Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
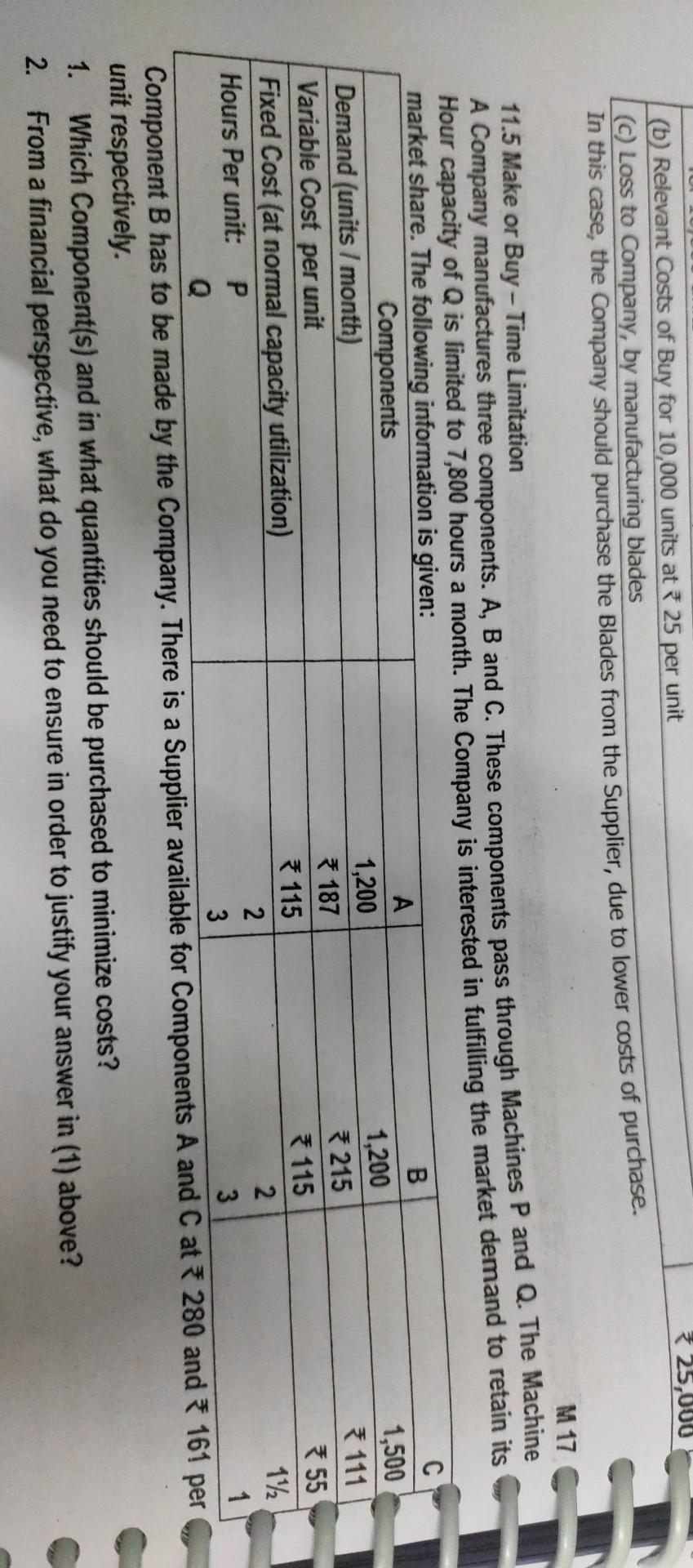
make project report on all * 25,000 (b) Relevant Costs of Buy for 10,000 units at 25 per unit (C) Loss to Company, by manufacturing
make project report on all
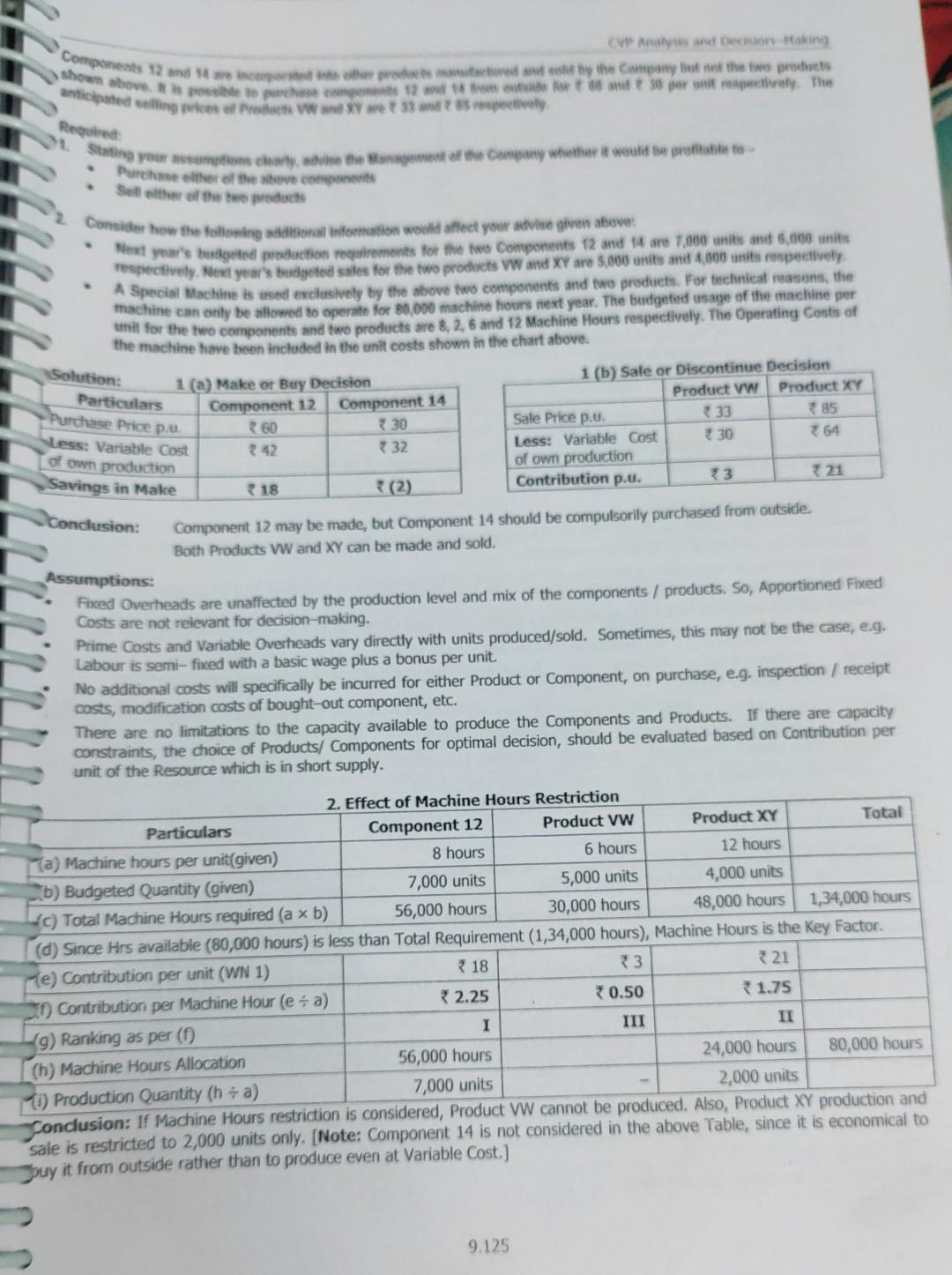
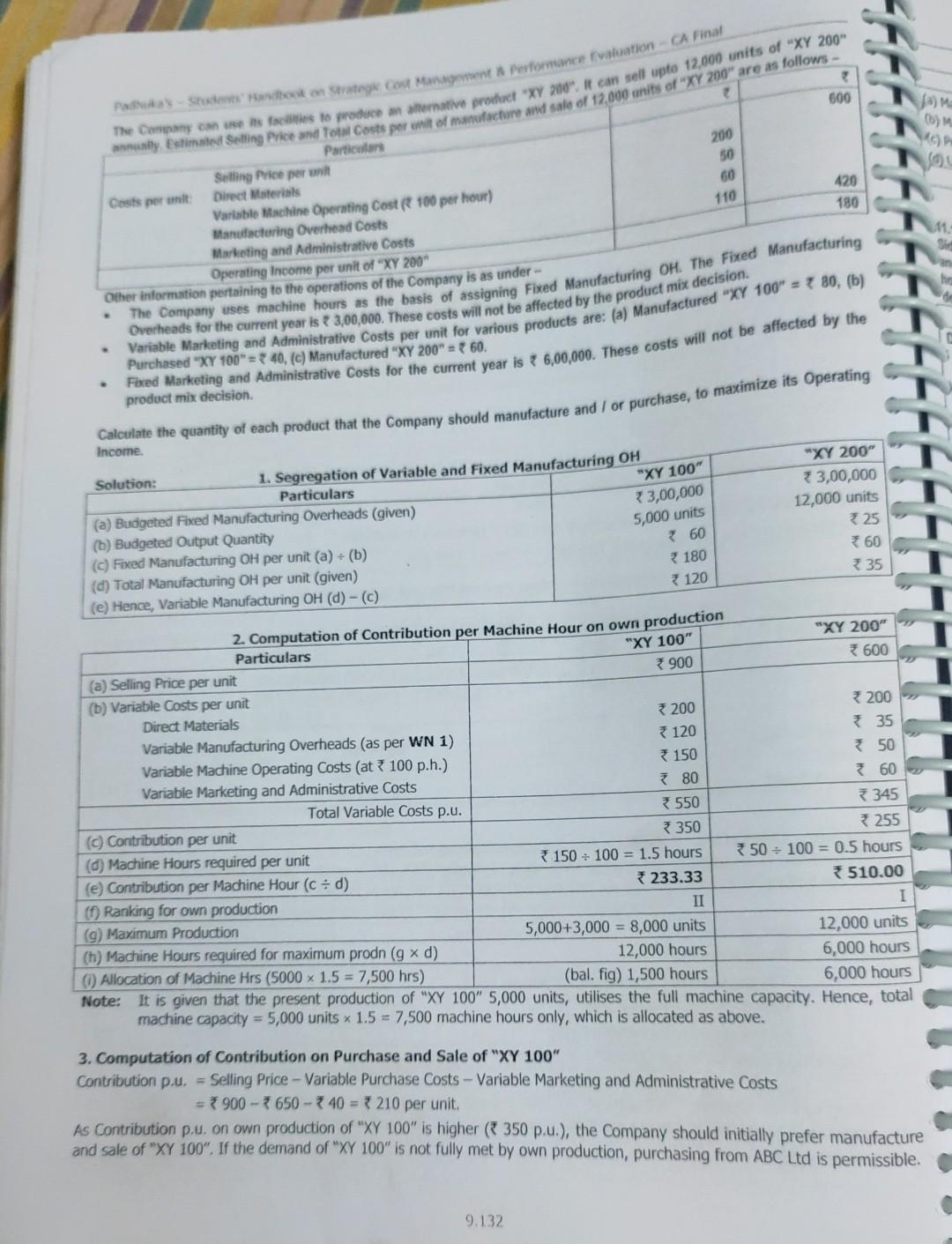
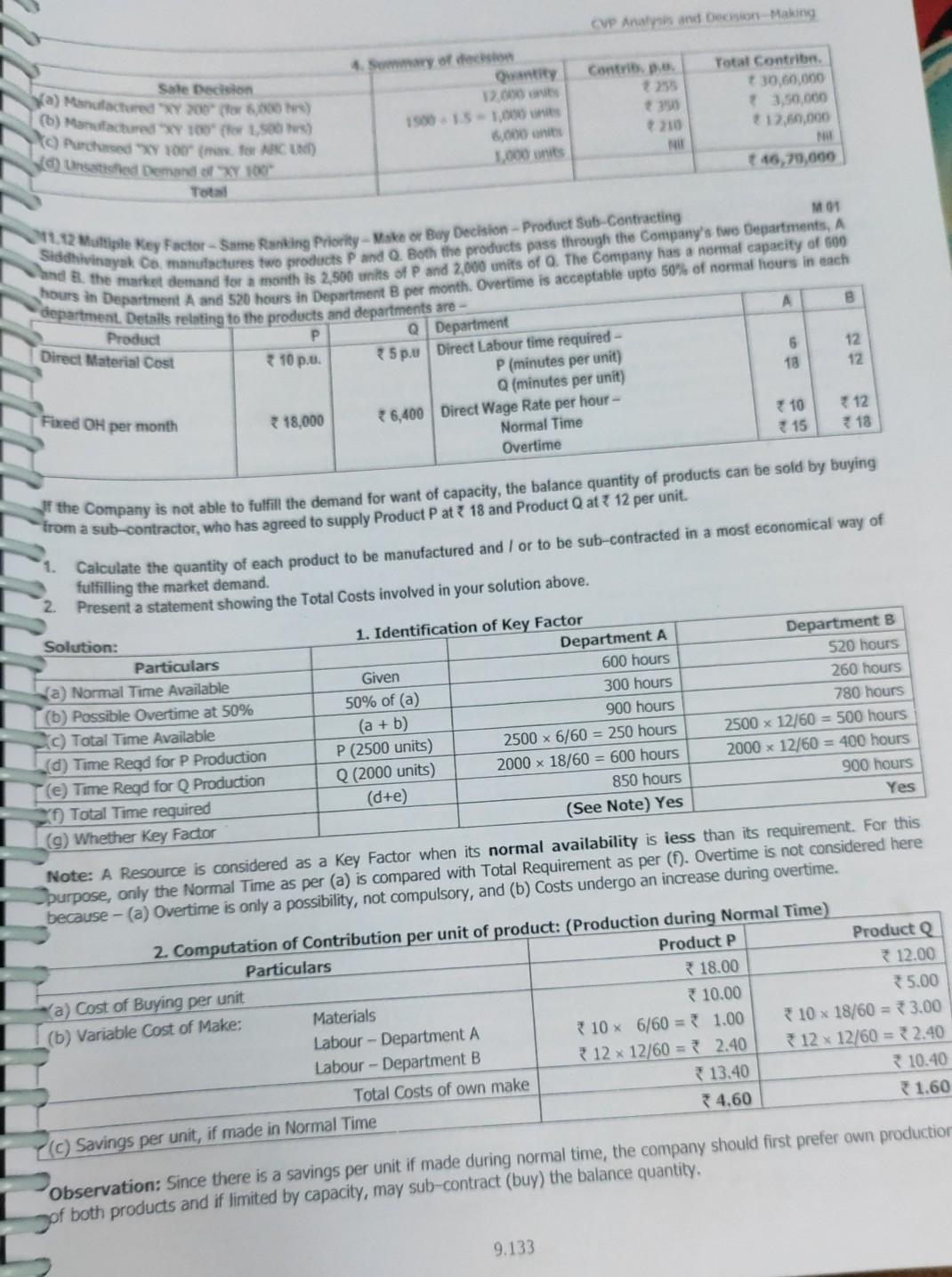
* 25,000 (b) Relevant Costs of Buy for 10,000 units at 25 per unit (C) Loss to Company, by manufacturing blades In this case, the company should purchase the Blades from the Supplier, due to lower costs of purchase. M 17 11.5 Make or Buy-Time Limitation A Company manufactures three components. A, B and C. These components pass through Machines P and Q. The Machine Hour capacity of Q is limited to 7,800 hours a month. The Company is interested in fulfilling the market demand to retain its market share. The following information is given: Components B A 1,500 Demand (units / month) 1,200 1,200 187 Variable Cost per unit * 111 215 115 Fixed Cost (at normal capacity utilization) 55 115 Hours Per unit: P 2 2 1/2 3 3 1 Component B has to be made by the Company. There is a Supplier available for Components A and C at 280 and 161 per unit respectively. 1. Which Component(s) and in what quantities should be purchased to minimize costs? 