Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Many companies make annual reports available on their corporate website. Annual reports on Form 10-K also can be accessed through the SEC's EDGAR system


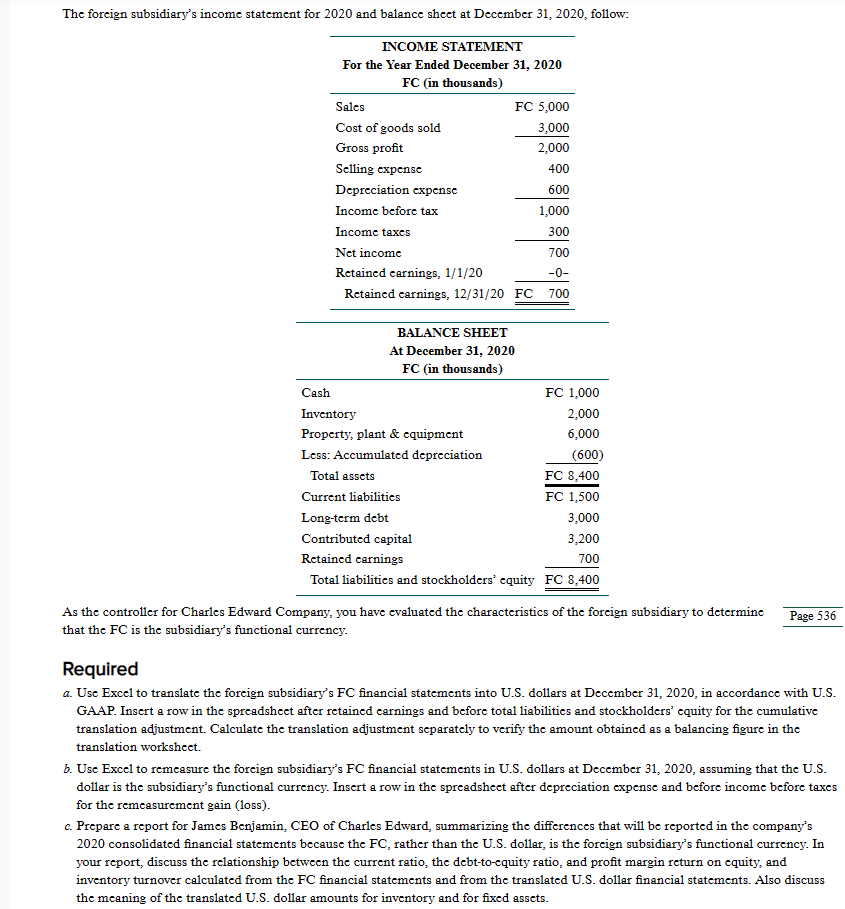

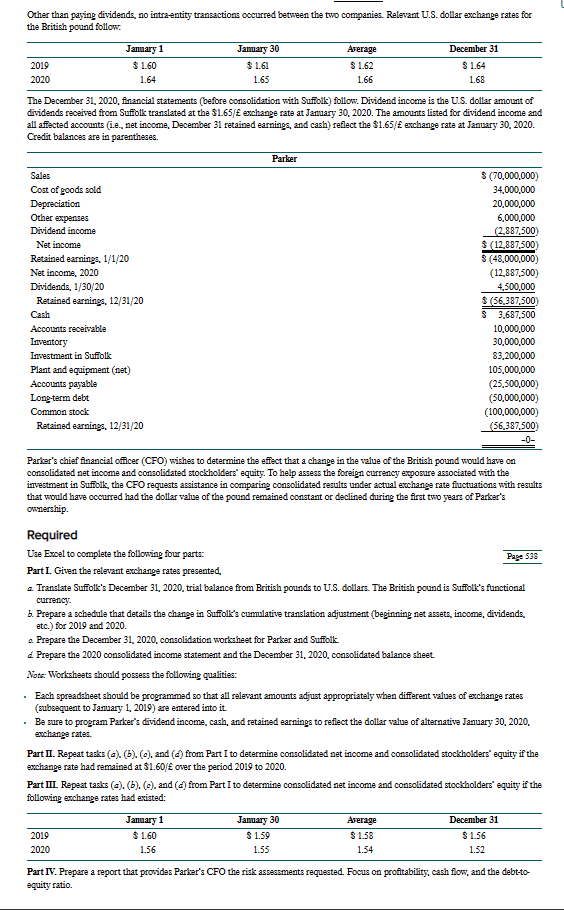



Many companies make annual reports available on their corporate website. Annual reports on Form 10-K also can be accessed through the SEC's EDGAR system at www.sec.gov (under Filing Type, search for 10-K). Access the most recent annual report for a U.S.-based multinational company with which you are familiar to complete the following requirements. Required a. Identify the location(s) in the annual report that provides disclosures related to the translation of foreign currency financial statements and foreign currency hedging. b. Determine whether the company's foreign operations have a predominant functional currency. c. List the amount of translation adjustment, if any, reported in other comprehensive income in each of the three most recent years. Explain the sign (positive or negative) of the translation adjustment in each of the three most recent years. d. Determine whether the company hedges net investments in foreign operations. If so, determine the type(s) of hedging instrument used. RESEARCH CASE 2-FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSLATION AND HEDGING DISCLOSURES CPA skills Many companies make annual reports (sometimes on Form 10-K) available on their corporate website. Access the annual report indicated for each of the following U.S.-based multinational corporations to complete the requirements: International Business Machines Corporation, 2017 Annual Report. Oracle Corporation, Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended May 31, 2018. Required a. Identify the location(s) in the annual report that provides disclosures related to foreign currency translation and foreign currency hedging. b. Determine whether the company's foreign operations have a predominant functional currency. c. List the amount of translation adjustment, if any, reported in other comprehensive income in each of the three most recent years. Explain the sign (positive or negative) of the translation adjustment in each of the three most recent years. d. Determine whether each company hedges net investments in foreign operations. If so, determine the type(s) of hedging instrument used. CPA skills Lynch Corporation has a wholly owned subsidiary in Mexico (Lynmex) with two distinct and unrelated lines of business. Lynmex's Small Appliance Division manufactures small household appliances such as toasters and coffeemakers at a factory in Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, and sells them directly to retailers such as Gigantes throughout Mexico. Lynmex's Electronics Division imports finished products produced by Lynch Corporation in the United States and sells them to a network of distributors operating throughout Mexico. Lynch's CFO believes that the two divisions have different functional currencies. The functional currency of the Small Appliance Division is the Mexican peso, whereas the functional currency of the Electronics Division is the U.S. dollar. The CFO is unsure whether to designate the Mexican peso or the U.S. dollar as Lynmex's functional currency, or whether the subsidiary can be treated as two separate foreign operations with different functional currencies. Required Search current U.S. authoritative accounting literature to determine how the functional currency should be determined for a foreign entity that has more than one distinct and separable operation. Identify the