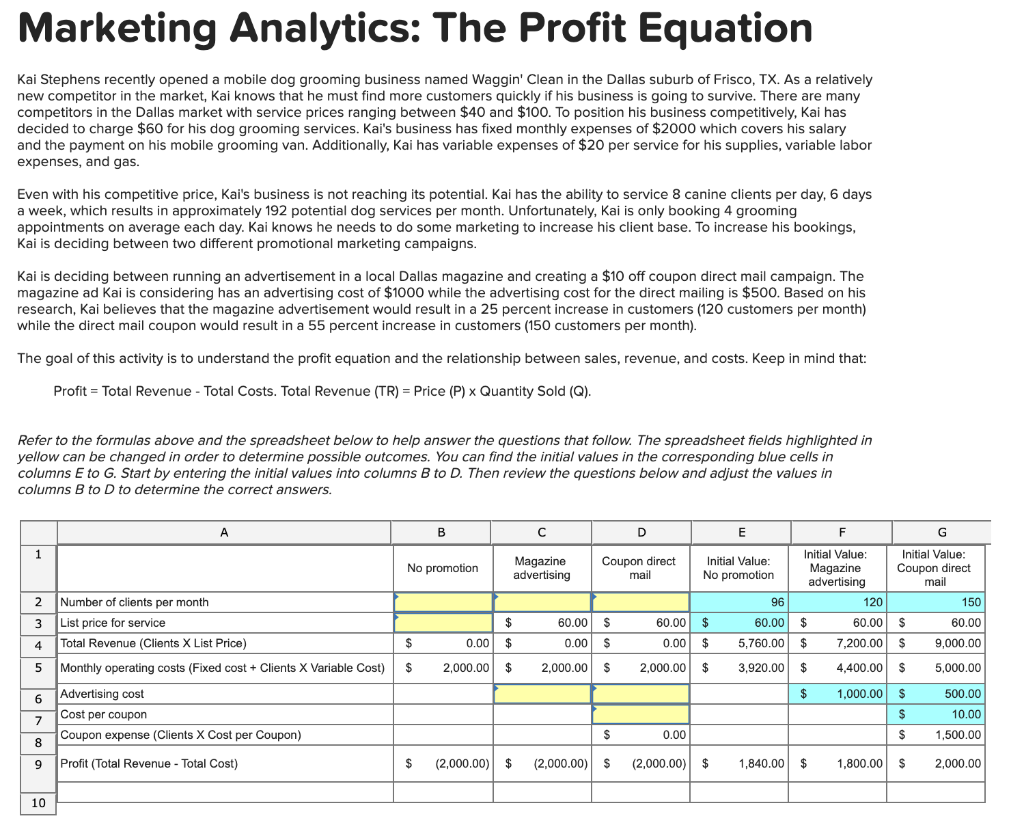
Marketing Analytics: The Profit Equation Kai Stephens recently opened a mobile dog grooming business named Waggin' Clean in the Dallas suburb of Frisco, TX. As a relatively new competitor in the market, Kai knows that he must find more customers quickly if his business is going to survive. There are many competitors in the Dallas market with service prices ranging between $40 and $100. To position his business competitively, Kai has decided to charge $60 for his dog grooming services. Kai's business has fixed monthly expenses of $2000 which covers his salary and the payment on his mobile grooming van. Additionally, Kai has variable expenses of $20 per service for his supplies, variable labor expenses, and gas. Even with his competitive price, Kai's business is not reaching its potential. Kai has the ability to service 8 canine clients per day, 6 days a week, which results in approximately 192 potential dog services per month. Unfortunately, Kai is only booking 4 grooming appointments on average each day. Kai knows he needs to do some marketing to increase his client base. To increase his bookings, Kai is deciding between two different promotional marketing campaigns. Kai is deciding between running an advertisement in a local Dallas magazine and creating a $10 off coupon direct mail campaign. The magazine ad kai is considering has an advertising cost of $1000 while the advertising cost for the direct mailing is $500. Based on his research, Kai believes that the magazine advertisement would result in a 25 percent increase in customers (120 customers per month) while the direct mail coupon would result in a 55 percent increase in customers (150 customers per month). The goal of this activity is to understand the profit equation and the relationship between sales, revenue, and costs. Keep in mind that: Profit = Total Revenue - Total Costs. Total Revenue (TR) = Price (P) x Quantity Sold (Q). Refer to the formulas above and the spreadsheet below to help answer the questions that follow. The spreadsheet fields highlighted in yellow can be changed in order to determine possible outcomes. You can find the initial values in the corresponding blue cells in columns E to G. Start by entering the initial values into columns B to D. Then review the questions below and adjust the values in columns B to D to determine the correct answers. A B 1 No promotion 2 3 Number of clients per month List price for service Total Revenue (Clients X List Price) D E F G Initial Value: Initial Value Magazine Coupon direct Initial Value: advertising Magazine No promotion Coupon direct mail advertising mail 96 120 150 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ $ 60.00 $ 0.00 $ 0.00 $ 5,760.00 $ 7,200.00 $ 9,000.00 $ 2,000.00 $ 2,000.00 $ 3,920.00 $ 4,400.00 $ 5,000.00 $ 1,000.00 $ 500.00 $ 10.00 $ 0.00 $ 1,500.00 4 $ 0.00 5 $ 2,000.00 6 Monthly operating costs (Fixed cost + Clients X Variable Cost) Advertising cost Cost per coupon Coupon expense (Clients X Cost per Coupon) 7 8 9 Profit (Total Revenue - Total Cost) $ (2,000.00) $ (2,000.00) $ (2,000.00) $ 1,840.00 $ 1,800.00 $ 2,000.00 10 Marketing Analytics: The Profit Equation Kai Stephens recently opened a mobile dog grooming business named Waggin' Clean in the Dallas suburb of Frisco, TX. As a relatively new competitor in the market, Kai knows that he must find more customers quickly if his business is going to survive. There are many competitors in the Dallas market with service prices ranging between $40 and $100. To position his business competitively, Kai has decided to charge $60 for his dog grooming services. Kai's business has fixed monthly expenses of $2000 which covers his salary and the payment on his mobile grooming van. Additionally, Kai has variable expenses of $20 per service for his supplies, variable labor expenses, and gas. Even with his competitive price, Kai's business is not reaching its potential. Kai has the ability to service 8 canine clients per day, 6 days a week, which results in approximately 192 potential dog services per month. Unfortunately, Kai is only booking 4 grooming appointments on average each day. Kai knows he needs to do some marketing to increase his client base. To increase his bookings, Kai is deciding between two different promotional marketing campaigns. Kai is deciding between running an advertisement in a local Dallas magazine and creating a $10 off coupon direct mail campaign. The magazine ad kai is considering has an advertising cost of $1000 while the advertising cost for the direct mailing is $500. Based on his research, Kai believes that the magazine advertisement would result in a 25 percent increase in customers (120 customers per month) while the direct mail coupon would result in a 55 percent increase in customers (150 customers per month). The goal of this activity is to understand the profit equation and the relationship between sales, revenue, and costs. Keep in mind that: Profit = Total Revenue - Total Costs. Total Revenue (TR) = Price (P) x Quantity Sold (Q). Refer to the formulas above and the spreadsheet below to help answer the questions that follow. The spreadsheet fields highlighted in yellow can be changed in order to determine possible outcomes. You can find the initial values in the corresponding blue cells in columns E to G. Start by entering the initial values into columns B to D. Then review the questions below and adjust the values in columns B to D to determine the correct answers. A B 1 No promotion 2 3 Number of clients per month List price for service Total Revenue (Clients X List Price) D E F G Initial Value: Initial Value Magazine Coupon direct Initial Value: advertising Magazine No promotion Coupon direct mail advertising mail 96 120 150 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ 60.00 $ $ 60.00 $ 0.00 $ 0.00 $ 5,760.00 $ 7,200.00 $ 9,000.00 $ 2,000.00 $ 2,000.00 $ 3,920.00 $ 4,400.00 $ 5,000.00 $ 1,000.00 $ 500.00 $ 10.00 $ 0.00 $ 1,500.00 4 $ 0.00 5 $ 2,000.00 6 Monthly operating costs (Fixed cost + Clients X Variable Cost) Advertising cost Cost per coupon Coupon expense (Clients X Cost per Coupon) 7 8 9 Profit (Total Revenue - Total Cost) $ (2,000.00) $ (2,000.00) $ (2,000.00) $ 1,840.00 $ 1,800.00 $ 2,000.00 10







