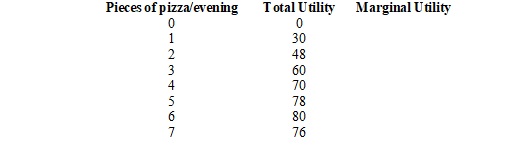Marginal Decision Rule
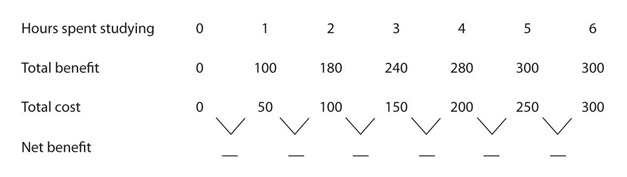
1. Joe Higgins is thinking about how much time to spend studying for a biology exam tomorrow. Using "utility units" he measures the benefits and costs of study; his calculations are shown in the following table.
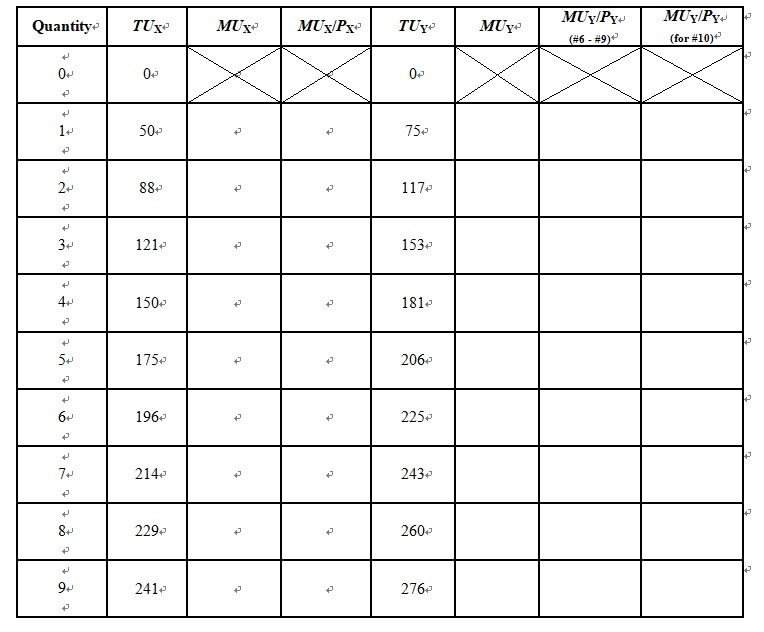
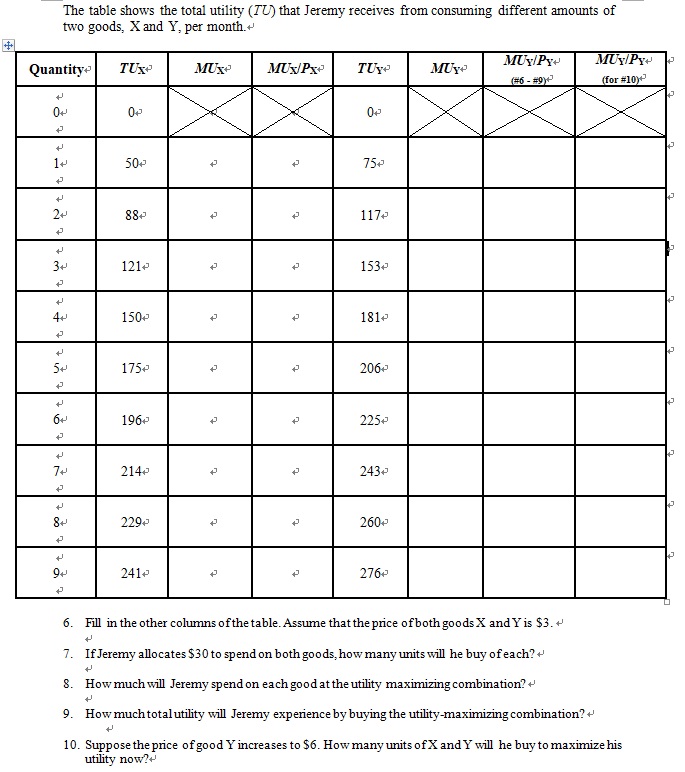
\f\f\f1. Joe Higgins is thinking about how much time to spend studying for a biology exam tomorrow. Using "utility units" he measures the benefits and costs of study; his calculations are shown in the following table.+ Hours spent studying O 2 4 6 Total benefit 0 100 180 240 280 300 300 Total cost 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 Net benefit a. Fill in the fourth row for net benefit in the table. Use the midpoint convention to emphasize that the net benefit is a marginal value showing the gain as hours spent increase by one-hour increments. + (In English, the "net benefit" is the increase in benefit minus the increase in cost. So if he moves from 0 to 1 hour, his benefit increases by 100, and costs increase by 50. 100-50=50 net benefit)+ b. Based on the marginal decision rule, how many hours should Joe spend studying for his biology exam?+ (don't go past the point where net benefit becomes negative. Another way to verify this is to find where total benefit-total cost is greatest. How many hours is that?)+ t Utility+ 2. Suppose you really, really like ice cream. You adore ice cream. Does the law of diminishing marginal utility apply to your ice cream consumption? + + t 3. Do you tend to get more food at a fixed-price buffet (Golden Corral) or when ordering from a menu? Is there a reason why you might get more at one than the other?+4. The table shows the total utility Joseph derives from eating pizza in the evening while studying. He has to pick some number to eat, 0-7. Remember that "total utility" is the total value (just a number that measures how "happy" he is) Joseph gets from eating the chosen number of slices. + Pieces of pizza/evening+ Total Utility+ Marginal Utility+ + 047 1+ 30+ tt t 2+ 48+ 3+ 60+ + 4+ 70+ 5+7 78+ 6+7 804 7+ 76+ ttt t t t t a. How much marginal utility does Joseph derive from the third piece of pizza? (moving from 2 to 3, total utility changes by how much?)