Question
Maggie's Magazines (MM) has straight nonconvertible bond that currently yield 9%. MM's stock sells for $22 per share, has an expected constant growth rate of
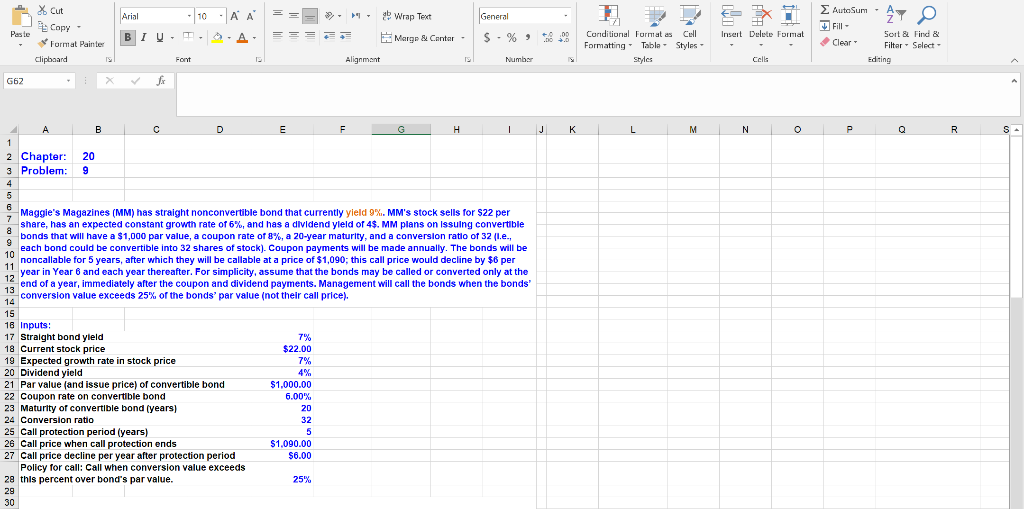
Maggie's Magazines (MM) has straight nonconvertible bond that currently yield 9%. MM's stock sells for $22 per share, has an expected constant growth rate of 6%, and has a dividend yield of 4$. MM plans on issuing convertible bonds that will have a $1,000 par value, a coupon rate of 8%, a 20-year maturity, and a conversion ratio of 32 (i.e., each bond could be convertible into 32 shares of stock). Coupon payments will be made annually. The bonds will be noncallable for 5 years, after which they will be callable at a price of $1,090; this call price would decline by $6 per year in Year 6 and each year thereafter. For simplicity, assume that the bonds may be called or converted only at the end of a year, immediately after the coupon and dividend payments. Management will call the bonds when the bonds conversion value exceeds 25% of the bonds par value (not their call price).