2. From a financial perspective, what do you need to ensure in order to justify your answer in (1) above? Analyseon Making Components 12 and 14 the Company but at the two products shown above. po prehrerepet. The antiche sings of Pro WXY we? 335 Required Starting your assumptions eksway, and to the Management of the Company whistor te would be prostate to - Purchase of these components Selle of two products Consider how the following stational information would atteet your suwwe given above: Meet your's bestigated frostinction regstrements for the two components 12 and 14 are 7,000 uniks and 5,000 units respectively. Next year's budgeted sales for the two products VW and XY are 5,000 units and 4,000 units respectively A Special Machine is used exclusively by the above two components and two products. For technical reasons, the machine can only be sllowed to operate for 80,000 machine hours next year. The budgeted usage of the machine per unit for the two components and two products are 8, 2, 6 and 12 Machine Hours respectively. The Operating costs of the machine have been included in the unit costs shown in the chart above. 1(a) Make or Buy Decision 1 (b) Sale or Discontinue Decision Component 12 Component 14 Product VW Product XY 360 30 Sale Price p.u. 33 85 42 732 Less: Variable Cost * 30 264 of own production 18 (2) Contribution p.u. 3 21 Solution: Particulars Purchase Price pu Less: Variable Cost of own production Savings in Make Condusion: Component 12 may be made, but Component 14 should be compulsorily purchased from outside. Both Products WW and XY can be made and