioxane/THF/Neat 110 C/145 C 2 CH OH TONC1 - 1155 TONC2 - 4700 H H Bu Bu N Bu Bu -No Ru N Er Et C-1 C-2 Overall: Co, + 3 H2 - CH2OH + H2O [B] 3H2 + CO2 CH,OH + H2O a. C. C-9 H2 C-2 2H2 -ROH b. Sc(OT), Cascade hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol at 40 bar. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: Scandium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate (Sc(OTf)3), hydroxyl radical: ROH-H20, Methanol-d3: (CD3OH)) HOR ROH -H20 H Megp PMey PMes Ru OAC N Bu Bu Ru Mep ci C-9 C-2 C-2, C-9 CO2 + 3H2 CH,OH + HCOOCD, Sc(OT), 135 C, 16 h CD OH 2.5 34 = TON Icontinued Scheme Cat. K, PO4, THE CO, H2 CH,OH + H2O + DMFA + DMF 2.5 bar 50 bar 7.6 mmol NHMez TON 220 TON-740 95 C (18) - 155 C (18h) [C] Additional information CO2 hydrogenation to methanol under basic condition. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: K3PO4: Tripotassium phosphate, Tetrahydrofuran: THF, with dimethylamine: NHMe2) H H H H Ph Ph . Bu Bu Ru CO Bu Bu Ru p- Ru N EN Ph Ph " H-BH C-1 C-2 C-11 (6 marks) APPENDIX 1. LIGANDS AND THEIR ELECTRON CONTRIBUTION LIGAND NEUTRAL, COVALENT OXID STATEI IONIC H 1 2 F, CI, Br, 1 1 2 OH 1 2 CN 1 2. CH3 1 2 R 1 -- Aryl CO, PR3, NH3, R2S, RCN, amines, ethers, olefins, ketones 2 2 Ethene (C2H4) 2 NO (linear M-N-O) 3 2 3 2 4 4 m3 - C3H5 (allyl) nt - C4H (butadiene) n C,H, (cyclopentadienyl) 5 6 (Cp) no - CH (benzene) 6 6 n? - C,H, (tropylium ion) 7 6 HOH a) The hydrogenation of carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce methanol (CH3OH) has been studied using different homogeneous catalysts. Compare the three approaches shown below (A, B and C) to: select a suitable route for methanol production, AND indicate what other information would be useful to take a final decision. TABLE Q1.1. Scheme [A] C-1/C-2 vio + 3H2 3 CH3OH 2CH OH 1,4-Dioxane/THF/Neat 145 C TONC1 - 2500 TONC2 = 4400 Additional information Indirect hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol via carbonates, carbamates or formate esters. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: 1,4- Dioxane and/or Tetrahydrofuran: THF) H2O C-2 NH -H.0 CO 2 CH,OHRNH2 + 3H2 THF 110 C 98% H2, CH OH -H20 C-1/C-2 + 3H2 1,4-Dioxane/THF/Neat 110 C/145 C 2 CH OH TONC1 - 1155 TONC2 - 4700 H H Bu Bu N Bu Bu -No Ru N Er Et C-1 C-2 Overall: Co, + 3 H2 - CH2OH + H2O [B] 3H2 + CO2 CH,OH + H2O a. C. C-9 H2 C-2 2H2 -ROH b. Sc(OT), Cascade hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol at 40 bar. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: Scandium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate (Sc(OTf)3), hydroxyl radical: ROH-H20, Methanol-d3: (CD3OH)) HOR ROH -H20 H Megp PMey PMes Ru OAC N Bu Bu Ru Mep ci C-9 C-2 C-2, C-9 CO2 + 3H2 CH,OH + HCOOCD, Sc(OT), 135 C, 16 h CD OH 2.5 34 = TON Icontinued Scheme Cat. K, PO4, THE CO, H2 CH,OH + H2O + DMFA + DMF 2.5 bar 50 bar 7.6 mmol NHMez TON 220 TON-740 95 C (18) - 155 C (18h) [C] Additional information CO2 hydrogenation to methanol under basic condition. (Additional catalysts or solvents used: K3PO4: Tripotassium phosphate, Tetrahydrofuran: THF, with dimethylamine: NHMe2) H H H H Ph Ph . Bu Bu Ru CO Bu Bu Ru p- Ru N EN Ph Ph " H-BH C-1 C-2 C-11 (6 marks) APPENDIX 1. LIGANDS AND THEIR ELECTRON CONTRIBUTION LIGAND NEUTRAL, COVALENT OXID STATEI IONIC H 1 2 F, CI, Br, 1 1 2 OH 1 2 CN 1 2. CH3 1 2 R 1 -- Aryl CO, PR3, NH3, R2S, RCN, amines, ethers, olefins, ketones 2 2 Ethene (C2H4) 2 NO (linear M-N-O) 3 2 3 2 4 4 m3 - C3H5 (allyl) nt - C4H (butadiene) n C,H, (cyclopentadienyl) 5 6 (Cp) no - CH (benzene) 6 6 n? - C,H, (tropylium ion) 7 6Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


