Question: Main Driver File: #define INSTRUCTOR_FILE #ifdef INSTRUCTOR_FILE #include #include extern const int DIM0, DIM1, DIM2, DIM3; extern float ***pointerArray4D[]; int main() { int value; //

Main Driver File:
#define INSTRUCTOR_FILE
#ifdef INSTRUCTOR_FILE
#include
#include
extern const int DIM0, DIM1, DIM2, DIM3;
extern float ***pointerArray4D[];
int main()
{
int value;
// Store all values.
value = 0;
for (int ix0 = 0; ix0
for (int ix1 = 0; ix1
for (int ix2 = 0; ix2
for (int ix3 = 0; ix3
pointerArray4D[ix0][ix1][ix2][ix3] = float(value++);
// Test all stored values.
value = 0;
for (int ix0 = 0; ix0
for (int ix1 = 0; ix1
for (int ix2 = 0; ix2
for (int ix3 = 0; ix3
if (pointerArray4D[ix0][ix1][ix2][ix3] != value++)
{
std::cerr ![int DIM0, DIM1, DIM2, DIM3; extern float ***pointerArray4D[]; int main() { int](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3a8efdbffc_52766f3a8ef67670.jpg)
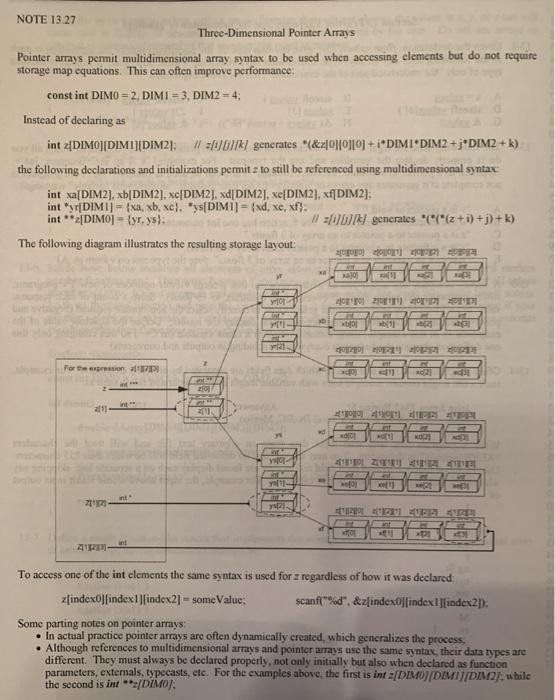 C2A4E3 (6 points - C++ Program) Exclude any existing source code files that may already be in your IDE project and add a new one. naming it C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp. Also add instructor-supplied source code file C2A4E3_main-Driver.cpp. Do not write a main function! main already exists in the instructor-supplied file and it will use the code you write. File C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp must contain a 4-dimensional pointer array of type float named pointerArray4D that you create using the method illustrated in notes 13.26 and 13.27. Specify the dimension sizes by defining identifiers DIMO, DIM1, DIM2, and DIM3 (left-to-right), which must have values of 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. pointerArray4D must be accessible to any other file (e.g., the instructor-supplied source code file) while the names of any other arrays must only be accessible within file C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp (note 5.14). Do not write any functions or macros or create any files other than C2A4E3 pointer Array4D.cpp. Submitting your solution Send both source code files to the assignment checker with the subject line C2A4E3_ID, where ID is your 9-character UCSD student ID. See the course document titled "How to Prepare and Submit Assignments" for additional exercise formatting, submission, and assignment checker requirements. Hints: There is no quick and easy way to fully test a pointer array. As a minimal test a different value can be stored into each element then read back to verify that no memory violations occur and that each element contains its original value. However, this does not guarantee that more memory than necessary hasn't been used or that an out-of-bounds access hasn'i occurred. NOTE 13.26 Multidimensional Arrays vs. Pointer Arrays The indices used in a multidimensional array reference are converted to a pointer to the desired element by what is known as a "storage map equation". Due to the multiplication operations these equations require, program efficiency can suffer. In addition, some environments may be unable to allocate the large contiguous block of memory required for large arrays, even though the total storage needed may be available in smaller blocks To avoid these problems, pointer arrays (arrays of pointers) may be used. Instead of storage map equations pointer arrays use multiple levels of indirection that often improve efficiency. The tradeoffs are that pointer arrays require somewhat more storage, limit data caching for the array, and prevent some compiler optimizations. A ragged array is a special case of a pointer array The following examples illustrate multidimensional array versus pointer array declaration syntax for a specific case. Although differing in declaration syntax, access syntar is identical for both types. Note that the generated code" for each multidimensional array is its storage map equation Type of Array Declaration(s) Vuln References Become Code Generated multidimensional int 34 int