Looking for help with this question! Thank you!
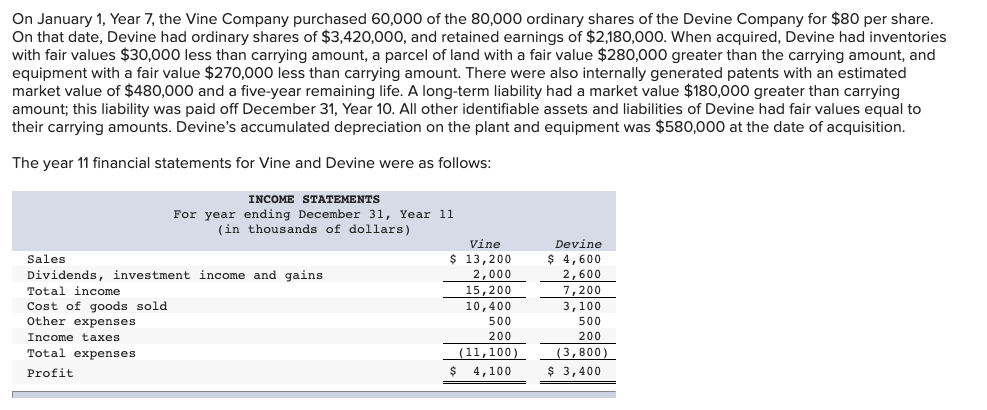
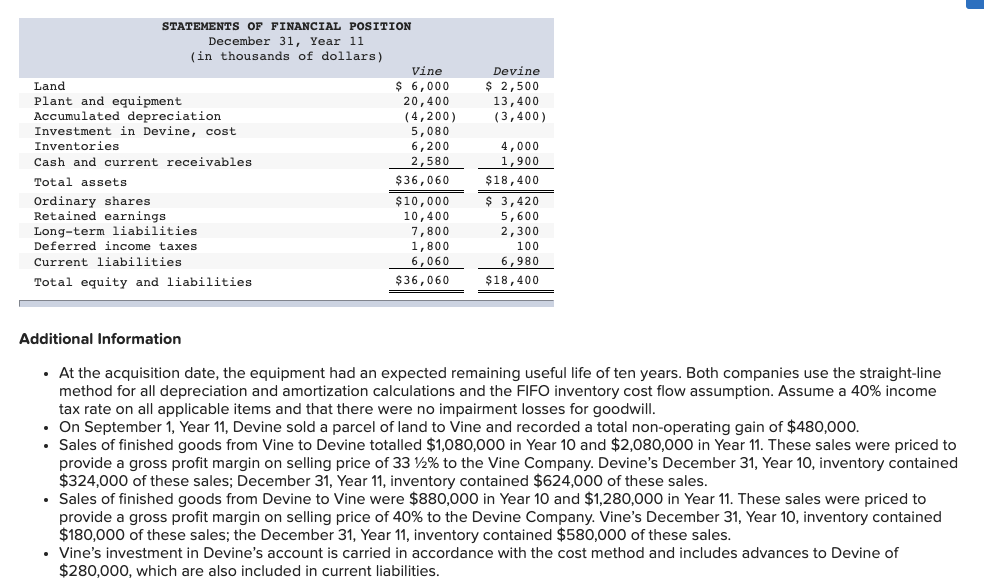
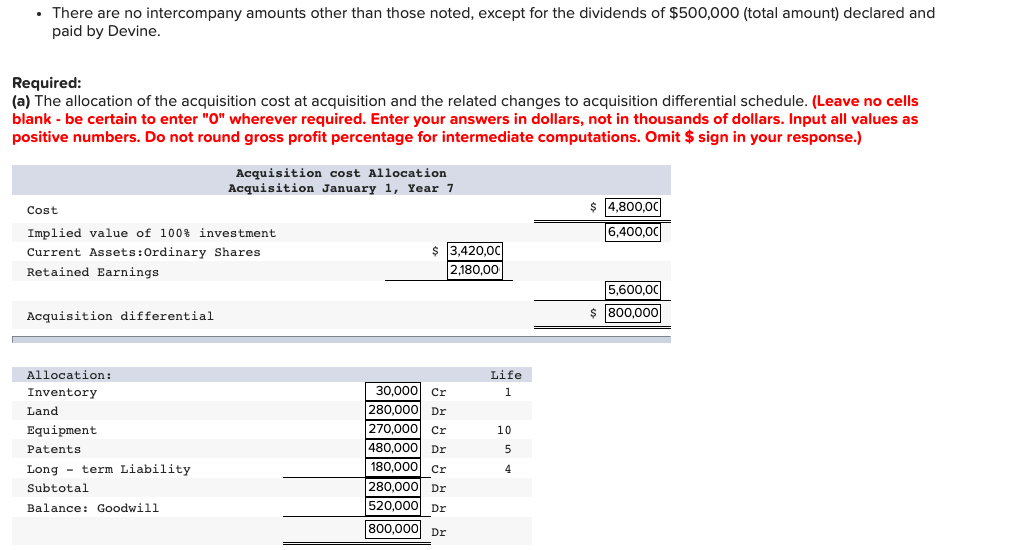
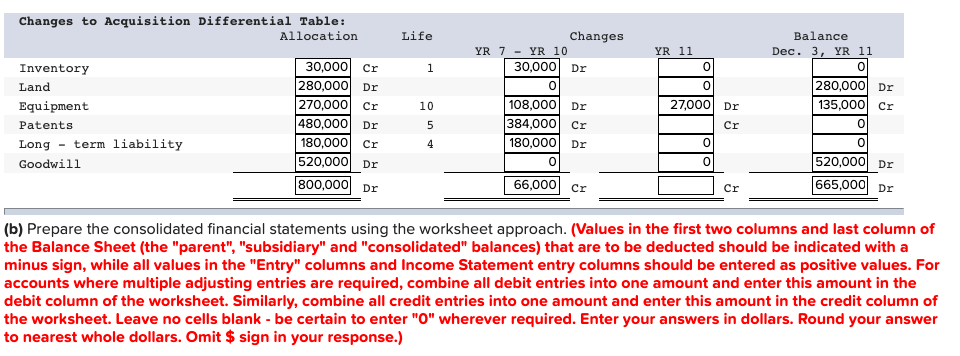
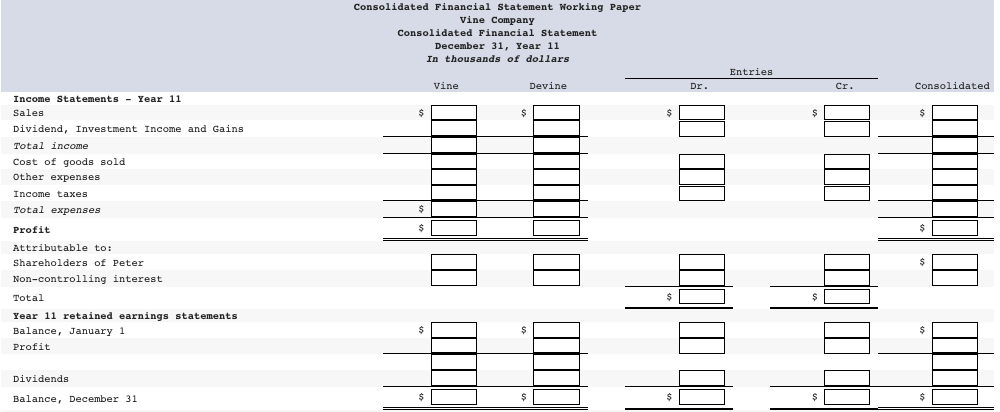
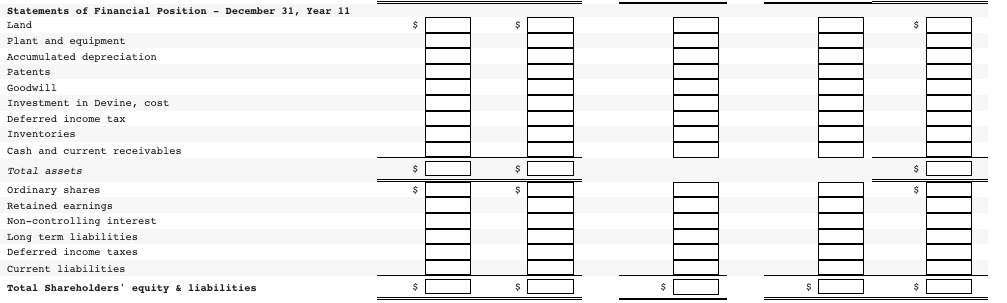
On January 1, Year 7, the Vine Company purchased 60,000 of the 80,000 ordinary shares of the Devine Company for $80 per share. On that date, Devine had ordinary shares of $3,420,000, and retained earnings of $2,180,000. When acquired, Devine had inventories with fair values $30,000 less than carrying amount, a parcel of land with a fair value $280,000 greater than the carrying amount, and equipment with a fair value $270,000 less than carrying amount. There were also internally generated patents with an estimated market value of $480,000 and a five-year remaining life. A long-term liability had a market value $180,000 greater than carrying amount; this liability was paid off December 31, Year 10. All other identifiable assets and liabilities of Devine had fair values equal to their carrying amounts. Devine's accumulated depreciation on the plant and equipment was $580,000 at the date of acquisition. The year 11 financial statements for Vine and Devine were as follows: Devine $ 4,600 2,600 INCOME STATEMENTS For year ending December 31, Year 11 (in thousands of dollars) Vine Sales $ 13,200 Dividends, investment income and gains 2,000 Total income 15,200 Cost of goods sold 10,400 Other expenses 500 Income taxes 200 Total expenses (11,100) Profit $ 4,100 7,200 3,100 500 200 (3,800) $ 3,400 Devine $ 2,500 13,400 (3,400) STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION December 31, Year 11 (in thousands of dollars) Vine Land $ 6,000 Plant and equipment 20,400 Accumulated depreciation (4,200) Investment in Devine, cost 5,080 Inventories 6,200 Cash and current receivables 2,580 Total assets $36,060 Ordinary shares $10,000 Retained earnings 10,400 Long-term liabilities 7,800 Deferred income taxes 1,800 Current liabilities 6,060 Total equity and liabilities $36,060 4,000 1,900 $18,400 $ 3,420 5,600 2,300 100 6,980 $18,400 Additional Information At the acquisition date, the