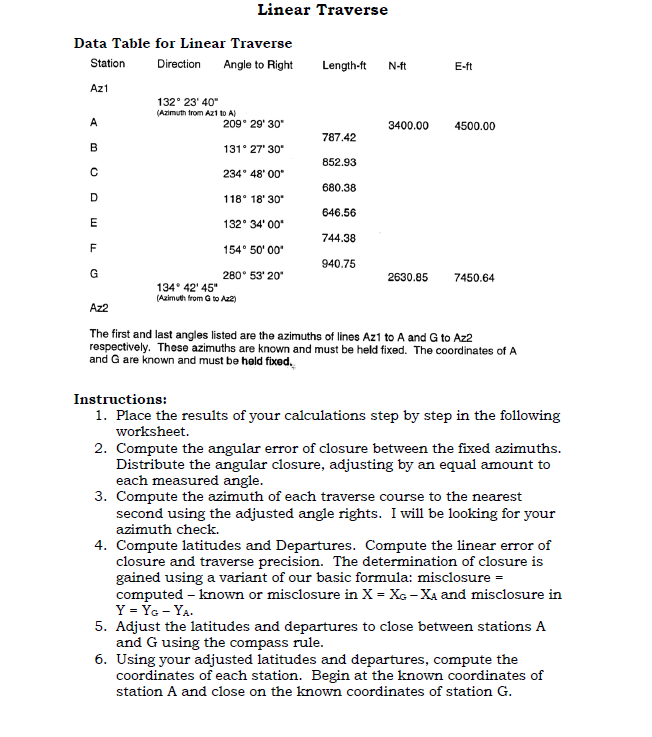
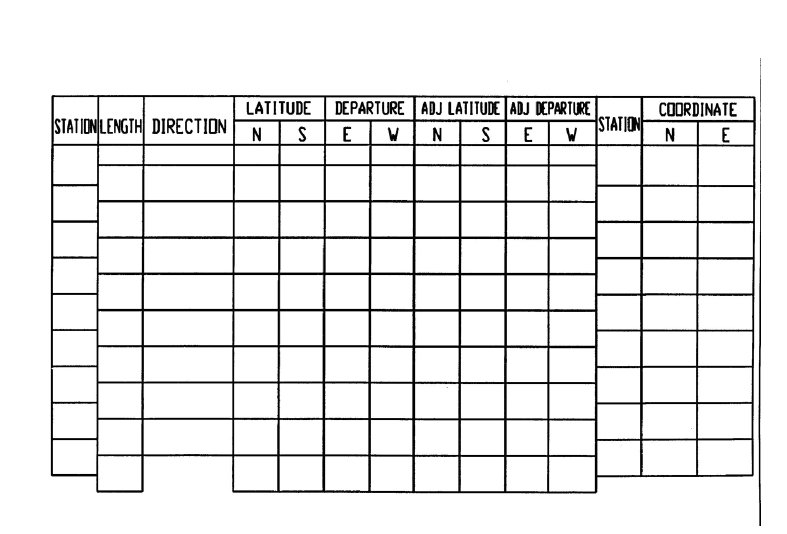
Linear Traverse Data Table for Linear Traverse Station Direction Angle to Right Length-ft N-ft E-ft Azt 132 23' 40" (Azimuth from Azt to A) 20929' 30" A 3400.00 4500.00 787.42 B 131 27' 30" 852.93 234 48' 00 680.38 D 118 18' 30" 646.56 132 34'00" 744.38 F 154 50'00 940.75 G 2630.85 7450.64 280 53' 20" 134 42' 45" (Azimuth from G to Az2) Az2 The first and last angles listed are the azimuths of lines Azi to A and G to Az2 respectively. These azimuths are known and must be held fixed. The coordinates of A and G are known and must be held fixed. Instructions: 1. Place the results of your calculations step by step in the following worksheet. 2. Compute the angular error of closure between the fixed azimuths. Distribute the angular closure, adjusting by an equal amount to each measured angle. 3. Compute the azimuth of each traverse course to the nearest second using the adjusted angle rights. I will be looking for your azimuth check. 4. Compute latitudes and Departures. Compute the linear error of closure and traverse precision. The determination of closure is gained using a variant of our basic formula: misclosure = computed - known or misclosure in X = Xo - XA and misclosure in Y = YG - YA. 5. Adjust the latitudes and departures to close between stations A and G using the compass rule. 6. Using your adjusted latitudes and departures, compute the coordinates of each station. Begin at the known coordinates of station A and close on the known coordinates of station G. STATION LENGTH DIRECTION LATITUDE DEPARTURE ADJ LATITUDE ADJ DEPARTURE STATION N S E W N S E W COORDINATE N E Linear Traverse Data Table for Linear Traverse Station Direction Angle to Right Length-ft N-ft E-ft Azt 132 23' 40" (Azimuth from Azt to A) 20929' 30" A 3400.00 4500.00 787.42 B 131 27' 30" 852.93 234 48' 00 680.38 D 118 18' 30" 646.56 132 34'00" 744.38 F 154 50'00 940.75 G 2630.85 7450.64 280 53' 20" 134 42' 45" (Azimuth from G to Az2) Az2 The first and last angles listed are the azimuths of lines Azi to A and G to Az2 respectively. These azimuths are known and must be held fixed. The coordinates of A and G are known and must be held fixed. Instructions: 1. Place the results of your calculations step by step in the following worksheet. 2. Compute the angular error of closure between the fixed azimuths. Distribute the angular closure, adjusting by an equal amount to each measured angle. 3. Compute the azimuth of each traverse course to the nearest second using the adjusted angle rights. I will be looking for your azimuth check. 4. Compute latitudes and Departures. Compute the linear error of closure and traverse precision. The determination of closure is gained using a variant of our basic formula: misclosure = computed - known or misclosure in X = Xo - XA and misclosure in Y = YG - YA. 5. Adjust the latitudes and departures to close between stations A and G using the compass rule. 6. Using your adjusted latitudes and departures, compute the coordinates of each station. Begin at the known coordinates of station A and close on the known coordinates of station G. STATION LENGTH DIRECTION LATITUDE DEPARTURE ADJ LATITUDE ADJ DEPARTURE STATION N S E W N S E W COORDINATE N E








