Mass Transfer:
please use fhe following numbers to help solve the problem
F= 559.6 ib-mole/hr
Tf=30.92 C
Methanol Mass % in feed= 29.95
Water mass % in feed = 70.05
methanol mass % in the distillate= 78.38
Methanol mole % in the bottom product = 2.75
external reflux radio= 4.04 rd
Please answer the questions fully!! (If not going to answer fully, just skip this question for the next person who will. Thank you!)
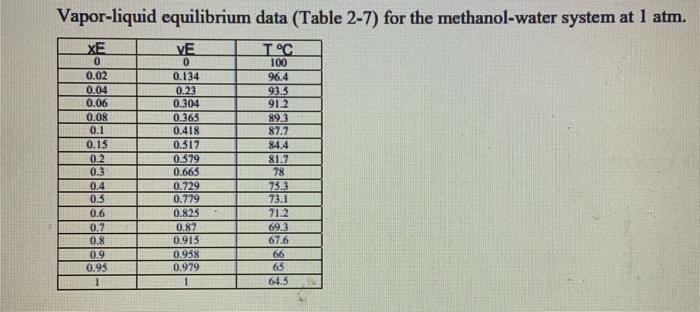
A continuous, steady-state distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler separates methanol from water at one atmosphere total pressure. The feed rate to the column is F lb-mole/hour and the feed temperature is maintained at T, C. The feed contains mwF mass % methanol and wwf mass % water. A distillate product contains mwD mass % methanol and a bottoms product contains mmB mole % methanol. The external reflux ratio L/D is rd. a 1. Sketch the problem according to the description of the problem. 2. Find the mean heat capacity (cal/g-mole-K) of the distillate stream over the temperature range of T (the feed temperature) - To the distillate (condensation) temperature). 3. Find the mean heat capacity (cal/g-mole-K) of the bottom product stream over the temperature range of T, (the feed temperature) - Tn (the bottom product temperature). 4. Find the specific enthalpy h(cal/g-mole) of the feed stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 5. Find the specific enthalpy hp (cal/g-mole) of the distillate stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 6. Find the specific enthalpy he (cal/g-mole) of the bottom product stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 7. Calculate the latent heat of vaporization (cal/g-mole) for the vapor stream at the distillate (condensation) temperature To, using Watson's correlation, shown below. 2: latent heat of vaporization at TK Az = 2.2: latent heat of vaporization at T "K T. critical temperature. K 8. Calculate the heat duty of the total condenser in calhr. 9. Calculate the heat duty of the reboiler in cal/hr. latent heat of vaporization for Watson's Method Liquid heat capacities . 2. at The Cp-1987 (cal/g-mole-K) (13.431-5. 1280x10T +1.3113x104 T5 kj/mole -1.987 (cal/g-mole-K) (8.712 - 12500x10 T 18000x109 methanol 35.27 513.20 40.656 Tin K T, K 1 2 64.7 100 water 647.4 Vapor-liquid equilibrium data (Table 2-7) for the methanol-water system at 1 atm. XE VE TC 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.15 0.2 03 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0.95 0 0.134 0.23 0.304 0.365 0.418 0.517 0.579 0.663 0.729 0.779 0.825 0.87 0.913 0.938 0.979 100 96.4 93.5 91.2 89.3 87.7 84.4 81.7 78 73.3 73.1 71.2 69.3 67.6 66 65 64.5 A continuous, steady-state distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler separates methanol from water at one atmosphere total pressure. The feed rate to the column is F lb-mole/hour and the feed temperature is maintained at T, C. The feed contains mwF mass % methanol and wwf mass % water. A distillate product contains mwD mass % methanol and a bottoms product contains mmB mole % methanol. The external reflux ratio L/D is rd. a 1. Sketch the problem according to the description of the problem. 2. Find the mean heat capacity (cal/g-mole-K) of the distillate stream over the temperature range of T (the feed temperature) - To the distillate (condensation) temperature). 3. Find the mean heat capacity (cal/g-mole-K) of the bottom product stream over the temperature range of T, (the feed temperature) - Tn (the bottom product temperature). 4. Find the specific enthalpy h(cal/g-mole) of the feed stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 5. Find the specific enthalpy hp (cal/g-mole) of the distillate stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 6. Find the specific enthalpy he (cal/g-mole) of the bottom product stream, using the feed temperature Tras a reference temperature. 7. Calculate the latent heat of vaporization (cal/g-mole) for the vapor stream at the distillate (condensation) temperature To, using Watson's correlation, shown below. 2: latent heat of vaporization at TK Az = 2.2: latent heat of vaporization at T "K T. critical temperature. K 8. Calculate the heat duty of the total condenser in calhr. 9. Calculate the heat duty of the reboiler in cal/hr. latent heat of vaporization for Watson's Method Liquid heat capacities . 2. at The Cp-1987 (cal/g-mole-K) (13.431-5. 1280x10T +1.3113x104 T5 kj/mole -1.987 (cal/g-mole-K) (8.712 - 12500x10 T 18000x109 methanol 35.27 513.20 40.656 Tin K T, K 1 2 64.7 100 water 647.4 Vapor-liquid equilibrium data (Table 2-7) for the methanol-water system at 1 atm. XE VE TC 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.15 0.2 03 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0.95 0 0.134 0.23 0.304 0.365 0.418 0.517 0.579 0.663 0.729 0.779 0.825 0.87 0.913 0.938 0.979 100 96.4 93.5 91.2 89.3 87.7 84.4 81.7 78 73.3 73.1 71.2 69.3 67.6 66 65 64.5