sold. Assumptions: Fixed Overheads are unaffected by the production level and mix of the components/products. So, Apportioned Fixed Costs are not relevant for decision-making. Prime Costs and Variable Overheads vary directly with units produced/sold. Sometimes, this may not be the case, e.g. Labour is semi-fixed with a basic wage plus a bonus per unit. No additional costs will specifically be incurred for either Product or Component, on purchase, e.g. inspection / receipt costs, modification costs of bought-out component, etc. There are no limitations to the capacity available to produce the Components and Products. If there are capacity constraints, the choice of Products/ Components for optimal decision, should be evaluated based on Contribution per unit of the Resource which is in short supply. * 18 2. Effect of Machine Hours Restriction Particulars Component 12 Product VW Product XY Total a) Machine hours per unit(given) 8 hours 6 hours 12 hours b) Budgeted Quantity (given) 7,000 units 5,000 units 4,000 units (c) Total Machine Hours required (a x b) 56,000 hours 30,000 hours 48,000 hours 1,34,000 hours (d) Since Hrs available (80,000 hours) is less than Total Requirement (1,34,000 hours), Machine Hours is the Key Factor re) Contribution per unit (WN 1) 73 321 Contribution per Machine Hour (e + a) 32.25 30.50 1.75 (9) Ranking as per (0) I III II (h) Machine Hours Allocation 56,000 hours 24,000 hours 80,000 hours 1) Production Quantity (h+ a) 7,000 