Question
Many models used in epidemiology for characterizing a disease outbreak split a population at a given time t into disjoint subsets called compartments. These models
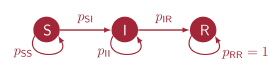
Many models used in epidemiology for characterizing a disease outbreak split a population at a given time t into disjoint subsets called compartments. These models are called compartmental models. One of the simplest of such models is the SIR model: the three compartments are Susceptible, Infectious, and Recovered (the latter including deceased). The population can be seen as a dynamic system with the compartments seen as states in which any individual can be at any time. Thus the SIR model can be written as a Markov chain with graph as depicted in Fig. 1, where the (typically time-dependent) transition probabilities are estimated by proportions based on random sampling.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


