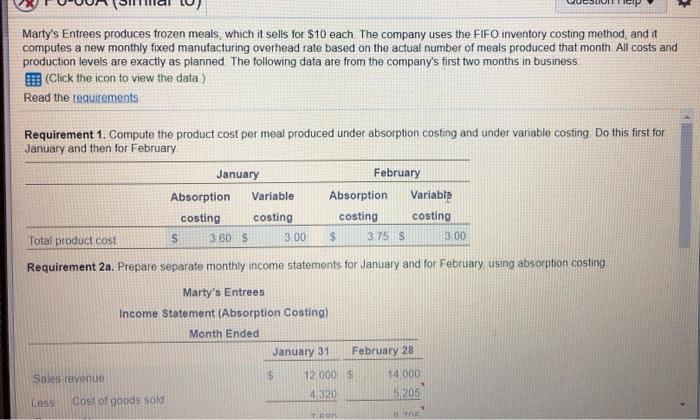
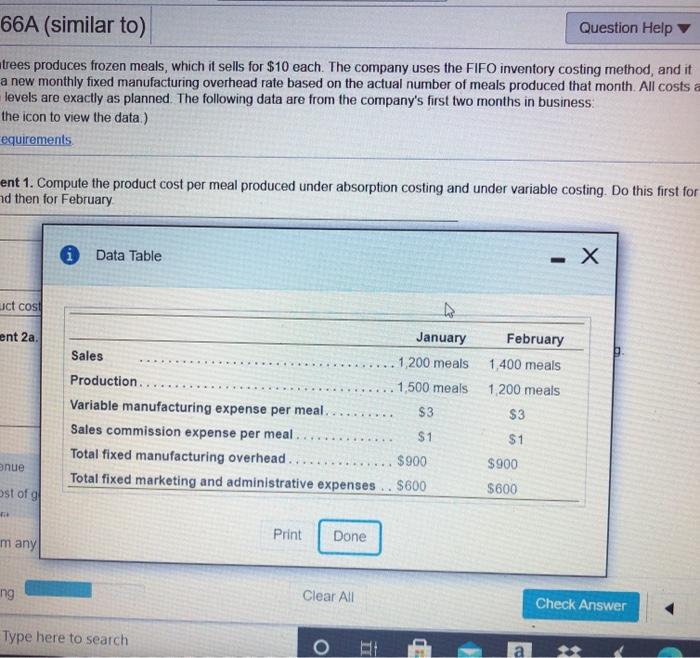
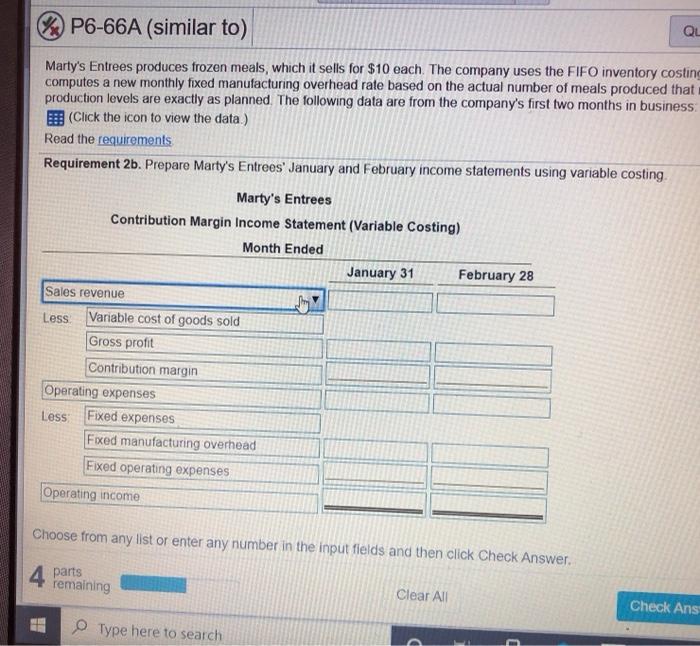
> Marty's Entrees produces frozen meals which it sells for $10 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month All costs and production levels are exactly as planned The following data are from the company's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data) Read the requirements: Requirement 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing Do this first for January and then for February January February Absorption Variable Absorption Variable costing costing costing costing Total product cost S 3.60 S 3.00 $ 3.75 S 3.00 Requirement 2a. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February using absorption costing Marty's Entrees Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Month Ended January 31 February 28 Sales revenue $ 12 000 $ 14000 4320 LOSS Cost of goods sold 5205 Ton 66A (similar to) Question Help trees produces frozen meals, which it sells for $10 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, and it a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All costs a levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business the icon to view the data) requirements ent 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this first for nd then for February Data Table -X uct cost ent 2a. January Sales 1.200 meals Production. 1,500 meals Variable manufacturing expense per meal. $3 Sales commission expense per meal. $1 Total fixed manufacturing overhead. $900 Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses .. $600 February 1.400 meals 1.200 meals $3 $1 nue $900 ost of $600 Print many Done ng Clear All Check Answer Type here to search 56A (similar to) Question Hel Tees produces frozen meals, which it sells for $10 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing method, a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that month. All evels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business the icon to view the data.) equirements ent 1. Compute the product cost per meal produced under absorption costing and under variable costing. Do this fir d then for February Requirements - X act cost ent 2a. Pr! ting Ind 1. Compute the product cost per meal prodaced under absorption costing and under variable costing Do this first for January and then for February 2. Prepare separate monthly income statements for January and for February using the following: a. Absorption costing b. Variable costing 3. Is operating income higher under absorption costing or variable costing in January? In February? Explain the pattern of differences in operating income based on absorption costing versus variable costing enue ost of good fe Print Done em any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check Answer ing Clear All Check Answer Tune horo & P6-66A (similar to) QL Marty's Entrees produces frozen meals, which it sells for $10 each. The company uses the FIFO inventory costing computes a new monthly fixed manufacturing overhead rate based on the actual number of meals produced that production levels are exactly as planned. The following data are from the company's first two months in business (Click the icon to view the data.) Read the requirements Requirement 2b. Prepare Marty's Entrees' January and February income statements using variable costing Marty's Entrees Contribution Margin Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended January 31 February 28 Sales revenue Less Variable cost of goods sold Gross profit Contribution margin Operating expenses Less Fixed expenses Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed operating expenses Operating income Choose from any list or enter any number in the input fields and then click Check Answer 4 parts remaining Clear All Check Ans Type here to search