Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Manufacturing material and process for guitars. Prepare a manucfacturing process of guitars, complete each table with the indication under the page of cost characteristics and
Manufacturing material and process for guitars.

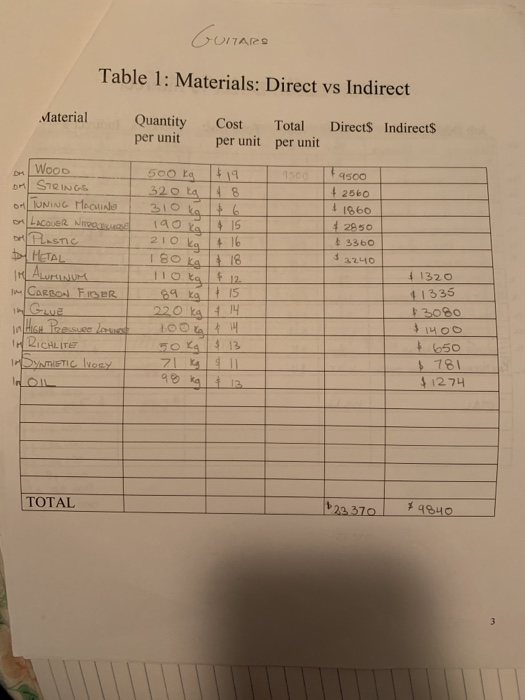
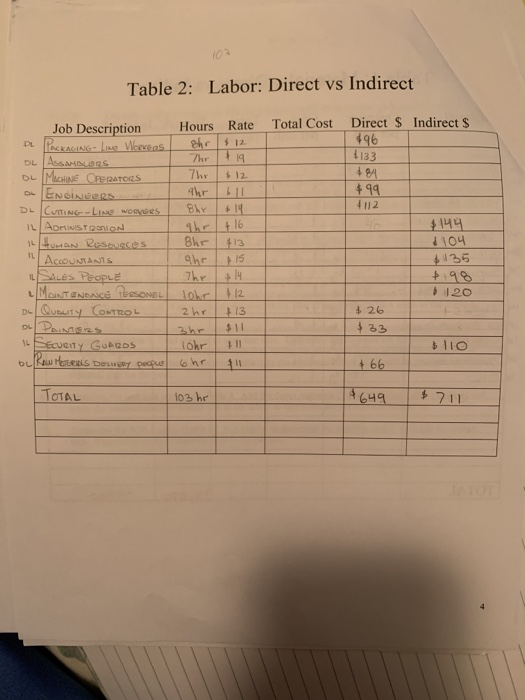
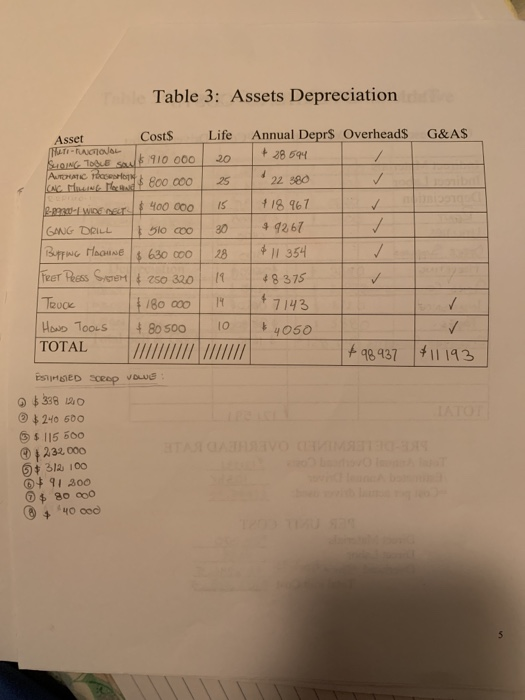
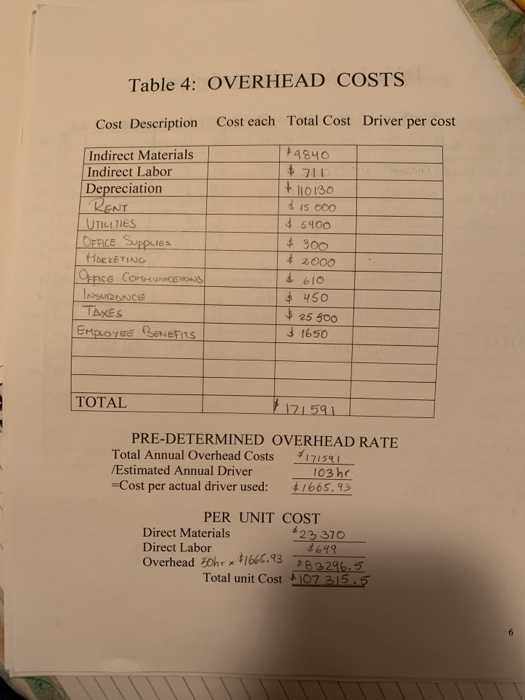
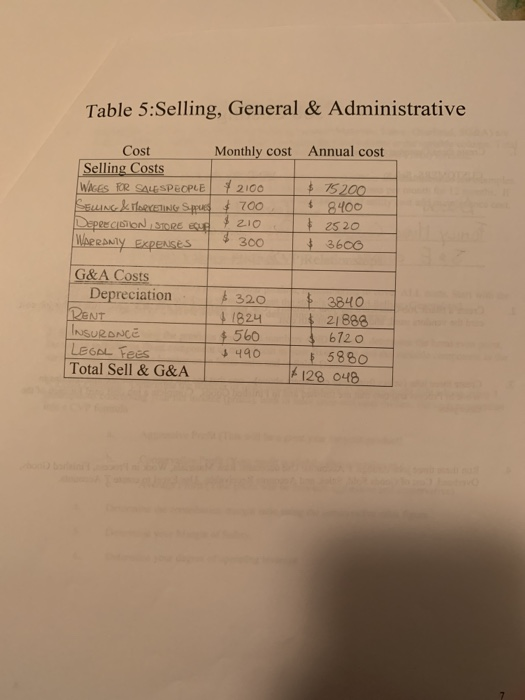


Prepare a manucfacturing process of guitars, complete each table with the indication under the page of cost characteristics and basics. The page of job costing has to be done with the information from the tables.
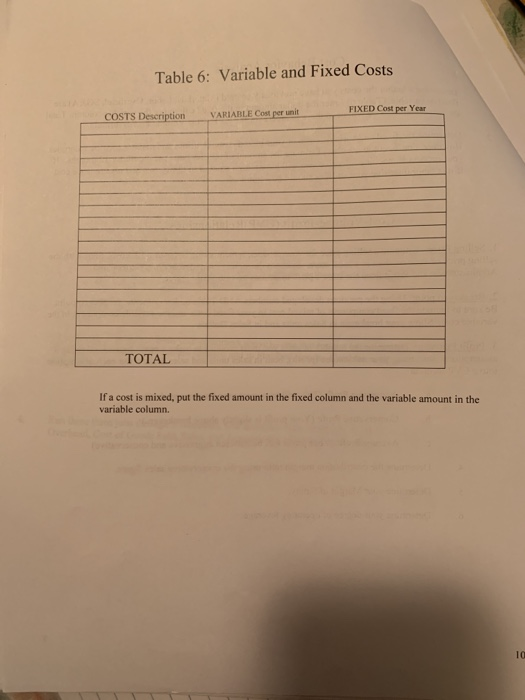
Cost Characteristics and Basics NOTE: Details and accuracy at the beginning will make your job easier in the lat. chapters and the presentation. Create a flow chart of the manufacturing process. Show each activity required to make the product Show the material and labor as it is added to each activity. Enter the materials from the flow chart on Table 1. Determine the quantity per unit (ex: pounds required for cach unit), cost per quantity (price per pound), total dollars per unit for each material and then determine whether it is direct or indirect. Total the direct material cost and indirect material cost. Transfer the indirect material costs to the overhead chart. (Table 4) Enter the labor from the flow chart on Table 2. Determine the hours per labor type (ex: 5 hrs for machine operator), determine an average rate for this type of labor. Total the cost and determine the direct labor and indirect labor dollars. Transfer the indirect labor costs to the overhead chart. (Table 4) Decide what assets (property plant and equipment) you will use to in your business to make your product and run the business. Enter the cost, life, and annual depreciation for each asset on Table 3. Decide whether the depreciation is an overhead cost or a SG&A cost. Transfer the SG&A costs to the Table 5 Add other overhead costs to the indirect materials, indirect labor and factory depreciation. (ex: rent, insurance) in Table 4. Total the cost of each line item. Determine the driver to use for your overhead costs. It may be helpful to determine driver for each cost, taking the most used driver as your overhead driver. Add the total annual overhead costs then divide it by the estimated driver. This will be your predetermined overhead rate for the year. 6. Complete the unit cost portion on Table 4. Add the direct materials (Table 1). Direct Labor (Table 2) and apply the predetermined overhead rate to the driver to determine the per unit overhead cost. 7. Determine the SG&A costs (Table 5). It is helpful to determine the monthly cost to calculate the annual cost. You will need these numbers later in the project. GUITARS Table 1: Materials: Direct vs Indirect Material Quantity per unit Cost Total per unit per unit Direct Indirects 114 4500 + 2560 1860 #2950 3360 Woon 500 Ls on STRINGS 320 La O TUNING Hone 310 kg OLACE MHO 190 kg on Plastic 210 kg METAL 180 K 18 IM ALUMINUM Tota F12 Corso FIBER 89 k tis GLE 220 k 14 IN HIGH Preisverlust INRICHLITE 50 kg $13 IMDYNTETIC IVORY HO 98 kg 13 | 1320 11335 1400 $ 650 . 