source of guidance for answering this question. ACCOUNTING STANDARDS CASE 2-CHANGE IN FUNCTIONAL CURRENCY CPA skills Hughes Inc. has a wholly owned subsidiary in Canada that previously had been determined as having the Canadian dollar as its functional currency. Due to a recent restructuring, Hughes Inc.'s CFO believes that the functional currency of the Canadian company has changed to the U.S. dollar. A large cumulative translation adjustment related to the Canadian subsidiary is included in accumulated other comprehensive income on Hughes Inc.'s balance sheet. The CFO is unsure whether the cumulative translation adjustment should be removed from equity, and if so, to what other account it should be transferred. He also questions whether the change in functional currency qualifies as a change in accounting principle, which would require retrospective application of the temporal method in translating the Canadian subsidiary's financial statements. He wonders, for example, whether the Canadian subsidiary's nonmonetary assets need to be restated as if the temporal method had been applied in previous years. Required Page 535 Search current U.S. authoritative accounting literature for guidance on how to handle a change in functional currency from a foreign currency to the U.S. dollar. Summarize that guidance to answer the CFO's questions. Identify the source of guidance for answering these questions. EXCEL CASE-TRANSLATING FOREIGN CURRENCY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS CPA skills Charles Edward Company established a subsidiary in a foreign country on January 1, 2020, by investing FC 3,200,000 when the exchange rate was $0.50/FC. Charles Edward negotiated a bank loan of FC 3,000,000 on January 5, 2020, and purchased plant and equipment in the amount of FC 6,000,000 on January 8, 2020. It depreciated plant and equipment on a straight-line basis over a 10-year useful life. It purchased its beginning inventory of FC 1,000,000 on January 10, 2020, and acquired additional inventory of FC 4,000,000 at three points in time during the year at an average exchange rate of $0.43/FC. It uses the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method to determine cost of goods sold. Additional exchange rates per FC 1 during the year 2020 follow: January 1-31, 2020 $0.50 Average 2020 0.45 December 31, 2020 0.38 The foreign subsidiary's income statement for 2020 and balance sheet at December 31, 2020, follow: INCOME STATEMENT For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 FC (in thousands) Sales FC 5,000 Cost of goods sold 3,000 Gross profit 2,000 Selling expense 400 Depreciation expense 600 Income before tax 1,000 Income taxes 300 Net income 700 Retained earnings, 1/1/20 -0- Retained earnings, 12/31/20 FC 700 BALANCE SHEET At December 31, 2020 FC (in thousands) Cash Inventory Property, plant & equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation Total assets Current liabilities Long-term debt Contributed capital Retained earnings FC 1,000 2,000 6,000 (600) FC 8,400 FC 1,500 3,000 3,200 700 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity FC 8,400 As the controller for Charles Edward Company, you have evaluated the characteristics of the foreign subsidiary to determine that the FC is the subsidiary's functional currency. Required Page 536 a. Use Excel to translate the foreign subsidiary's FC financial statements into U.S. dollars at December 31, 2020, in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Insert a row in the spreadsheet after retained earnings and before total liabilities and stockholders' equity for the cumulative translation adjustment. Calculate