Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Marks received (Include this question page in your report) On 1 July 2017, Parent Ltd acquired all the shares of Son Ltd, on a cum-div.
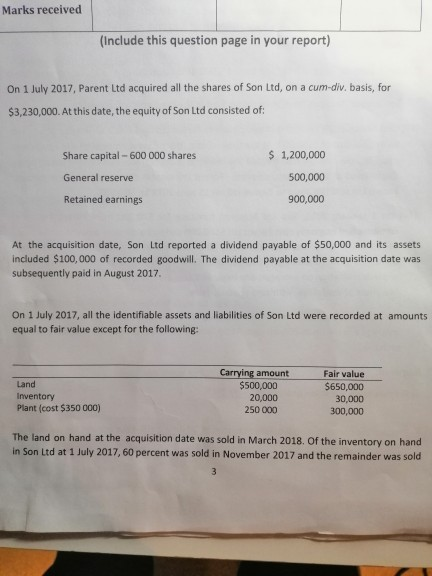


Marks received (Include this question page in your report) On 1 July 2017, Parent Ltd acquired all the shares of Son Ltd, on a cum-div. basis, for $3,230,000. At this date, the equity of Son Ltd consisted of: Share capital - 600 000 shares General reserve $ 1,200,000 500,000 900,000 Retained earnings At the acquisition date, Son Ltd reported a dividend payable of $50,000 and its assets included $100,000 of recorded goodwill. The dividend payable at the acquisition date was subsequently paid in August 2017 On 1 July 2017, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Son Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value except for the following: Land Inventory Plant (cost $350 000) Carrying amount $500,000 20,000 250 000 Fair value $650,000 30,000 300,000 The land on hand at the acquisition date was sold in March 2018. Of the inventory on hand in Son Ltd at 1 July 2017, 60 percent was sold in November 2017 and the remainder was sold Son Ltd was involved in a court case that could potentially result in the company paying damages to customers. At the acquisition date, Parent Ltd calculated the fair value of this liability to be $30,000, even though Son Ltd had not recorded any provision for damages liability). On 29 June 2019 Son Ltd reassessed the liability in relation to the court case as the chance of winning the case had improved. The fair value on 29 June 2019 was considered to be $10,000. The company applies the partial goodwill method. The income tax rate is 30%. During the period 1 July 2017 to 30 June 2019, the following intragroup transactions have occurred between Parent Ltd and Son Ltd: (T1) At 30 June 2019, Parent Ltd approved and declared a final dividend of $80,000 and Son Ltd approved and declared a final dividend of $50,000. Son Ltd subsequently paid its dividend on 20 August 2019. (T2) On 1 October 2018, Parent Ltd issued 5,000 10% debentures of $100 at nominal value. Son Ltd acquired 1,000 of these. Interest is paid half-yearly on 31 March and 30 September. Accruals have been recognised in the legal entities' accounts. (T3) On 1 March 2019, Son Ltd sold equipment to Parent Ltd for $100,000. The equipment had an original cost of $150,000. At the time of sale, the carrying amount of the equipment was 580,000. Son Ltd had treated the asset as a depreciable non-current asset, being depreciated at 10% on cost, whereas Parent Ltd records the equipment as inventory. Parent Ltd sold this asset to Beanie Ltd on 15 June 2019 for $90,500. (T4) On 1 January 2018, Son Ltd acquired furniture for $70,000 from Parent Ltd. The furniture had originally cost Parent Ltd $100,000 and had a carrying amount at the time of sale of $80,000. The sale was made on credit and, at 30 June 2018, $30,000 was outstanding. At 30 June 2019, $10,000 was still not paid and outstanding. Both entities apply depreciation on a straight-line basis. At 1 January 2018, the furniture had a further five years of useful life with zero residual value. (TS) On 3 December 2018, Son Ltd sold inventory to Parent Ltd for 596,000. The transfer price included a mark-up of 20% on cost. At 30 June 2019, 30 percent of this inventory was still on hand. Required: a) Prepare the acquisition analysis at 1 July 2017 (11 marks) b) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries at 30 June 2019. Your answer should include: 1. BCVR entries, 2. Pre-acquisition entries, and 3. Intragroup transaction adjustment entries (T1 to T4). (53 marks) The adjusting consolidation entries at 30 June 2019 for the last intragroup transaction (T5) is provided below. Sales revenue 96 000 Cost of sales 91 200 Inventory 4 800 1 440 Deferred tax asset (30%) Income tax expense 1 440 Explain