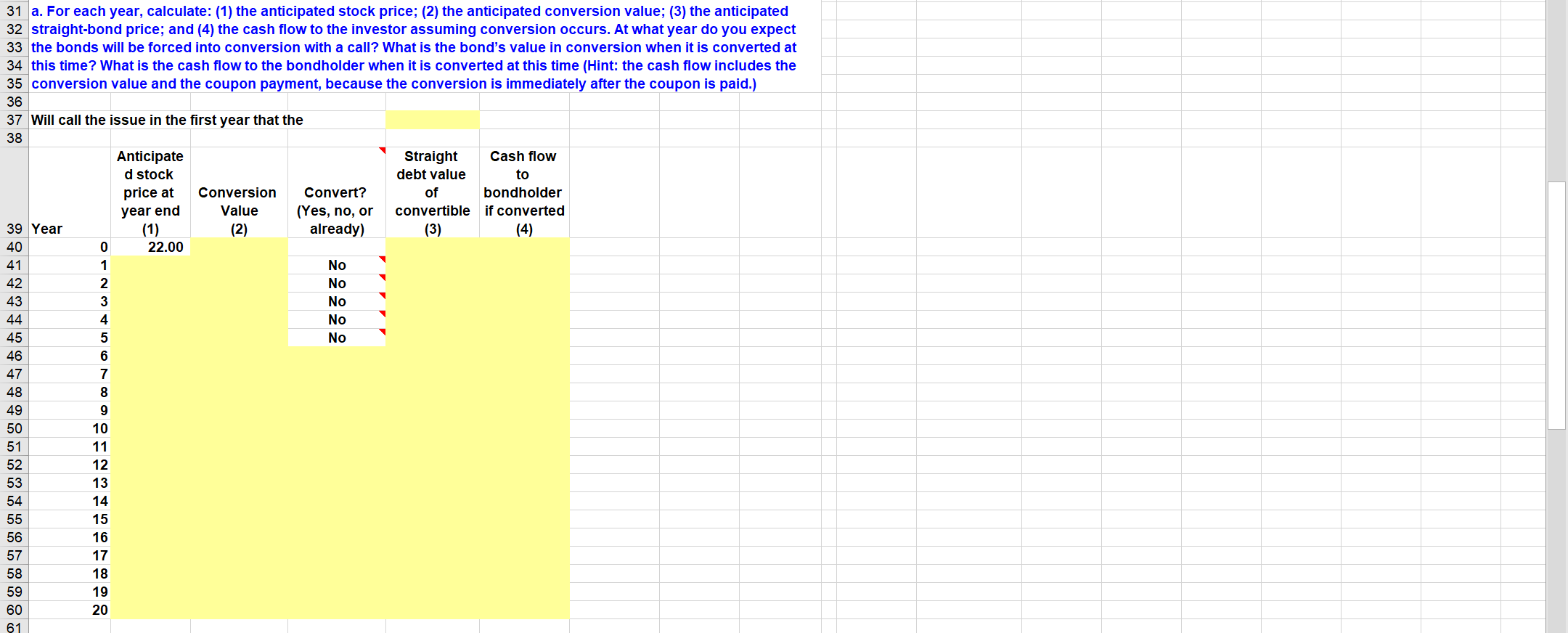
a. For each year, calculate: (1) the anticipated stock price; (2) the anticipated conversion value; (3) the anticipated straight-bond price; and (4) the cash flow to the investor assuming conversion occurs. At what year do you expect the bonds will be forced into conversion with a call? What is the bonds value in conversion when it is converted at this time? What is the cash flow to the bondholder when it is converted at this time (Hint: the cash flow includes the conversion value and the coupon payment, because the conversion is immediately after the coupon is paid.)
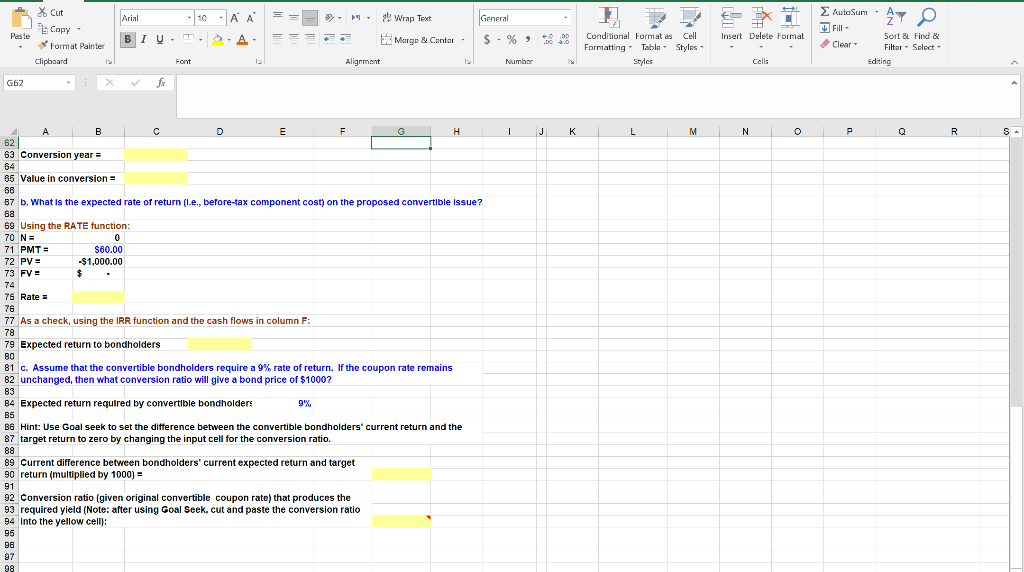
b. What is the expected rate of return (i.e., before-tax component cost) on the proposed convertible issue?
c. Assume that the convertible bondholders require a 9% rate of return. If the coupon rate remains unchanged, then what conversion ratio will give a bond price of $1000?