equipment had an expected remaining useful life of ten years. Both companies use the straight-line method for all depreciation and amortization calculations and the FIFO inventory cost flow assumption. Assume a 40% income tax rate on all applicable items and that there were no impairment losses for goodwill. On September 1, Year 11, Devine sold a parcel of land to Vine and recorded a total non-operating gain of $480,000. Sales of finished goods from Vine to Devine totalled $1,080,000 in Year 10 and $2,080,000 in Year 11. These sales were priced to provide a gross profit margin on selling price of 33 12% to the Company. vine's Dece ber 31, Year 10, inventory contained $324,000 of these sales; December 31, Year 11, inventory contained $624,000 of these sales. Sales of finished goods from Devine to Vine were $880,000 in Year 10 and $1,280,000 in Year 11. These sales were priced to provide a gross profit margin on selling price of 40% to the Devine Company. Vine's December 31, Year 10, inventory contained $180,000 of these sales; the December 31, Year 11, inventory contained $580,000 of these sales. Vine's investment in Devine's account is carried in accordance with the cost method and includes advances to Devine of $280,000, which are also included in current liabilities. There are no intercompany amounts other than those noted, except for the dividends of $500,000 (total amount) declared and paid by Devine. Required: (a) The allocation of the acquisition cost at acquisition and the related changes to acquisition differential schedule. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "O" wherever required. Enter your answers in dollars, not in thousands of dollars. Input all values as positive numbers. Do not round gross profit percentage for intermediate computations. Omit $ sign in your response.) Acquisition cost Allocation Acquisition January 1, Year 7 Cost Implied value of 100% investment Current Assets: Ordinary Shares $ 3,420,00 Retained Earnings 2,180,00 $ 4,800,00 6,400,00 5,600,00) $ 800,000 Acquisition differential Life 1 10 Allocation: Inventory Land Equipment Patents Long - term Liability Subtotal Balance: Goodwill 5 30,000 Cr 280,000 Dr 270,000 