why the above entries are made for T5, noting the adjustments to each account separately. (6 marks) Marks received (Include this question page in your report) On 1 July 2017, Parent Ltd acquired all the shares of Son Ltd, on a cum-div. basis, for $3,230,000. At this date, the equity of Son Ltd consisted of: Share capital - 600 000 shares General reserve $ 1,200,000 500,000 900,000 Retained earnings At the acquisition date, Son Ltd reported a dividend payable of $50,000 and its assets included $100,000 of recorded goodwill. The dividend payable at the acquisition date was subsequently paid in August 2017 On 1 July 2017, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Son Ltd were recorded at amounts equal to fair value except for the following: Land Inventory Plant (cost $350 000) Carrying amount $500,000 20,000 250 000 Fair value $650,000 30,000 300,000 The land on hand at the acquisition date was sold in March 2018. Of the inventory on hand in Son Ltd at 1 July 2017, 60 percent was sold in November 2017 and the remainder was sold Son Ltd was involved in a court case that could potentially result in the company paying damages to customers. At the acquisition date, Parent Ltd calculated the fair value of this liability to be $30,000, even though Son Ltd had not recorded any provision for damages liability). On 29 June 2019 Son Ltd reassessed the liability in relation to the court case as the chance of winning the case had improved. The fair value on 29 June 2019 was considered to be $10,000. The company applies the partial goodwill method. The income tax rate is 30%. During the period 1 July 2017 to 30 June 2019, the following intragroup transactions have occurred between Parent Ltd and Son Ltd: (T1) At 30 June 2019, Parent Ltd approved and declared a final dividend of $80,000 and Son Ltd approved and declared a final dividend of $50,000. Son Ltd subsequently paid its dividend on 20 August 2019. (T2) On 1 October 2018, Parent Ltd issued 5,000 10% debentures of $100 at nominal value. Son Ltd acquired 1,000 of these. Interest is paid half-yearly on 31 March and 30 September. Accruals have been recognised in the legal entities' accounts. (T3) On 1 March 2019, Son Ltd sold equipment to Parent Ltd for $100,000. The equipment had an original cost of $150,000. At the time of sale, the carrying amount of the equipment was 580,000. Son Ltd had treated the asset as a depreciable non-current asset, being depreciated at 10% on cost, whereas Parent Ltd records the equipment as inventory. Parent Ltd sold this asset to Beanie Ltd on 15 June 2019 for $90,500. (T4) On 1 January 2018, Son Ltd acquired furniture for $70,000 from Parent Ltd. The furniture had originally cost Parent Ltd $100,000 and had a carrying amount at the time of sale of $80,000. The sale was made on credit and, at 30 June 2018, $30,000 was outstanding. At 30 June 2019, $10,000 was still not paid and outstanding. Both entities apply depreciation on a straight-line basis. At 1 January 2018, the furniture had a further five years of useful life with zero residual value. (TS) On 3 December 2018, Son Ltd sold inventory to Parent Ltd for 596,000. The transfer price included a mark-up of 20% on cost. At 30 June 2019, 30 percent of this inventory was still on hand. Required: a) Prepare the acquisition analysis at 1 July 2017 (11 marks) b) Prepare the consolidation worksheet entries at 30 June 2019. Your answer should include: 1. BCVR entries, 2. Pre-acquisition entries, and 3. Intragroup transaction adjustment entries (T1 to T4). (53 marks) The adjusting consolidation entries at 30 June 2019 for the last intragroup transaction (T5) is provided below. Sales revenue 96 000 Cost of sales 91 200 Inventory 4 800 1 440 Deferred tax asset (30%) Income tax expense 1 440 Explain why the above entries are made for T5, noting the adjustments to each account separately. (6 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