781 $1274 TOTAL 223370 $9840 Table 2: Labor: Direct vs Indirect Total Cost Direct 1 496 1133 Job Description Hours Rate De Packaginko - Line Merves shr & 12 DL ASS The 19 DL MCINE CREATORS Ihr & 12 ENGINEERS thr DL Cuti -Lin woes Shr 14 IL AON STORION shr 16 man Resources Bhr $13 ACCOUNTANTS ahr 15 SALES PEOPLE Thr +14 MOTINDAKE TONEL Du QuouTY CONTROL 2hr & 131 9 120 SECURITY GUARDS ou Raw MOTERINS DELvery poopu Lohr ohr] 1 TOTAL | 103 hr Table 3: Assets Depreciation G&AS Asset Costs Life HATI- SONGTE SU 910 000 ATC for Ano 000 25 c heap 600 8.23-WDENS 400 000 GANG DRILL 1 510 cool 30 Buprug Hoone 8 630 000 28 FRET PRess Soen/ & 250 320 19 Truck 180 000 140 HOND TOOLS + 80 500 10 TOTAL // // Annual Deprs Overheads + 28594 22380 418 967 & 9267 1 & 11 354 48375 +7143 4050 +98 937 $11193 MED Scrop VOLUE $338 120 $240 500 3 $ 115 600 2.32000 $ 312 100 + 91 300 $ 80 000 'MOOD Table 4: OVERHEAD COSTS Cost Description Cost each Total Cost Driver per cost Indirect Materials Indirect Labor Depreciation KENT UTILITIES OFFICE Suppies Hoe KETING OFFICE COLUMCISIONS INSURANCE TAXES Employee Benefits 4840 $ 711 + 110130 815 000 5400 $ 300 + 2000 610 450 25 500 3 1650 TOTAL 171591 PRE-DETERMINED OVERHEAD RATE Total Annual Overhead Costs 171591 /Estimated Annual Driver 103 hr =Cost per actual driver used: #1665.93 PER UNIT COST Direct Materials *23 370 Direct Labor $649 Overhead zohrx1666.13 83,296.5 Total unit Cost - 107 215.5 Table 5:Selling, General & Administrative Cost Monthly cost Annual cost Selling Costs WAGES FOR SALE SPEOPLE #2100 $ 75200 SELING & MARKETING Spucs $ 700 $ 8400 Depee cION, STORE E $ 210 2520 WARRANTY Expenses $ 300 $ 3600 $ 32.0 G&A Costs Depreciation RENT INSURANCE LEGAL Fees Total Sell & G&A 24 +560 $ 3840 $21888 & 6720 $ 5880 128 048 490 Job Costing Create three Customers & three Vendors. CUSTOMERS. Sell to VENDORS- Buy from AMAZON Forly Music CENTERS 5% E GUMORS FENDER MUSICAL INTRUMENTS Plus GUITARS YonoHA 2. Create a Blank Job Cost Card for your company. Use your textbook for a basic sample. Add to this job cost card the vendors used, and previous month cost. 3. Create three jobs (select from your customers above) one that has not been completed and remains in Work In Process and two that are finished and in Finished Goods. Complete a job cost card for each of the three jobs. 4. Run these three jobs through T Accounts. Use accounts: Raw Materials, Work in Process, Finished Goods, Overhead, Cost of Goods Sold, Sales, and Accounts Receivable. Use Excel to create T Accounts. Cost Behavior Analysis Determine whether the costs you have previously entered (Materials, Labor, Overhead, SG&A) are fixed or variable. (Table 6) Enter the dollar amount in the fixed column or the variable column. Total the two columns. You will need these