+ + b. After eating how many pieces of pizza does marginal utility start to decline?+ (hint: when does marginal utility decline. ..not total utility)+ c. If the pizza were free, what is the maximum number of pieces Joseph would eat in an evening?+ d. After eating how many pieces of pizza does foral utility start to decline (negative marginal utility. This is different than question b)?+ Suppose the marginal utility of good A is 20 and its price is $4, and the marginal utility of good B is 50 and its price is $5. The individual to whom this information applies is spending $20 on each good. Is he or she maximizing satisfaction? If not, what should the individual do to increase total satisfaction?+ (Suppose the marginal product of unskilled workers is 20 and their wage is $4. The marginal product of skilled workers is 50 and their wage is $5. If we're spending $20/hour on each type of worker, are we minimizing our production costs? Could we find a way to produce more at the same costs? --this is the same question with more of a "real world" application.) (Questions 6-10 can also be thought of this way. Think of factory X and factory Y. How many units should you produce in each factory to minimize costs at a given level of output, or maximize output at a given level of costs?)Quantity+ MUY/PY+ (for #10)+ + 1 + 121+ 150+ +7 181+ 175+ 206+7 196+7 225+7 7 + 214+ 243+ 8+ 229+ 260+ 9+ 241+ 276+ 6. Fill in the other columns of the table. Assume that the price of both goods X and Y is $3. + 7. If Jeremy allocates $30 to spend on both goods, how many units will he buy of each?+ How much will Jeremy spend on each good at the utility maximizing combination? + 9. How much total utility will Jeremy experience by buying the utility-maximizing combination? + 10. Suppose the price of good Y increases to $6. How many units of X and Y will he buy to maximize his utility now?+