units 2,000 units Conclusion: If Machine Hours restriction is considered, Product VW cannot be produced. Also, Product XY production and Sale is restricted to 2,000 units only. (Note: Component 14 is not considered in the above Table, since it is economical to buy it from outside rather than to produce even at Variable Cost.) 9.125 600 Shadon Strateg Content Performance Evaluation CA Final The Canyon is to producerative product "XY 200". I can sell upto 12,000 units of "XY 200" y Estimated Selling Price and To Costs per of manufacture and sale of 12,000 units of "XY 200" are as follows - 200 50 60 110 420 180 Particulars Selling Price per i Costs per mit Direct Materials Variable Machine Operating cost R100 per hour) Manufacturing Overhead Costs Marketing and Administrativo Costs Operating Income per unit of "XY 200" Other information pertaining to the operations of the Company is as under- The Company uses machine hours as the basis of assigning Fixed Manufacturing OH. The Fixed Manufacturing Overheads for the current year is 80, (b) Fixed Marketing and Administrative Costs for the current year is 6,00,000. These costs will not be affected by the product mix decision Calculate the quantity of each product that the Company should manufacture and / or purchase, to maximize its Operating "XY 100" 73,00,000 5,000 units 60 180 *120 Income "XY 200" Solution: 1. Segregation of Variable and Fixed Manufacturing OH Particulars * 3,00,000 (a) Budgeted