numbers for the CVP (Cost Volume Profit) formula. Determine the fixed and variable costs of your mixed costs. (Utilities and maintenance are examples. However, don't get too creative) Estimate the amount of utilities costs per month for 12 months. If your process is machine intensive you will have a high amount of utility cost and maintenance cost. if it is labor intensive your utilities should be a minimal Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP)Relationships 1. Selling Price: Estimate a selling price for your product, remembering to cover ALL costs. Start with the selling price of your product in a local store. Subtract the store's estimated Selling. General and Administration and Profit from the store's price to determine your selling price. 2. Breakeven point: Using the previous developed numbers AND Table 6. determine the breakeven point. Be sure to include the fixed component of mixed cost in your fixed costs and the variable component in the variable cost. Show your breakeven in Sales units and in Sales Dollars 3. Profit Planning: Determine the number of units you must produce to make a profit (not a loss) using 3 assumptions concerning your net income (profit), both in sales units and sales dollars. Put each assumption into a CVP formula a. Aggressive Profit (This will be a great year for your product) b. Conservative Profit (Your profit is slightly above breakeven.) e. Average Profit (Your profit will be between aggressive and conservative) 4. Determine the contribution margin ratio using the conservative sales figure. 5. Determine your Margin of Safety. 6. Determine your degree of operating leverage Table 6: Variable and Fixed Costs FIXED Cost per Year COSTS Description VARIABLE Cost per unit TOTAL If a cost is mixed, put the fixed amount in the fixed column and the variable amount in the variable column Cost Characteristics and Basics NOTE: Details and accuracy at the beginning will make your job easier in the lat. chapters and the presentation. Create a flow chart of the manufacturing process. Show each activity required to make the product Show the material and labor as it is added to each activity. Enter the materials from the flow chart on Table 1. Determine the quantity per unit (ex: pounds required for cach unit), cost per quantity (price per pound), total dollars per unit for each material and then determine whether it is direct or indirect. Total the direct material cost and indirect material cost. Transfer the indirect material costs to the overhead chart. (Table 4) Enter the labor from the flow chart on Table 2. Determine the hours per labor type (ex: 5 hrs for machine operator), determine an average rate for this type of labor. Total the cost and determine the direct labor and indirect labor dollars. Transfer the indirect labor costs to the overhead chart. (Table 4) Decide what assets (property plant and equipment) you will use to in your business to make your product and run the business. Enter the cost, life, and annual depreciation for each