a[4], [4], [41. int V 31 - {a,b,c): (10 + 1) =*f*(y + i) + i)(&[0][0] + 1*4+1) same as above "("(y + i) +i) pointer The first example creates the true multidimensional array y containing 12 ints and allocated as a contiguous block of memory as shown by the connection from the end of one row to the beginning of the next YO! int y101 ind YON) int YO2) v031 Y II ind yo Y1001 int 11121 Yp 1 1 7121 int 71200) inc 11211 y[212] 712131 The second example creates the int arrays a, b, and c, and pointer array y. The 3 elements of y are initialized to point to the first element of the corresponding int arrays. Although each of the three int arrays occupies its own contiguous memory block, the individual blocks may not be adjacent to each other. V100 11 VIOLIZI int int 10 For the expression: 121 Y14 10 M b 111 YA YRI 19 YTI VIZIRI [1] 21 int YRIR NOTE 13.27 Three-Dimensional Pointer Arrays Pointer arrays permit multidimensional array syntax to be used when accessing elements but do not require storage map equations. This can often improve performance: const int DIMO = 2, DIMI = 3, DIM2 = 4; Instead of declaring as int z[DIMO]DIMI]IDIM2); //=0/07/k/ generates *(&z[0]0]0+ i*DIMI DIM2 + j*DIM2 + k) the following declarations and initializations permitz to still be referenced using multidimensional syntax int sa[DIM2], xb[DIM21, xe[DIM2), xd[DIM2], xe[DIM2), xf[DIM2]:. int * [DIM1] = {xa, xb, xe}, "s[DIM1] = {xd, xe, xf}. int **2|DIMO] - Cyrys): il 2007 generates "C"("(z+i) +j)+k) The following diagram illustrates the resulting storage layout: 2010 2009 al YO or ZU TS For the express ce 20 alt ti yu 27 int 212 ?! 2011 ITA To access one of the int elements the same syntax is used for z regardless of how it was declared: x[index][index 1|findex2] = someValue: scanf("%d", &z[index][index][index2D. Some parting notes on pointer arrays In actual practice pointer arrays are often dynamically created, which generalizes the process . Although references to multidimensional arrays and pointer arrays use the same syntax, their data types are different. They must always be declared properly, not only initially but also when declared as function parameters, externals, typecasts, etc. For the examples above, the first is int=[DIMO)/DIMIJ/DIM2), while the second is int **/DIMOJ
C2A4E3 (6 points - C++ Program) Exclude any existing source code files that may already be in your IDE project and add a new one. naming it C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp. Also add instructor-supplied source code file C2A4E3_main-Driver.cpp. Do not write a main function! main already exists in the instructor-supplied file and it will use the code you write. File C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp must contain a 4-dimensional pointer array of type float named pointerArray4D that you create using the method illustrated in notes 13.26 and 13.27. Specify the dimension sizes by defining identifiers DIMO, DIM1, DIM2, and DIM3 (left-to-right), which must have values of 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively. pointerArray4D must be accessible to any other file (e.g., the instructor-supplied source code file) while the names of any other arrays must only be accessible within file C2A4E3_pointerArray4D.cpp (note 5.14). Do not write any functions or macros or create any files other than C2A4E3 pointer Array4D.cpp. Submitting your solution Send both source code files to the assignment checker with the subject line C2A4E3_ID, where ID is your 9-character UCSD student ID. See the course document titled "How to Prepare and Submit Assignments" for additional exercise formatting, submission, and assignment checker requirements. Hints: There is no quick and easy way to fully test a pointer array. As a minimal test a different value can be stored into each element then read back to verify that no memory violations occur and that each element contains its original value. However, this does not guarantee that more memory than necessary hasn't been used