((( Please provide the formulas for each Cell ))))
Arial - 10 == ab Wrap Text General Paste * Cut Copy Format Painter Clipboard BIV- A Marge & Centar - $ . % 6.0 Insert Delute Format Conditional Formatas Cell Formatting - Table Styles - Styles AutoSum - Fill- Sort & Find & Clear Filter - Select - Editing Font Alignment Numby Cells G62 Fx J L M N 0 P Q R S B D E F G H 1 2 Chapter: 20 3 Problem: 9 4 5 6 Maggie's Magazines (MM) has straight nonconvertible bond that currently yield 9%. MM's stock sells for $22 per 7 share, has an expected constant growth rate of 6%, and has a dividend yleld of 4$. MM plans on Issuing convertible 8 bonds that will have a $1,000 par value, a coupon rate of 8%, a 20-year maturity, and a conversion ratio of 32 (1.e., 9 each bond could be convertible into 32 shares of stock). Coupon payments will be made annually. The bonds will be 10 noncallable for 5 years, after which they will be callable at a price of $1,090; this call price would decline by $8 per 11 year in Year 6 and each year thereafter. For simplicity, assume that the bonds may be called or converted only at the 12 end of a year, immediately after the coupon and dividend payments. Management will call the bonds when the bonds 13 conversion value exceeds 25% of the bonds' par value (not their call price). 14 15 18 Inputs: 17 Straight bond yield 7% 18 Current stock price $22.00 $ 19 Expected growth rate in stock price 20 Dividend yield 21 Par value (and issue price) of convertible bond $1,000.00 22 Coupon rate on convertible bond 6.00% 23 Maturity of convertible bond (years) 20 24 Conversion ratio 32 25 Call protection period (years) 5 26 Call price when call protection ends $1.090.00 27 Call price decline per year after protection period $6.00 Policy for call: Call when conversion value exceeds 28 this percent over bond's par value. 25% 29 30 31 a. For each year, calculate: (1) the anticipated stock price; (2) the anticipated conversion value; (3) the anticipated 32 straight-bond price; and (4) the cash flow to the investor assuming conversion occurs. At what year do you expect 33 the bonds will be forced into conversion with a call? What is the bond's value in conversion when it is converted at 34 this time? What is the cash flow to the bondholder when it is converted at this time (Hint: the cash flow includes the 35 conversion value and the coupon payment, because the conversion is immediately after the coupon is paid.) 36 37 Will call the issue in the first year that the 38 Anticipate Straight Cash flow d stock debt value to price at Conversion Convert? of bondholder year end Value (Yes, no, or convertible if converted 39 Year (1) (2) already) (3) (4) 40 0 22.00 41 1 No 42 2 No 43 3 No 44 4 No 45 5 No 46 6 47 7 48 8 49 9 50 10 51 11 52 12 53 13 54 14 55 15 56 16 57 17 58 18 59 19 60 20 61 == Arial - 10 General X Cut Copy - Format Painter Clipboard AA A - 1-2 Wrap Text Margo & Contar- Peste BIU- = = = $ - % ) Insert Delete Format Conditional Format as Cell Formatting - Table - Styles Styles AutoSum Fill- - Sort & Find & Clear Filtar - Select - Editing .00.0 Font Alignment Number Cells G62 fa J L M M N o Q R S A B D E F G H 62 63 Conversion year 64 85 Value in conversion 88 87 b. What is the expected rate of return (l.e., before-tax component cost) on the proposed convertible Issue? B8 69 Using the RATE function: 70 N= 0 71 PMT = $60.00 72 PV = -$1,000.00 73 FV = $ 74 75 Rate = 76 77 As a check, using the IRR function and the cash flows in column F 78 79 Expected return to bondholders 81 c. Assume that the convertible bondholders require a 9% rate of return. If the coupon rate remains 82 unchanged, then what conversion ratio will give a bond price of $1000? 83 B4 Expected return required by convertible bondholders 9 9% B5 86 Hint: Use Goal seek to set the difference between the convertible bondholders' current return and the 87 target return to zero by changing the input cell for the conversion ratio. 