asset on Table 3. Decide whether the depreciation is an overhead cost or a SG&A cost. Transfer the SG&A costs to the Table 5 Add other overhead costs to the indirect materials, indirect labor and factory depreciation. (ex: rent, insurance) in Table 4. Total the cost of each line item. Determine the driver to use for your overhead costs. It may be helpful to determine driver for each cost, taking the most used driver as your overhead driver. Add the total annual overhead costs then divide it by the estimated driver. This will be your predetermined overhead rate for the year. 6. Complete the unit cost portion on Table 4. Add the direct materials (Table 1). Direct Labor (Table 2) and apply the predetermined overhead rate to the driver to determine the per unit overhead cost. 7. Determine the SG&A costs (Table 5). It is helpful to determine the monthly cost to calculate the annual cost. You will need these numbers later in the project. GUITARS Table 1: Materials: Direct vs Indirect Material Quantity per unit Cost Total per unit per unit Direct Indirects 114 4500 + 2560 1860 #2950 3360 Woon 500 Ls on STRINGS 320 La O TUNING Hone 310 kg OLACE MHO 190 kg on Plastic 210 kg METAL 180 K 18 IM ALUMINUM Tota F12 Corso FIBER 89 k tis GLE 220 k 14 IN HIGH Preisverlust INRICHLITE 50 kg $13 IMDYNTETIC IVORY HO 98 kg 13 | 1320 11335 1400 $ 650 . 781 $1274 TOTAL 223370 $9840 Table 2: Labor: Direct vs Indirect Total Cost Direct 1 496 1133 Job Description Hours Rate De Packaginko - Line Merves shr & 12 DL ASS The 19 DL MCINE CREATORS Ihr & 12 ENGINEERS thr DL Cuti -Lin woes Shr 14 IL AON STORION shr 16 man Resources Bhr $13 ACCOUNTANTS ahr 15 SALES PEOPLE Thr +14 MOTINDAKE TONEL Du QuouTY CONTROL 2hr & 131 9 120 SECURITY GUARDS ou Raw MOTERINS DELvery poopu Lohr ohr] 1 TOTAL | 103 hr Table 3: Assets Depreciation G&AS Asset Costs Life HATI- SONGTE SU 910 000 ATC for Ano 000 25 c heap 600 8.23-WDENS 400 000 GANG DRILL 1 510 cool 30 Buprug Hoone 8 630 000 28 FRET PRess Soen/ & 250 320 19 Truck 180 000 140 HOND TOOLS + 80 500 10 TOTAL // // Annual Deprs Overheads + 28594 22380 418 967 & 9267 1 & 11 354 48375 +7143 4050 +98 937 $11193 MED Scrop VOLUE $338 120 $240 500 3 $ 115 600 2.32000 $ 312 100 + 91 300 $ 80 000 'MOOD Table 4: OVERHEAD COSTS Cost Description Cost each Total Cost Driver per cost Indirect Materials Indirect Labor Depreciation KENT UTILITIES OFFICE Suppies Hoe KETING OFFICE COLUMCISIONS INSURANCE TAXES Employee Benefits 4840 $ 711 + 110130 815 000 5400 $ 300 + 2000 610 450 25 500 3 1650 TOTAL 171591 PRE-DETERMINED OVERHEAD RATE Total Annual Overhead Costs 171591 /Estimated Annual Driver 103 hr =Cost per actual driver used: #1665.93 PER UNIT COST Direct Materials *23 370 Direct Labor $649 Overhead zohrx1666.13 83,296.5 Total unit Cost - 107 215.5 Table 5:Selling, General & Administrative Cost Monthly cost Annual cost Selling Costs WAGES FOR SALE SPEOPLE #2100 $ 75200 SELING & MARKETING Spucs $ 700 $ 8400 Depee cION, STORE E $ 210 2520 WARRANTY Expenses $ 300 $ 3600 $ 32.0 G&A Costs