Maple Leaf Production manufactures truck tires. The following information is available for the last operating period. Maple Leaf produced and sold 92,000 tires for
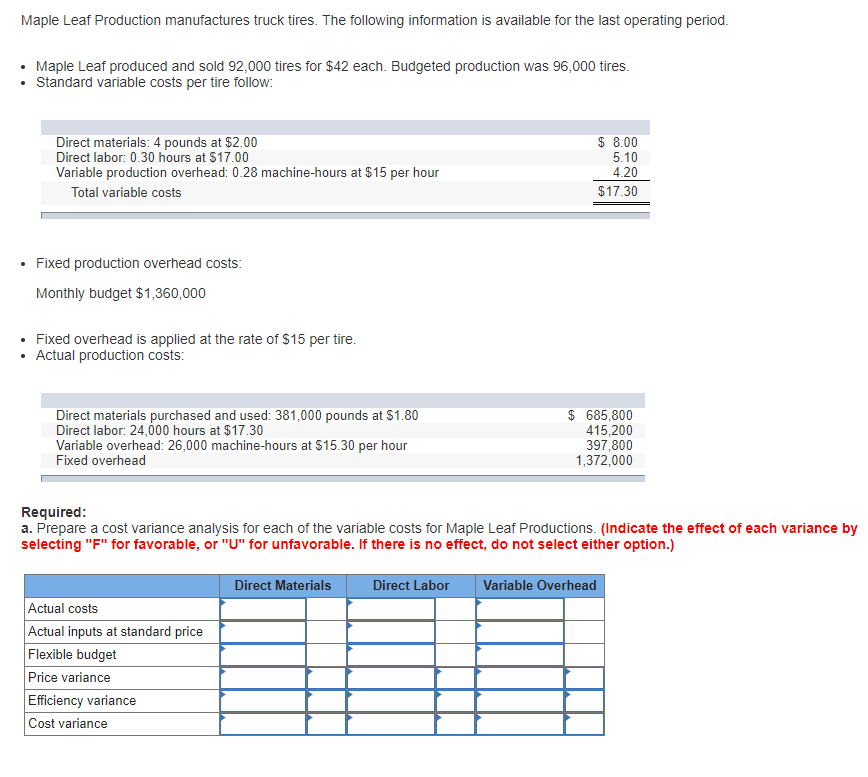
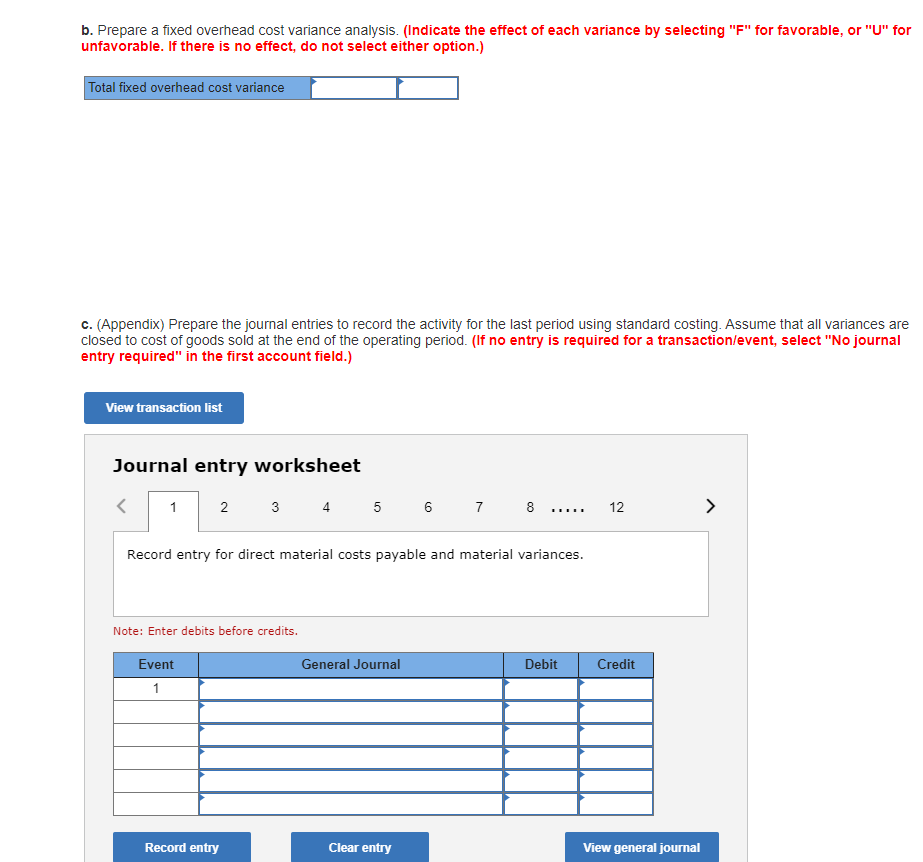
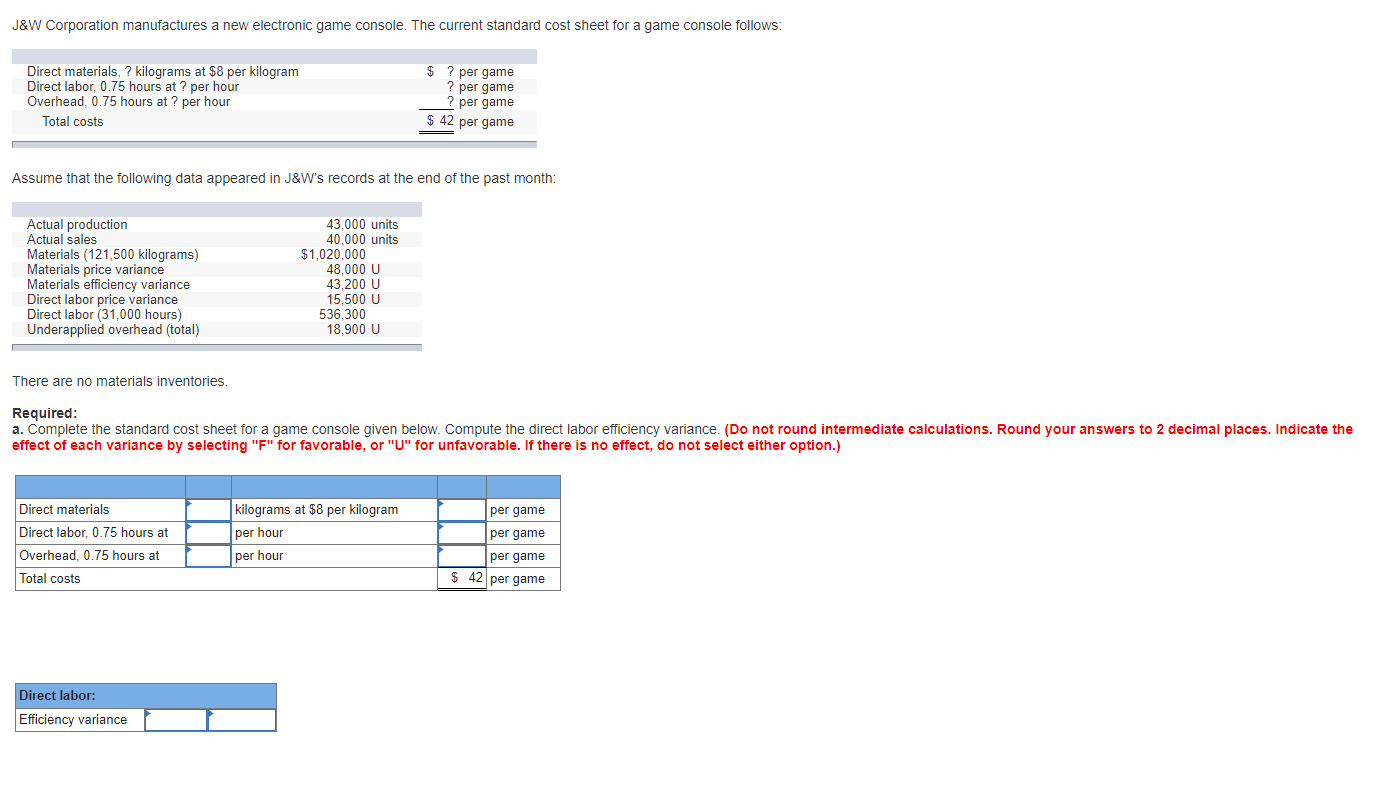

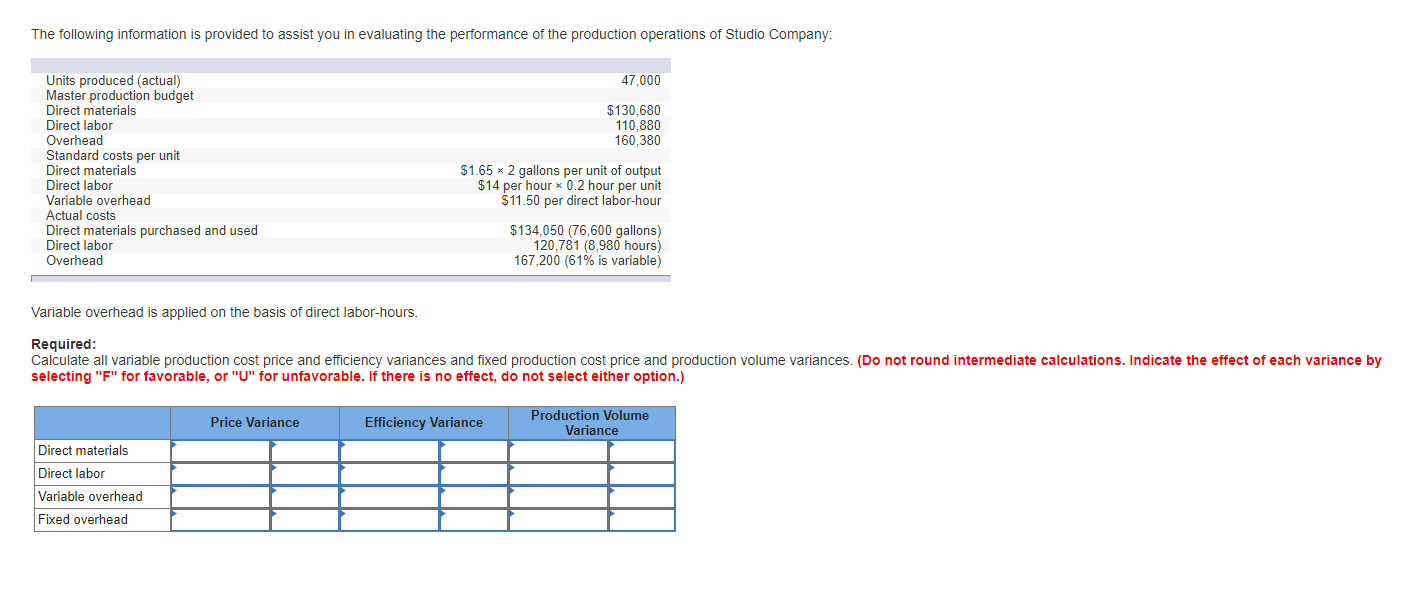
Maple Leaf Production manufactures truck tires. The following information is available for the last operating period. Maple Leaf produced and sold 92,000 tires for $42 each. Budgeted production was 96,000 tires. Standard variable costs per tire follow: Direct materials: 4 pounds at $2.00 Direct labor: 0.30 hours at $17.00 Variable production overhead: 0.28 machine-hours at $15 per hour Total variable costs Fixed production overhead costs: Monthly budget $1,360,000 Fixed overhead is applied at the rate of $15 per tire. Actual production costs: Direct materials purchased and used: 381,000 pounds at $1.80 Direct labor: 24,000 hours at $17.30 Variable overhead: 26,000 machine-hours at $15.30 per hour Fixed overhead Required: $ 8.00 5.10 4.20 $17.30 $ 685,800 415,200 397,800 1,372,000 a. Prepare a cost variance analysis for each of the variable costs for Maple Leaf Productions. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.) Actual costs Actual inputs at standard price Flexible budget Price variance Efficiency variance Cost variance Direct Materials Direct Labor Variable Overhead b. Prepare a fixed overhead cost variance analysis. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.) Total fixed overhead cost variance c. (Appendix) Prepare the journal entries to record the activity for the last period using standard costing. Assume that all variances are closed to cost of goods sold at the end of the operating period. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet < 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 12 Record entry for direct material costs payable and material variances. Note: Enter debits before credits. Event 1 General Journal Debit Credit Record entry Clear entry View general journal J&W Corporation manufactures a new electronic game console. The current standard cost sheet for a game console follows: Direct materials, ? kilograms at $8 per kilogram Direct labor, 0.75 hours at? per hour Overhead, 0.75 hours at ? per hour Total costs $ ? per game ? per game ? per game $ 42 per game Assume that the following data appeared in J&W's records at the end of the past month: Actual production Actual sales Materials (121,500 kilograms) Materials price variance Materials efficiency variance 43,000 units 40,000 units $1,020,000 48,000 U 43,200 U Direct labor price variance Direct labor (31,000 hours) Underapplied overhead (total) 15,500 U 536,300 18,900 U There are no materials inventories. Required: a. Complete the standard cost sheet for a game console given below. Compute the direct labor efficiency variance. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.) Direct materials kilograms at $8 per kilogram per game Direct labor, 0.75 hours at per hour per game Overhead, 0.75 hours at per hour per game Total costs $ 42 per game Direct labor: Efficiency variance b. Assume that all production overhead is fixed and that the $18,900 underapplied is the only overhead variance that can be computed. What are the actual and applied overhead amounts? Actual Applied Overhead The following information is provided to assist you in evaluating the performance of the production operations of Studio Company: Units produced (actual) Master production budget Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Standard costs per unit Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Actual costs Direct materials purchased and used Direct labor Overhead 47,000 $130,680 110,880 160,380 $1.65 x 2 gallons per unit of output $14 per hour x 0.2 hour per unit $11.50 per direct labor-hour $134,050 (76,600 gallons) 120,781 (8,980 hours) 167,200 (61% is variable) Variable overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor-hours. Required: Calculate all variable production cost price and efficiency variances and fixed production cost price and production volume variances. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option.) Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Price Variance Efficiency Variance Production Volume Variance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