the translation adjustment separately to verify the amount obtained as a balancing figure in the translation worksheet. b. Use Excel to remeasure the foreign subsidiary's FC financial statements in U.S. dollars at December 31, 2020, assuming that the U.S. dollar is the subsidiary's functional currency. Insert a row in the spreadsheet after depreciation expense and before income before taxes for the remeasurement gain (loss). c. Prepare a report for James Benjamin, CEO of Charles Edward, summarizing the differences that will be reported in the company's 2020 consolidated financial statements because the FC, rather than the U.S. dollar, is the foreign subsidiary's functional currency. In your report, discuss the relationship between the current ratio, the debt-to-equity ratio, and profit margin return on equity, and inventory turnover calculated from the FC financial statements and from the translated U.S. dollar financial statements. Also discuss the meaning of the translated U.S. dollar amounts for inventory and for fixed assets. COMMUNICATION CASE-FUNCTIONAL CURRENCY OF A FOREIGN SUBSIDIARY Earlier this year, Alltime Company (headquartered in Kansas City, Missouri) acquired a small watch manufacturer in Berlin, Germany, that keeps its books in euros. (This is the first foreign direct investment made by Alltime.) The end of the fiscal year is approaching, and the company's CFO is beginning to plan for the financial statement consolidation of the Germany subsidiary. The CFO has heard that she must determine the "functional currency" of the foreign subsidiary to be able to comply with U.S. GAAP, and she has asked you to provide her with answers to the following questions. 1. What is the functional currency of a foreign subsidiary? 2. Why must the functional currency of a foreign subsidiary be determined? 3. How is the functional currency of a foreign subsidiary determined? Required Draft a memorandum to the company's CFO answering the preceding questions. EXCEL AND ANALYSIS CASE-PARKER, INC., AND SUFFOLK PLC CPA skills On January 1, 2019, Parker, Inc., a U.S.-based firm, acquired 100 percent of Suffolk PLC located in Great Britain for consideration paid of 52,000,000 British pounds (), which was equal to fair value. The excess of fair value over book value is attributable to land (part of property, plant, and equipment) and is not subject to depreciation. Parker accounts for its investment in Suffolk at cost. On January 1, 2019, Suffolk reported the following balance sheet: Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Property, plant, and equipment (net) $ 1,000,000 8,000,000 44,000,000 6,000,000 $59,000,000 $ 2,000,000 Accounts payable 3,000,000 Long-term debt 14,000,000 Common stock 40,000,000 Retained carnings $59,000,000 Suffolk's 2019 income was recorded at 2,000,000. It declared and paid no dividends in 2019. On December 31, 2020, two years after the date of acquisition, Suffolk submitted the following trial balance to Parker for consolidation: Page 537 Cash $ 1,500,000 Accounts Receivable Inventory 5,200,000 18,000,000 Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) 36,000,000 Accounts Payable (1,450,000) Long-Term Debt (5,000,000) Common Stock (44,000,000) Retained Earnings, 1/1/20 (8,000,000) Sales (28,000,000) Cost of Goods Sold 16,000,000 Depreciation 2,000,000 Other Expenses 6,000,000 Dividends, 1/30/20 1,750,000 -0- Other than paying dividends, no intra-entity transactions occurred between the two companies. Relevant U.S. dollar exchange rates for the British pound follow. 