Depreciation RENT INSURANCE LEGAL Fees Total Sell & G&A 24 +560 $ 3840 $21888 & 6720 $ 5880 128 048 490 Job Costing Create three Customers & three Vendors. CUSTOMERS. Sell to VENDORS- Buy from AMAZON Forly Music CENTERS 5% E GUMORS FENDER MUSICAL INTRUMENTS Plus GUITARS YonoHA 2. Create a Blank Job Cost Card for your company. Use your textbook for a basic sample. Add to this job cost card the vendors used, and previous month cost. 3. Create three jobs (select from your customers above) one that has not been completed and remains in Work In Process and two that are finished and in Finished Goods. Complete a job cost card for each of the three jobs. 4. Run these three jobs through T Accounts. Use accounts: Raw Materials, Work in Process, Finished Goods, Overhead, Cost of Goods Sold, Sales, and Accounts Receivable. Use Excel to create T Accounts. Cost Behavior Analysis Determine whether the costs you have previously entered (Materials, Labor, Overhead, SG&A) are fixed or variable. (Table 6) Enter the dollar amount in the fixed column or the variable column. Total the two columns. You will need these numbers for the CVP (Cost Volume Profit) formula. Determine the fixed and variable costs of your mixed costs. (Utilities and maintenance are examples. However, don't get too creative) Estimate the amount of utilities costs per month for 12 months. If your process is machine intensive you will have a high amount of utility cost and maintenance cost. if it is labor intensive your utilities should be a minimal Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP)Relationships 1. Selling Price: Estimate a selling price for your product, remembering to cover ALL costs. Start with the selling price of your product in a local store. Subtract the store's estimated Selling. General and Administration and Profit from the store's price to determine your selling price. 2. Breakeven point: Using the previous developed numbers AND Table 6. determine the breakeven point. Be sure to include the fixed component of mixed cost in your fixed costs and the variable component in the variable cost. Show your breakeven in Sales units and in Sales Dollars 3. Profit Planning: Determine the number of units you must produce to make a profit (not a loss) using 3 assumptions concerning your net income (profit), both in sales units and sales dollars. Put each assumption into a CVP formula a. Aggressive Profit (This will be a great year for your product) b. Conservative Profit (Your profit is slightly above breakeven.) e. Average Profit (Your profit will be between aggressive and conservative) 4. Determine the contribution margin ratio using the conservative sales figure. 5. Determine your Margin of Safety. 6. Determine your degree of operating leverage Table 6: Variable and Fixed Costs FIXED Cost per Year COSTS Description VARIABLE Cost per unit TOTAL If a cost is mixed, put the fixed amount in the fixed column and the variable amount in the variable column Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