Cr 480,000 Dr 180.000 Cr 280,000 Dr 520,000 Dr 800,000 Dr Changes to Acquisition Differential Table: Allocation Life YR 11 1 0 Inventory Land Equipment Patents Long - term liability Goodwill Changes YR 7 - YR 10 30,000 Dr 0 108,000 Dr 384,000 Cr 180,000 Dr 0 Balance Dec. 3, YR 11 0 280,000 Dr 135,000 cr 0 10 30,000 Cr 280,000 Dr 270,000 Cr 480,000 Dr 180,000 Cr 520,000 Dr 800,000 Dr 0 27,000 Dr Cr 5 4 0 0 0 520,000 Dr 665,000 Dr 66,000 cr Cr (b) Prepare the consolidated financial statements using the worksheet approach. (Values in the first two columns and last column of the Balance Sheet (the "parent", "subsidiary" and "consolidated" balances) that are to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign, while all values in the "Entry" columns and Income Statement entry columns should be entered as positive values. For accounts where multiple adjusting entries are required, combine all debit entries into one amount and enter this amount in the debit column of the worksheet. Similarly, combine all credit entries into one amount and enter this amount in the credit column of the worksheet. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required. Enter your answers in dollars. Round your answer to nearest whole dollars. Omit $ sign in your response.) Consolidated Financial Statement Working Paper Vine Company Consolidated Financial Statement December 31, Year 11 In thousands of dollars Entries Vine Devine Dr. Cr. Consolidated $ Income Statements - Year 11 Sales Dividend, Investment Income and Gains Total income Cost of goods sold Other expenses Income taxes Total expenses Profit Attributable to: Shareholders of Peter Non-controlling interest Total Year 11 retained earnings statements Balance, January 1 Profit $ $ $ Dividends Balance, December 31 $ $ Statements of Financial Position - December 31, Year 11 Land Plant and equipment Accumulated depreciation Patents Goodwill Investment in Devine, cost Deferred income tax Inventories Cash and current receivables Total assets $ $ Ordinary shares Retained earnings Non-controlling interest Long term liabilities Deferred income taxes Current liabilities Total Shareholders' equity & liabilities