88 89 Current difference between bondholders' current expected return and target 90 return (multiplied by 1000) = 91 92 Conversion ratio (given original convertible coupon rate) that produces the 93 required yield (Note: after using Goal Seek, cut and paste the conversion ratio 94 Into the yellow cell): 95 96 97 98 Arial - 10 == ab Wrap Text General Paste * Cut Copy Format Painter Clipboard BIV- A Marge & Centar - $ . % 6.0 Insert Delute Format Conditional Formatas Cell Formatting - Table Styles - Styles AutoSum - Fill- Sort & Find & Clear Filter - Select - Editing Font Alignment Numby Cells G62 Fx J L M N 0 P Q R S B D E F G H 1 2 Chapter: 20 3 Problem: 9 4 5 6 Maggie's Magazines (MM) has straight nonconvertible bond that currently yield 9%. MM's stock sells for $22 per 7 share, has an expected constant growth rate of 6%, and has a dividend yleld of 4$. MM plans on Issuing convertible 8 bonds that will have a $1,000 par value, a coupon rate of 8%, a 20-year maturity, and a conversion ratio of 32 (1.e., 9 each bond could be convertible into 32 shares of stock). Coupon payments will be made annually. The bonds will be 10 noncallable for 5 years, after which they will be callable at a price of $1,090; this call price would decline by $8 per 11 year in Year 6 and each year thereafter. For simplicity, assume that the bonds may be called or converted only at the 12 end of a year, immediately after the coupon and dividend payments. Management will call the bonds when the bonds 13 conversion value exceeds 25% of the bonds' par value (not their call price). 14 15 18 Inputs: 17 Straight bond yield 7% 18 Current stock price $22.00 $ 19 Expected growth rate in stock price 20 Dividend yield 21 Par value (and issue price) of convertible bond $1,000.00 22 Coupon rate on convertible bond 6.00% 23 Maturity of convertible bond (years) 20 24 Conversion ratio 32 25 Call protection period (years) 5 26 Call price when call protection ends $1.090.00 27 Call price decline per year after protection period $6.00 Policy for call: Call when conversion value exceeds 28 this percent over bond's par value. 25% 29 30 31 a. For each year, calculate: (1) the anticipated stock price; (2) the anticipated conversion value; (3) the anticipated 32 straight-bond price; and (4) the cash flow to the investor assuming conversion occurs. At what year do you expect 33 the bonds will be forced into conversion with a call? What is the bond's value in conversion when it is converted at 34 this time? What is the cash flow to the bondholder when it is converted at this time (Hint: the cash flow includes the 35 conversion value and the coupon payment, because the conversion is immediately after the coupon is paid.) 36 37 Will call the issue in the first year that the 38 Anticipate Straight Cash flow d stock debt value to price at Conversion Convert? of bondholder year end Value (Yes, no, or convertible if converted 39 Year (1) (2) already) (3) (4) 40 0 22.00 41 1 No 42 2 No 43 3 No 44 4 No 45 5 No 46 6 47 7 48 8 49 9 50 10 51 11 52 12 53 13 54 14 55 15 56 16 57 17 58 18 59 19 60 20 61 == Arial - 10 General X Cut Copy - Format Painter Clipboard AA A - 1-2 Wrap Text Margo & Contar- Peste BIU- = = = $ - % ) Insert Delete Format Conditional Format as Cell Formatting - Table - Styles Styles AutoSum Fill- - Sort & Find & Clear Filtar - Select - Editing .00.0 Font Alignment Number Cells G62 fa J L M M N o Q R S A B D E F G H 62 63 Conversion year 64 85 Value in conversion 88 87 b. What is the expected rate of return (l.e., before-tax component cost) on the proposed convertible Issue? B8 69 Using the RATE function: 70 N= 0 71 PMT = $60.00 72 PV = -$1,000.00 73 FV = $ 74 75 Rate = 76 77 As a check, using the IRR function and the cash flows in column F 78 79 Expected return to bondholders 81 c. Assume that the convertible bondholders require a 9% rate of return. If the coupon rate remains 82 unchanged, then what conversion ratio will give a bond price of $1000? 83 B4 Expected return required by convertible bondholders 9 9% B5 86 Hint: Use Goal seek to set the difference between the convertible bondholders' current return and the 87 target return to zero by changing the input cell for the conversion ratio. 88 89 Current difference between bondholders' current expected return and target 90 return (multiplied by 1000) = 91 92 Conversion ratio (given original convertible coupon rate) that produces the 93 required yield (Note: after using Goal Seek, cut and paste the conversion ratio 94 Into the yellow cell): 95 96 97 98
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