or that an out-of-bounds access hasn'i occurred. NOTE 13.26 Multidimensional Arrays vs. Pointer Arrays The indices used in a multidimensional array reference are converted to a pointer to the desired element by what is known as a "storage map equation". Due to the multiplication operations these equations require, program efficiency can suffer. In addition, some environments may be unable to allocate the large contiguous block of memory required for large arrays, even though the total storage needed may be available in smaller blocks To avoid these problems, pointer arrays (arrays of pointers) may be used. Instead of storage map equations pointer arrays use multiple levels of indirection that often improve efficiency. The tradeoffs are that pointer arrays require somewhat more storage, limit data caching for the array, and prevent some compiler optimizations. A ragged array is a special case of a pointer array The following examples illustrate multidimensional array versus pointer array declaration syntax for a specific case. Although differing in declaration syntax, access syntar is identical for both types. Note that the generated code" for each multidimensional array is its storage map equation Type of Array Declaration(s) Vuln References Become Code Generated multidimensional int 34 int a[4], [4], [41. int V 31 - {a,b,c): (10 + 1) =*f*(y + i) + i)(&[0][0] + 1*4+1) same as above "("(y + i) +i) pointer The first example creates the true multidimensional array y containing 12 ints and allocated as a contiguous block of memory as shown by the connection from the end of one row to the beginning of the next YO! int y101 ind YON) int YO2) v031 Y II ind yo Y1001 int 11121 Yp 1 1 7121 int 71200) inc 11211 y[212] 712131 The second example creates the int arrays a, b, and c, and pointer array y. The 3 elements of y are initialized to point to the first element of the corresponding int arrays. Although each of the three int arrays occupies its own contiguous memory block, the individual blocks may not be adjacent to each other. V100 11 VIOLIZI int int 10 For the expression: 121 Y14 10 M b 111 YA YRI 19 YTI VIZIRI [1] 21 int YRIR NOTE 13.27 Three-Dimensional Pointer Arrays Pointer arrays permit multidimensional array syntax to be used when accessing elements but do not require storage map equations. This can often improve performance: const int DIMO = 2, DIMI = 3, DIM2 = 4; Instead of declaring as int z[DIMO]DIMI]IDIM2); //=0/07/k/ generates *(&z[0]0]0+ i*DIMI DIM2 + j*DIM2 + k) the following declarations and initializations permitz to still be referenced using multidimensional syntax int sa[DIM2], xb[DIM21, xe[DIM2), xd[DIM2], xe[DIM2), xf[DIM2]:. int * [DIM1] = {xa, xb, xe}, "s[DIM1] = {xd, xe, xf}. int **2|DIMO] - Cyrys): il 2007 generates "C"("(z+i) +j)+k) The following diagram illustrates the resulting storage layout: 2010 2009 al YO or ZU TS For the express ce 20 alt ti yu 27 int 212 ?! 2011 ITA To access one of the int elements the same syntax is used for z regardless of how it was declared: x[index][index 1|findex2] = someValue: scanf("%d", &z[index][index][index2D. Some parting notes on pointer arrays In actual practice pointer arrays are often dynamically created, which generalizes the process . Although references to multidimensional arrays and pointer arrays use the same syntax, their data types are different. They must always be declared properly, not only initially but also when declared as function parameters, externals, typecasts, etc. For the examples above, the first is int=[DIMO)/DIMIJ/DIM2), while the second is int **/DIMOJ
std::cerr
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::cout
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
![int DIM0, DIM1, DIM2, DIM3; extern float ***pointerArray4D[]; int main() { int](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3a8efdbffc_52766f3a8ef67670.jpg)

notes 13.26 and 13.27 added. That is all the information i have
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