2019 2020 January 1 $ 1.60 1.64 January 30 $ 1.61 1.65 Average $ 1.62 1.66 December 31 $ 1.64 1.68 The December 31, 2020, financial statements (before consolidation with Suffolk) follow. Dividend income is the U.S. dollar amount of dividends received from Suffolk translated at the $1.65/ exchange rate at January 30, 2020. The amounts listed for dividend income and all affected accounts (ie., net income, December 31 retained earnings, and cash) reflect the $1.65/ exchange rate at January 30, 2020. Credit balances are in parentheses. Sales Cost of goods sold Parker $ (70,000,000) 34,000,000 Depreciation Other expenses Dividend income Net income Retained earnings, 1/1/20 Net income, 2020 Dividends, 1/30/20 Retained earnings, 12/31/20 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Investment in Suffolk Plant and equipment (net) Accounts payable Long-term debt Common stock Retained earnings, 12/31/20 20,000,000 6,000,000 (2,887,500) $ (12,887,500) $ (48,000,000) (12,887,500) 4,500,000 $ (56,387,500) $ 3,687,500 10,000,000 30,000,000 83,200,000 105,000,000 (25,500,000) (50,000,000) (100,000,000) (56,387,500) -0- Parker's chief financial officer (CFO) wishes to determine the effect that a change in the value of the British pound would have on consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders' equity. To help assess the foreign currency exposure associated with the investment in Suffolk, the CFO requests assistance in comparing consolidated results under actual exchange rate fluctuations with results that would have occurred had the dollar value of the pound remained constant or declined during the first two years of Parker's ownership. Required Use Excel to complete the following four parts: Part I. Given the relevant exchange rates presented, Page 538 a Translate Suffolk's December 31, 2020, trial balance from British pounds to U.S. dollars. The British pound is Suffolk's functional currency. b. Prepare a schedule that details the change in Suffolk's cumulative translation adjustment (beginning net assets, income, dividends. etc.) for 2019 and 2020. a. Prepare the December 31, 2020, consolidation worksheet for Parker and Suffolk. Prepare the 2020 consolidated income statement and the December 31, 2020, consolidated balance sheet. Note: Worksheets should possess the following qualities: Each spreadsheet should be programmed so that all relevant amounts adjust appropriately when different values of exchange rates (subsequent to January 1, 2019) are entered into it. . Be sure to program Parker's dividend income, cash, and retained earnings to reflect the dollar value of alternative January 30, 2020, exchange rates. Part II. Repeat tasks (a), (b), (c), and (d) from Part I to determine consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders' equity if the exchange rate had remained at $1.60/ over the period 2019 to 2020. Part III. Repeat tasks (a). (b), (c), and (d) from Part I to determine consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders' equity if the following exchange rates had existed: 2019 2020 January 1 $1.60 1.56 January 30 $ 1.59 Average $ 1.58 1.55 1.54 December 31 $ 1.56 1.52 Part IV. Prepare a report that provides Parker's CFO the risk assessments requested. Focus on profitability, cash flow, and the debt-to- equity ratio. Excel Case - Translating Foreign Currency Financial Statements Your prepared report should be approximately 500 words, citing at least two external sources. Papers must be submitted by the due date provided in your classroom. Name the file LastnameFirstinitial.ACC460.EC, where the EC refers to Excel Case. submit both the completed Excel spreadsheet along with your prepared report.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