Fixed Manufacturing Overheads (given) 12,000 units (b) Budgeted Output Quantity 325 (c) Fixed Manufacturing OH per unit (a) (b) 360 (d) Total Manufacturing OH per unit (given) 35 (e) Hence, Variable Manufacturing OH (d) -(0) 2. Computation of Contribution per Machine Hour on own production "XY 200" Particulars "XY 100" 900 3600 (a) Selling Price per unit (b) Variable costs per unit * 200 200 Direct Materials Variable Manufacturing Overheads (as per WN 1) 120 35 Variable Machine Operating costs (at 100 p.h.) * 150 50 Variable Marketing and Administrative Costs 80 360 Total Variable Costs p.u. 3550 345 (c) Contribution per unit 350 * 255 (d) Machine Hours required per unit 150 - 100 = 1.5 hours 750 - 100 = 0.5 hours (e) Contribution per Machine Hour (c + d) 233.33 * 510.00 Ranking for own production II (g) Maximum Production 5,000+3,000 = 8,000 units 12,000 units (h) Machine Hours required for maximum prodn (g x d) 12,000 hours 6,000 hours (1) Allocation of Machine Hrs (5000 1.5 = 7,500 hrs) (bal. fig) 1,500 hours Note: It is given that the present production of "XY 100" 5,000 units, utilises the full machine capacity. Hence, total 6,000 hours machine capacity = 5,000 units X 1.5 = 7,500 machine hours only, which is allocated as above. 