Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
LINKEDLIST: public class LinkedList { Item head; Item tail; public LinkedList() { head = null ; tail = null ; } // Add an item
LINKEDLIST:
public class LinkedList { Item head; Item tail; public LinkedList() { head = null; tail = null; } // Add an item to the end of the list public void add(Item x) { if (tail == null) { tail = x; head = x; } else { tail.next = x; x.previous = tail; tail = x; } } // Remove the given item from the list public void remove(Item x) { if (x == head) { if (x == tail) { head = tail = null; } else { head = x.next; head.previous = null; } } else { if (x == tail) { tail = x.previous; tail.next = null; } else { x.previous.next = x.next; x.next.previous = x.previous; } } } // Return a string representation of the list public String toString() { if (head == null) return "[EMPTY]"; String s = "[H:"; Item currentItem = head; while (currentItem != null) { s += currentItem.data; if (currentItem != tail) s += "]["; currentItem = currentItem.next; } return s + ":T]"; } // Add up the total data in the list public int totalData() { if (head == null) return 0; int total = 0; Item currentItem = head; while (currentItem != null) { total += currentItem.data; currentItem = currentItem.next; } return total; } // Add up the total data in the list using recursion public int totalDataRecursive() { return totalDataRecursive(head); } // Add up the total data in the list using recursion private int totalDataRecursive(Item start) { if (start == null) return 0; return start.data + totalDataRecursive(start.next); } // Return a new linked list containing all items with odd data from this list using recursion public LinkedList oddItems() { return oddItems(head); } // Return all items with odd data in the list using recursion private LinkedList oddItems(Item start) { if (start == null) return new LinkedList(); LinkedList result = oddItems(start.next); if (start.data %2 != 0) result.add(new Item(start.data)); return result; } // Return all items with odd data in the list using recursion private LinkedList oddItems2(Item startItem, LinkedList resultList) { if (startItem == null) return resultList; if (startItem.data %2 != 0) resultList.add(new Item(startItem.data)); return oddItems2(startItem.next, resultList); } // Return a new linked list containing all common elements of the two lists public LinkedList inCommon(LinkedList aList) { return inCommon(this.head, aList.head, new LinkedList()); } // Return all items which are common between the two lists private LinkedList inCommon(Item start1, Item start2, LinkedList result) { if ((start1 == null) || (start2 == null)) return result; if (contains(start1,start2.data)) result.add(new Item(start2.data)); return inCommon(start1, start2.next, result); } // Return a boolean indicating whether or not the list contains a given item's data public boolean contains(Item startItem, byte data) { if (startItem == null) return false; if (startItem.data == data) return true; else return contains(startItem.next, data); } public boolean isInIncreasingOrder() { return false; //. Replace this code with your own } } ITEM :
public class Item { public byte data; public Item previous; public Item next; public Item(int d) { data = (byte)d; previous = null; next = null; } } SORTEDLINKEDLIST:
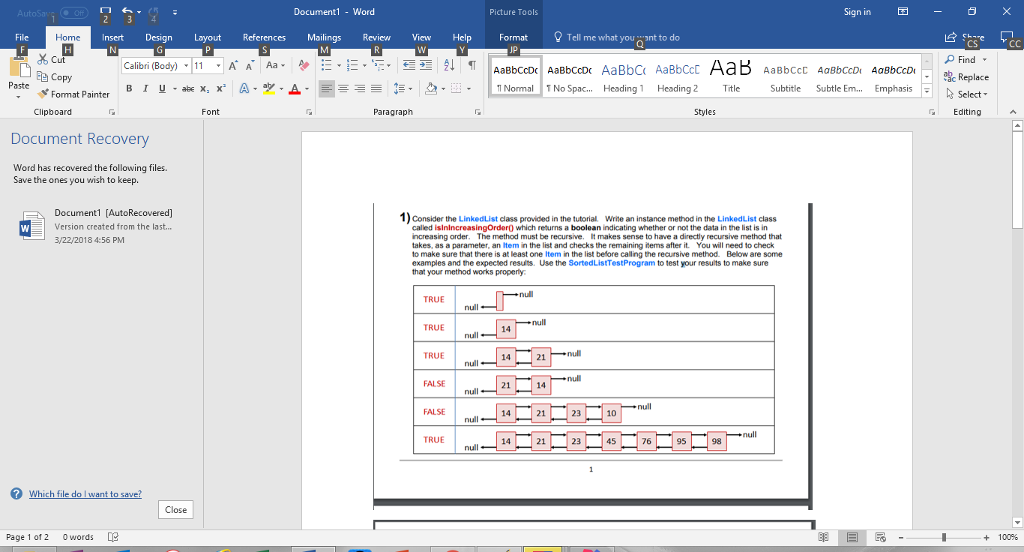
public class SortedListTestProgram { public static void main(String args[]) { LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); list = new LinkedList(); list.add(new Item(14)); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); list = new LinkedList(); list.add(new Item(14)); list.add(new Item(21)); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); list = new LinkedList(); list.add(new Item(21)); list.add(new Item(14)); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); list = new LinkedList(); list.add(new Item(14)); list.add(new Item(21)); list.add(new Item(23)); list.add(new Item(10)); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); list = new LinkedList(); list.add(new Item(14)); list.add(new Item(21)); list.add(new Item(23)); list.add(new Item(45)); list.add(new Item(76)); list.add(new Item(95)); list.add(new Item(98)); System.out.println(" Here is the list: " + list); System.out.println("The list is sorted: " + list.isInIncreasingOrder()); } } Document1 - Word Picture Tools Sign in -0 Insert Design Layout References Mailings Review View Help Format Tell me what yount to do Jp IAaBbCcDReplace Copy Paste Normal T No Spac.. Heading1 Heading 2 Title Subtitle Subtle Em.... Emphasis Select Fonmat Painter Clipboard Font Paragraph Styles Editing Document Recovery Word has recovered the following files Save the ones you wish to keep. Document1 [AutoRecovered] Version created from the last... 3/22/2018 4:56 PM 1) Consider the LinkedList class provided in the tutorial Write an instance method in the LinkedList class called isinincreasingrderO which returns a boolean indicating whether or not the data in the list is in increasing order. The method must be recursive. makes sense to have a directly recursive method that takes, as a parameter, an Item in the list and checks the remaining tems after it. You will need to check to make sure that there is at least one Item in the list belore caling the recursive method Below are some examples and the expected resuits. Use the SortedListTestProgram to test your results to make sure that your method works properly TRUE null TRUE nul TRUE null 14 FALSE 14 null 21 FALSE 10 null 21 23 TRUE null 98nul 23 76 Close Page 1 of 2 0 words + 100% Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