3. Computation of Contribution on Purchase and Sale of "XY 100" Contribution p.u. = Selling Price - Variable Purchase Costs - Variable Marketing and Administrative Costs = 900 - 3650 - 340 = 210 per unit. As Contribution p.u. on own production of "XY 100" is higher (* 350 p.u.), the Company should initially prefer manufacture and sale of "XY 100". If the demand of "XY 100" is not fully met by own production, purchasing from ABC Ltd is permissible. 9.132 CV Analysis and Decision Making 4. Sway of decision Contrib. p. Sate Decision a) Manufactured X200" (for 6,000) (6) Manufactured 10 to 1.500) Purchased "100 (AC) NO Unsatisfied Demand of X 100 Total Contrib +30.60,000 13,50.000 12,60,000 12.000 1500-1.5 -1.000 nits 6,000 units 1,000 units 30 210 NII 46,70,000 Tot 1.12 Multiple Key Factor - Same Ranking Priority - Make or Buy Decision - Product Sub-Contracting Product Direct Material Cost 12 12 *10 p.. Fored OH per month hours, the market demand fores for free on and Bondine, o inces or a five company has an emas capacity of som tws Departments, A hours in Department A and 120 hours in sepertinente e per more to cover fine fis acceptable upto so% of normal hours in each department. Details relating to the products and departments are -- Q Department 5. Direct Labour time required - P (minutes per unit) 5 Q(minutes per unit) 18 18,000 6,400 Direct Wage Rate per hour - Normal Time 710 * 12 Overtime 15 18 of the Company is not able to fulfill the demand for want of capacity, the balance quantity of products can be sold by buying from a sub-contractor, who has agreed to supply Product PatStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


